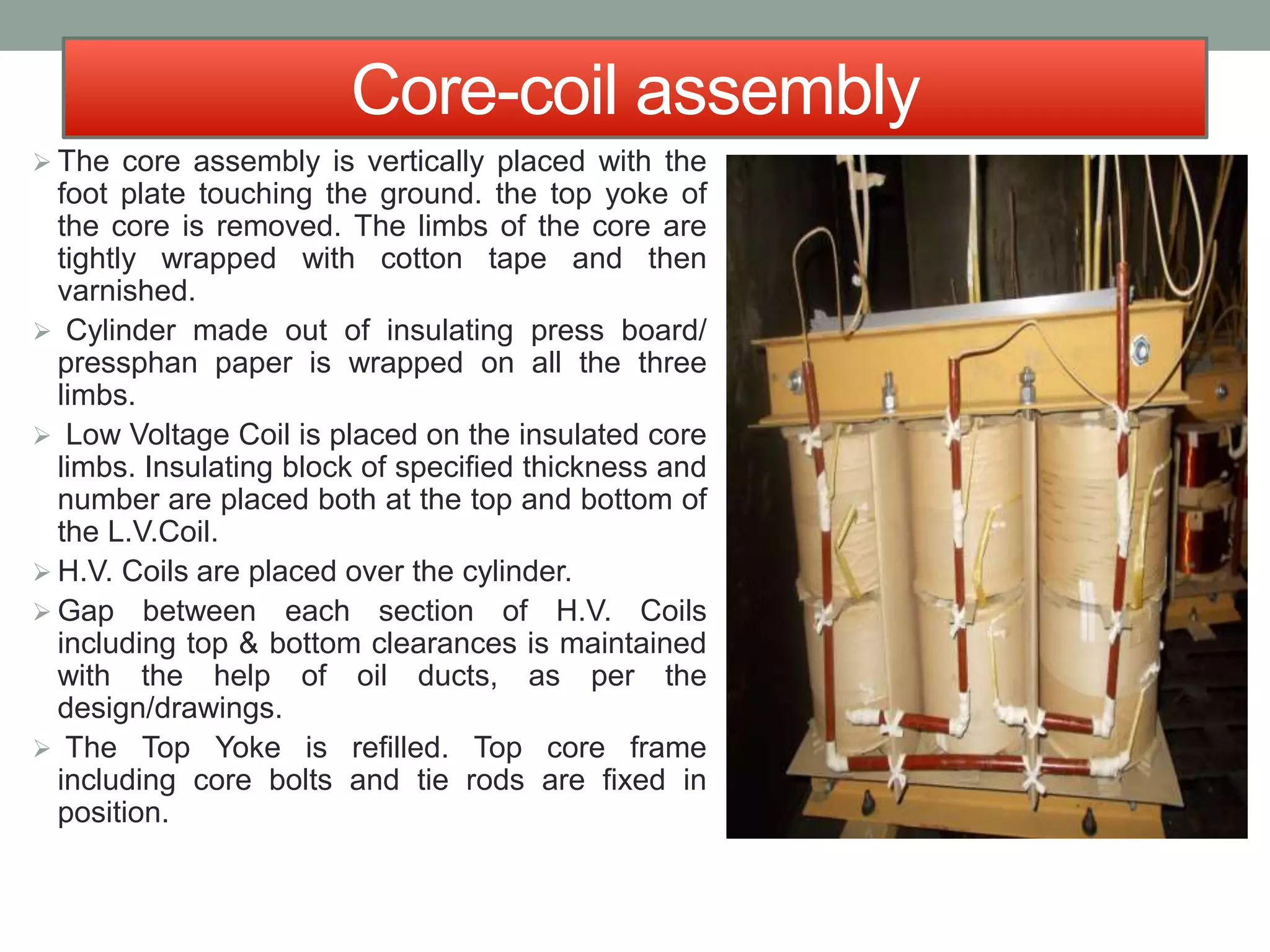
The document outlines the field training and manufacturing processes of transformers at Datta Electricals, detailing stages such as core assembly, core-coil assembly, tank-up, painting, and testing. It highlights a significant problem of sludge formation in transformer oil over time and presents a novel method using OM4 optical fiber for detecting oil deterioration. The author concludes with insights gained during the training, emphasizing the high efficiency of transformers and the challenges in improving designs past 98% efficiency.