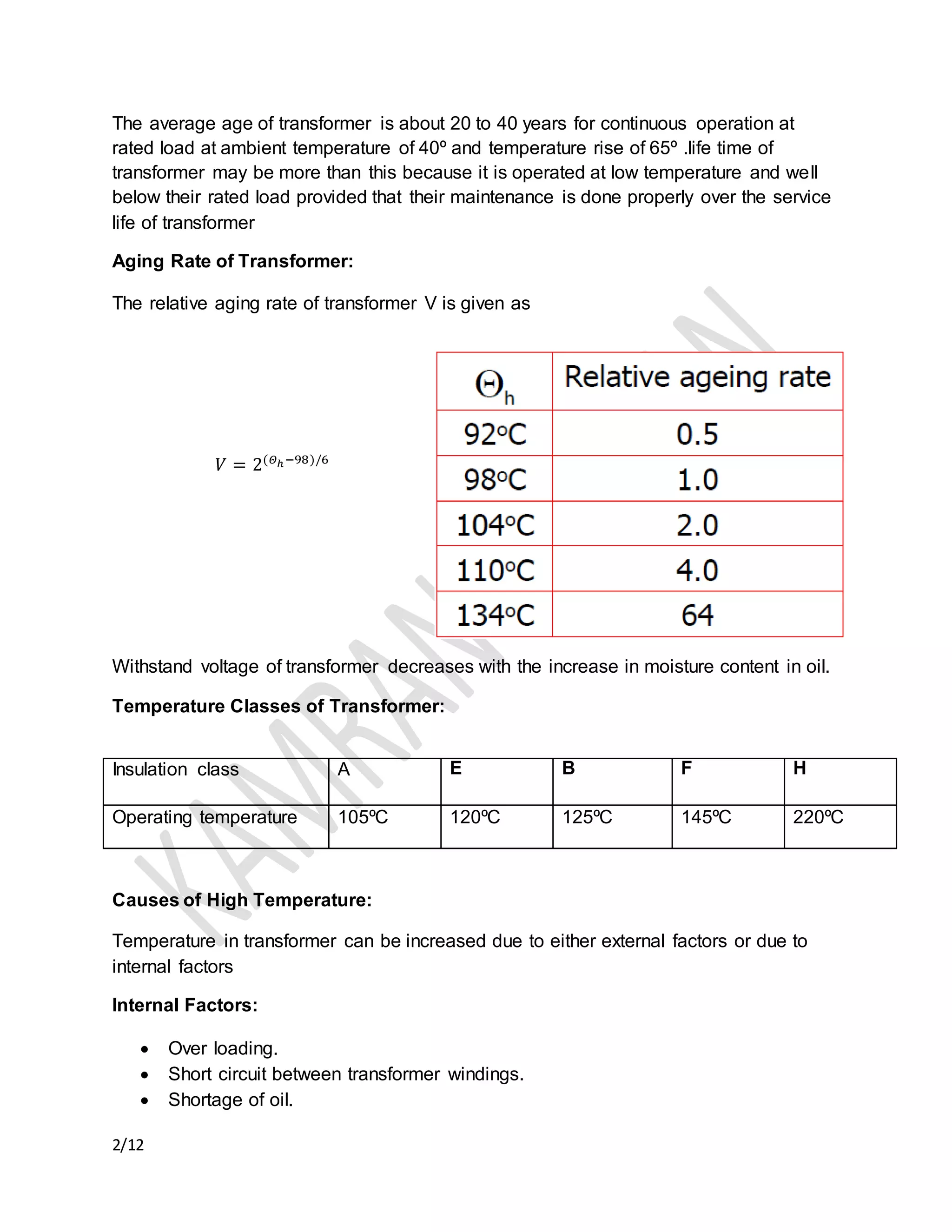
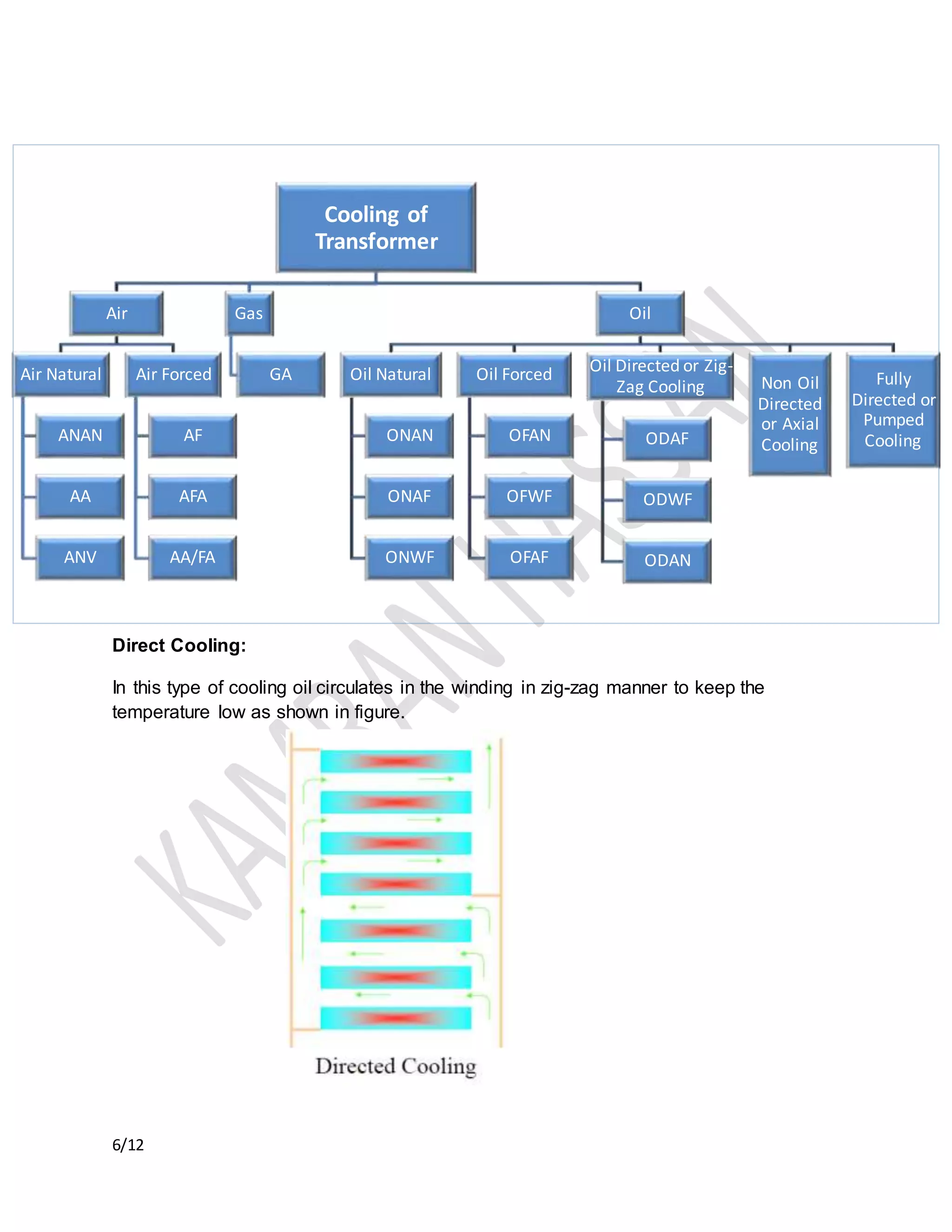
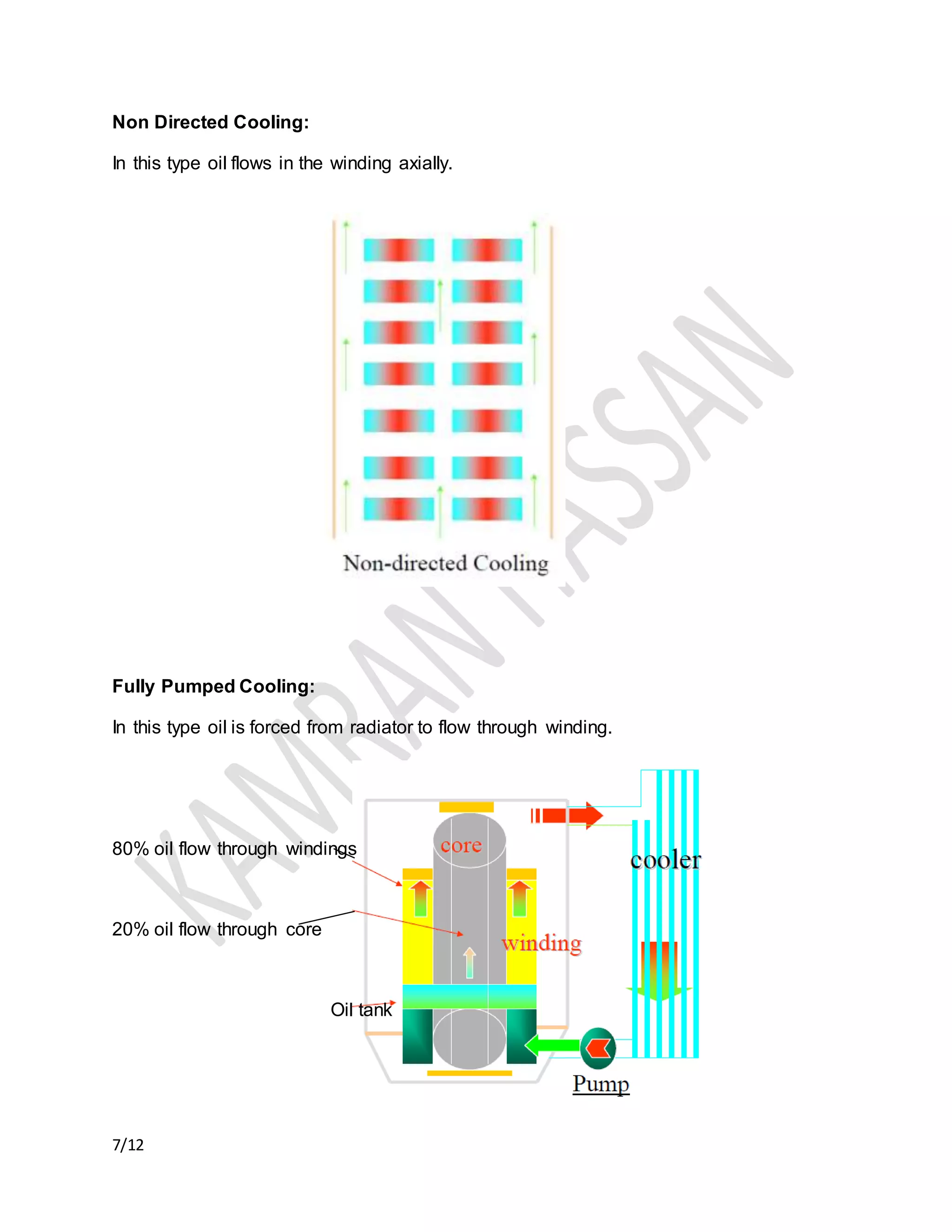
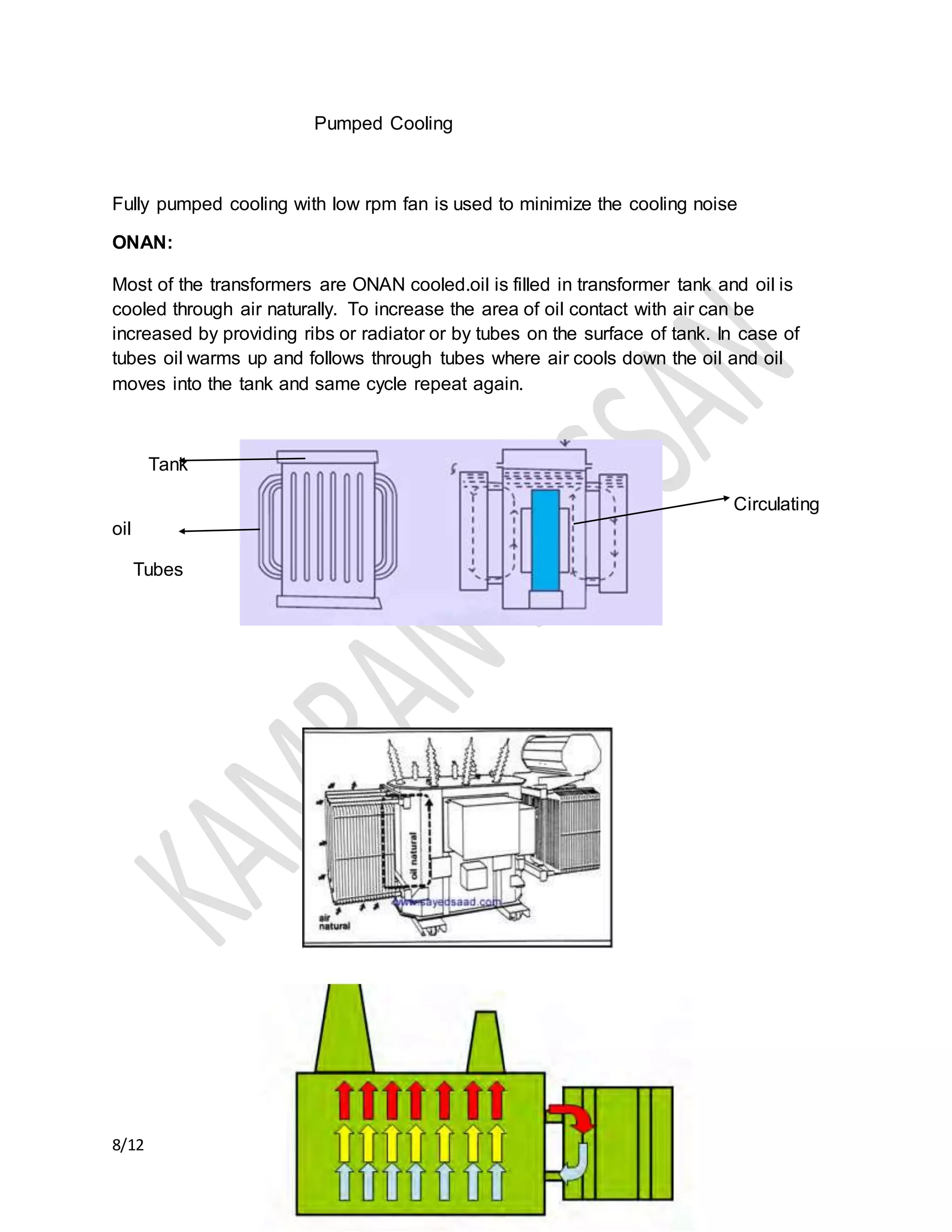
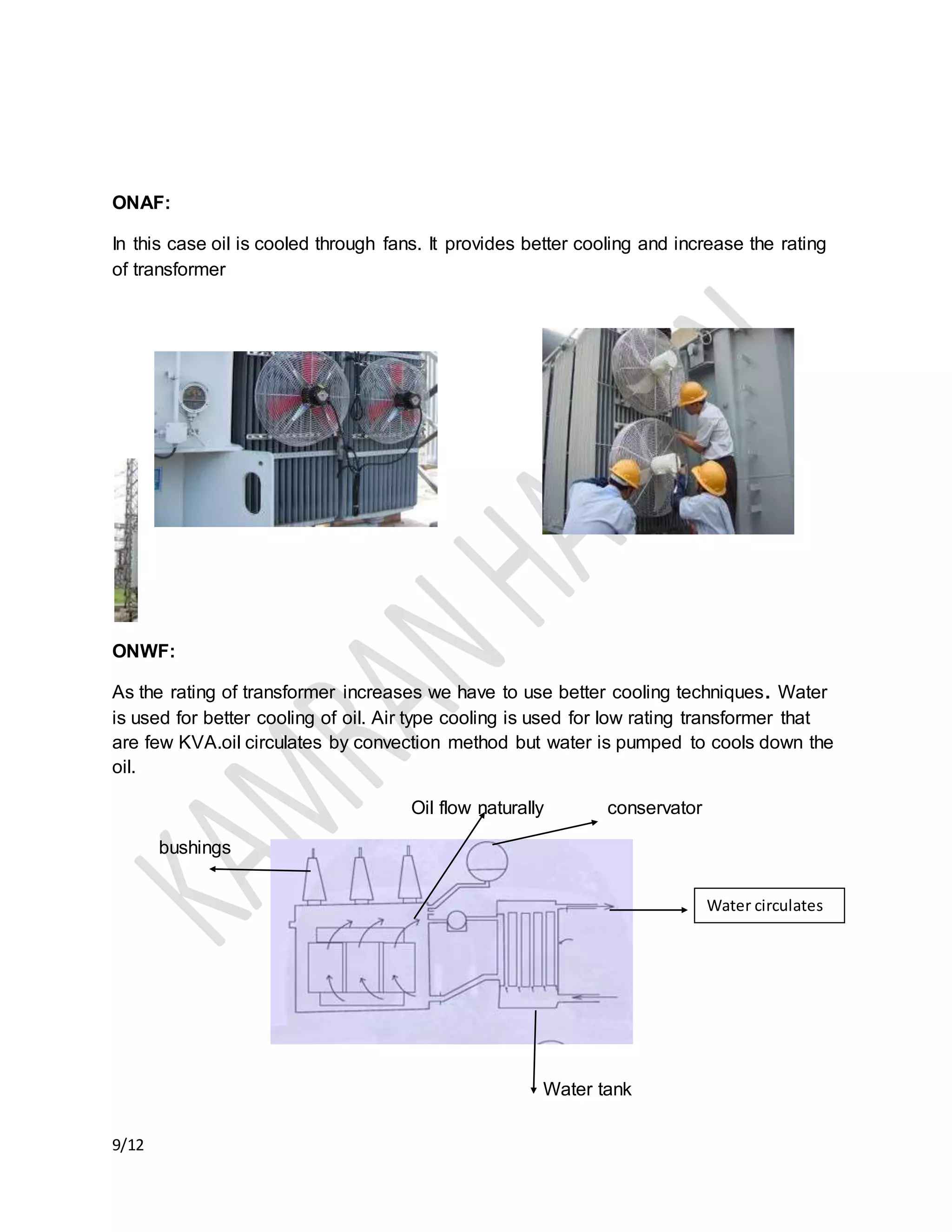
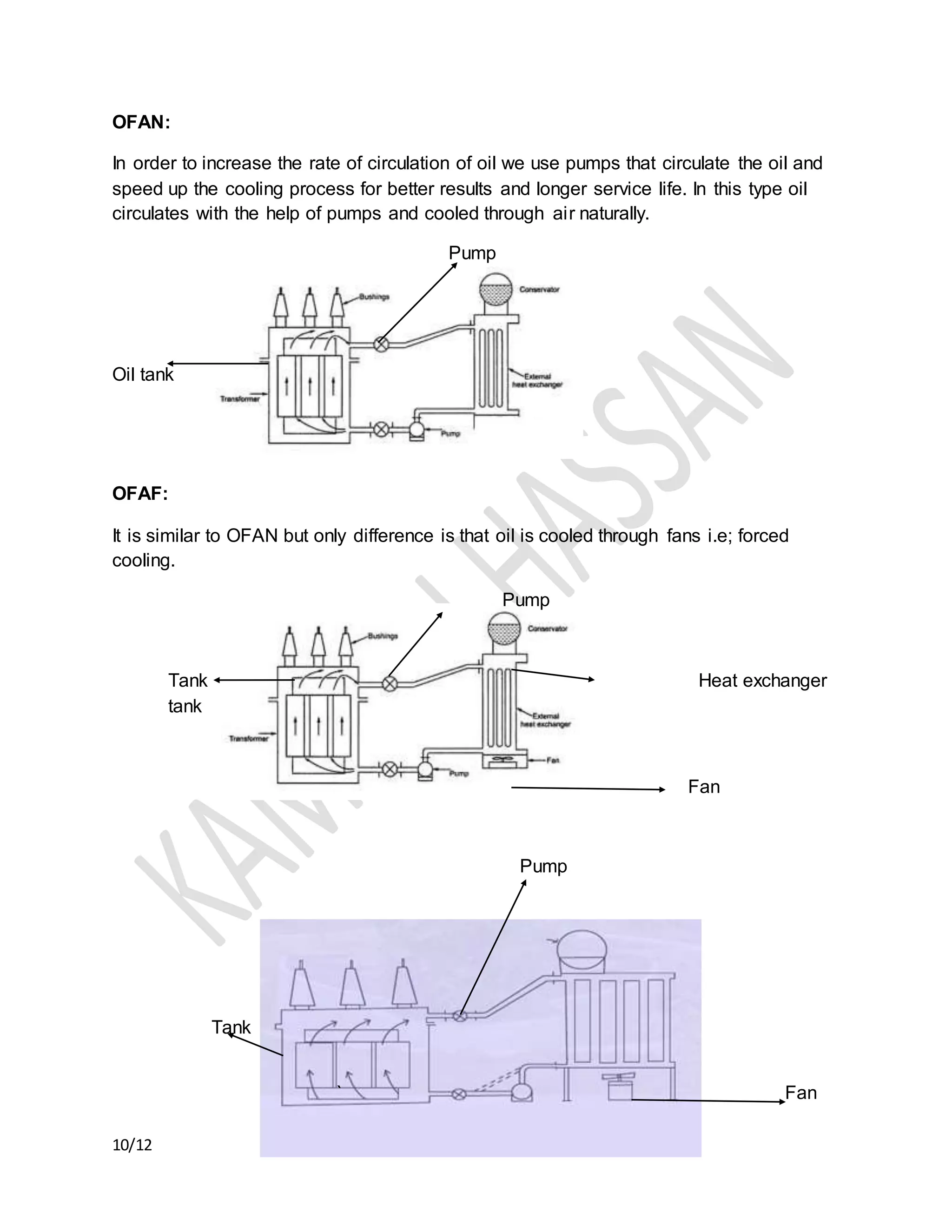
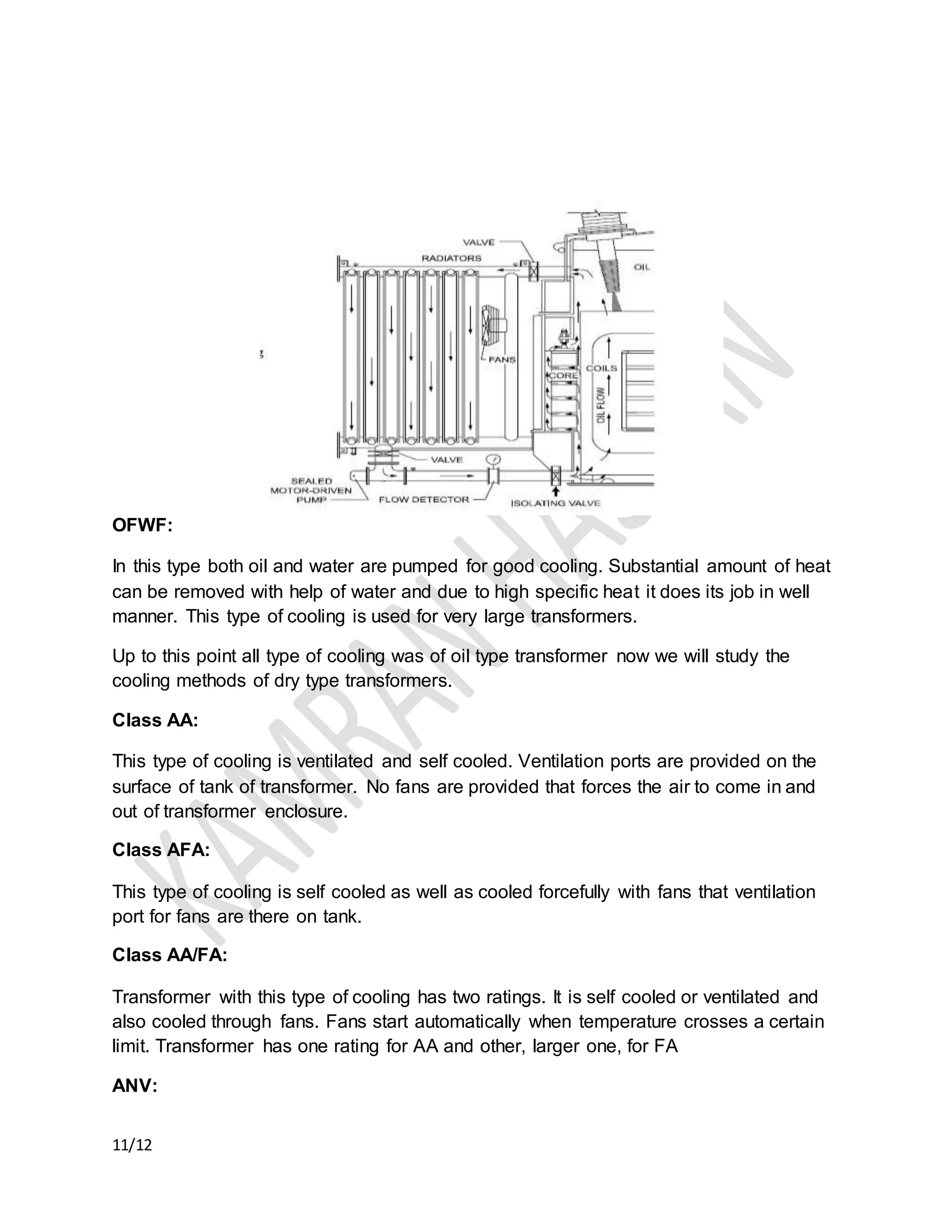
The document discusses the importance of transformer cooling, highlighting that temperature significantly affects transformer lifespan, with higher operational temperatures leading to faster insulation degradation. It describes various internal and external cooling methods, their mechanisms, and symbols used to represent them, concluding that inadequate cooling methods can prevent transformers from maintaining efficiency and longevity. Methods include natural and forced cooling techniques using air or water, as well as specific categorizations of cooling based on design and application.