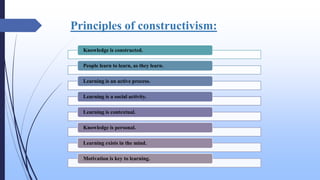
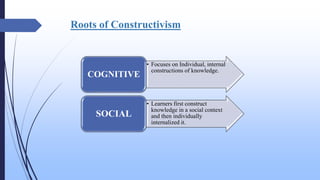
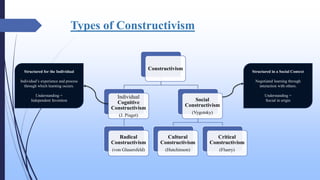
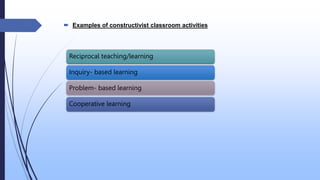
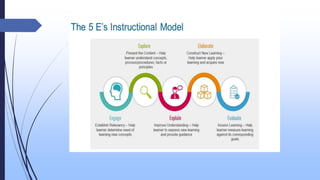
The document discusses the constructivist approach to learning, specifically the 5E model. It provides background on constructivism, outlining key principles like knowledge being actively constructed by learners based on their experiences. The 5E model is then explained in detail, with each "E" standing for a phase of instruction: Engage, Explore, Explain, Elaborate, Evaluate. Examples of activities for each phase are given. The document also discusses benefits and criticisms of constructivism, noting it emphasizes collaborative, active learning but may disadvantage some students.