Embed presentation








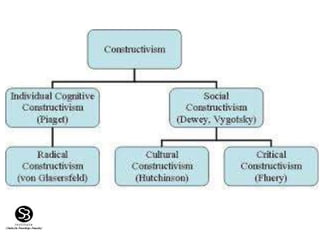
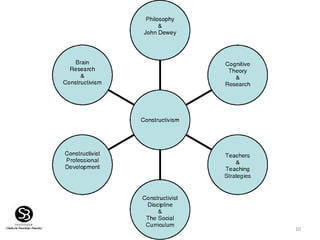
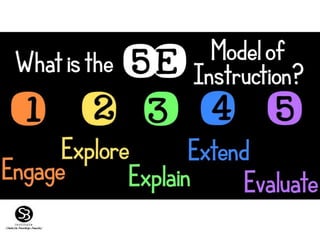
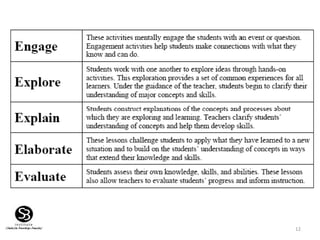
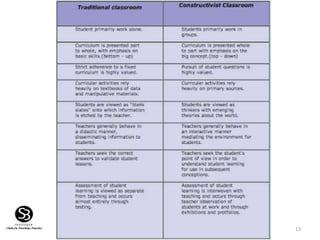

Constructivism is a learning theory that emphasizes how individuals acquire knowledge through their experiences, with a focus on the learner rather than traditional teaching methods. It posits that knowledge is constructed based on prior experiences, and teachers act as facilitators to help students 'learn how to learn' through questioning and experimentation. Key figures in the development of constructivism include Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, Lev Vygotsky, and John Dewey.












