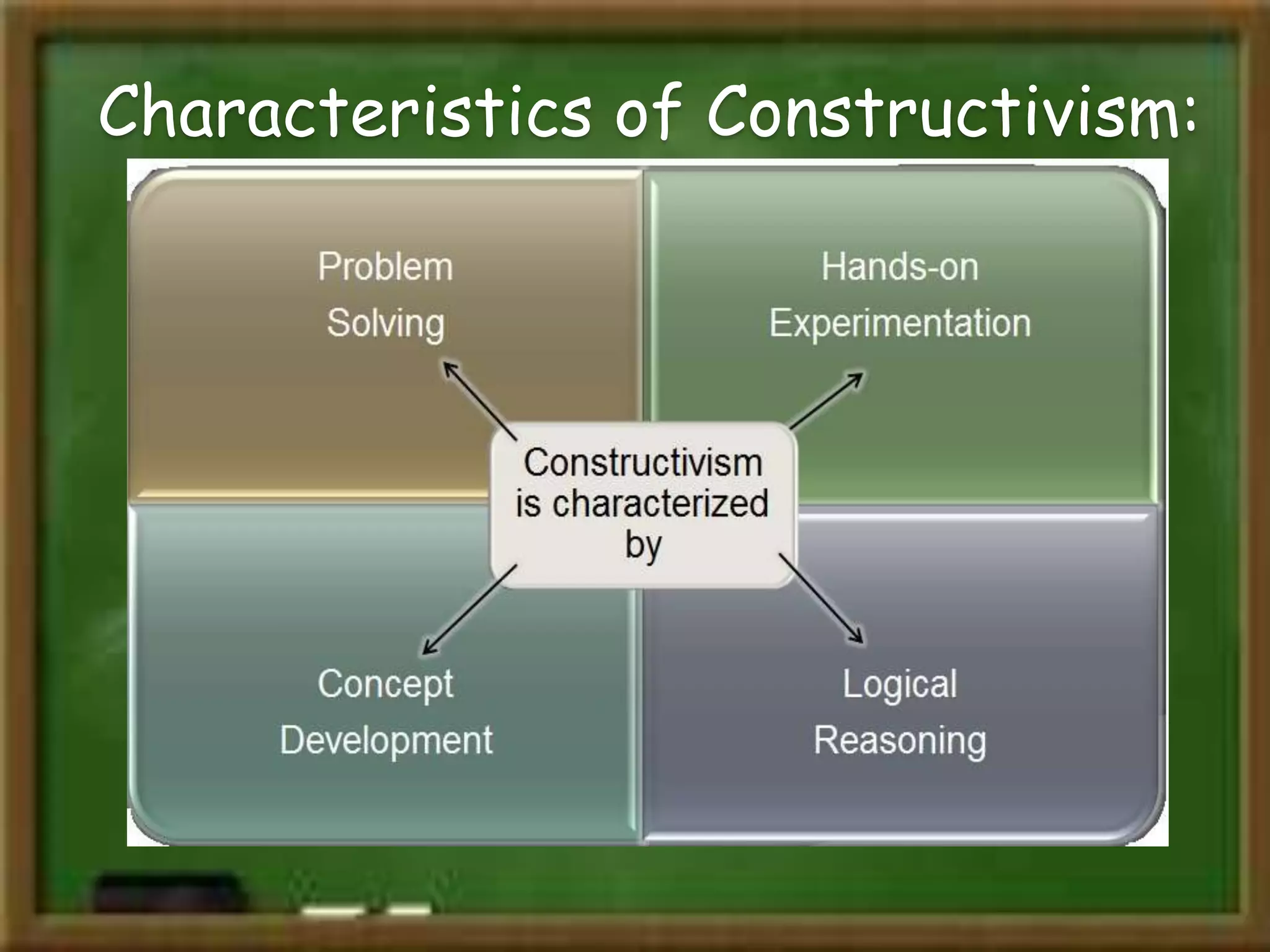
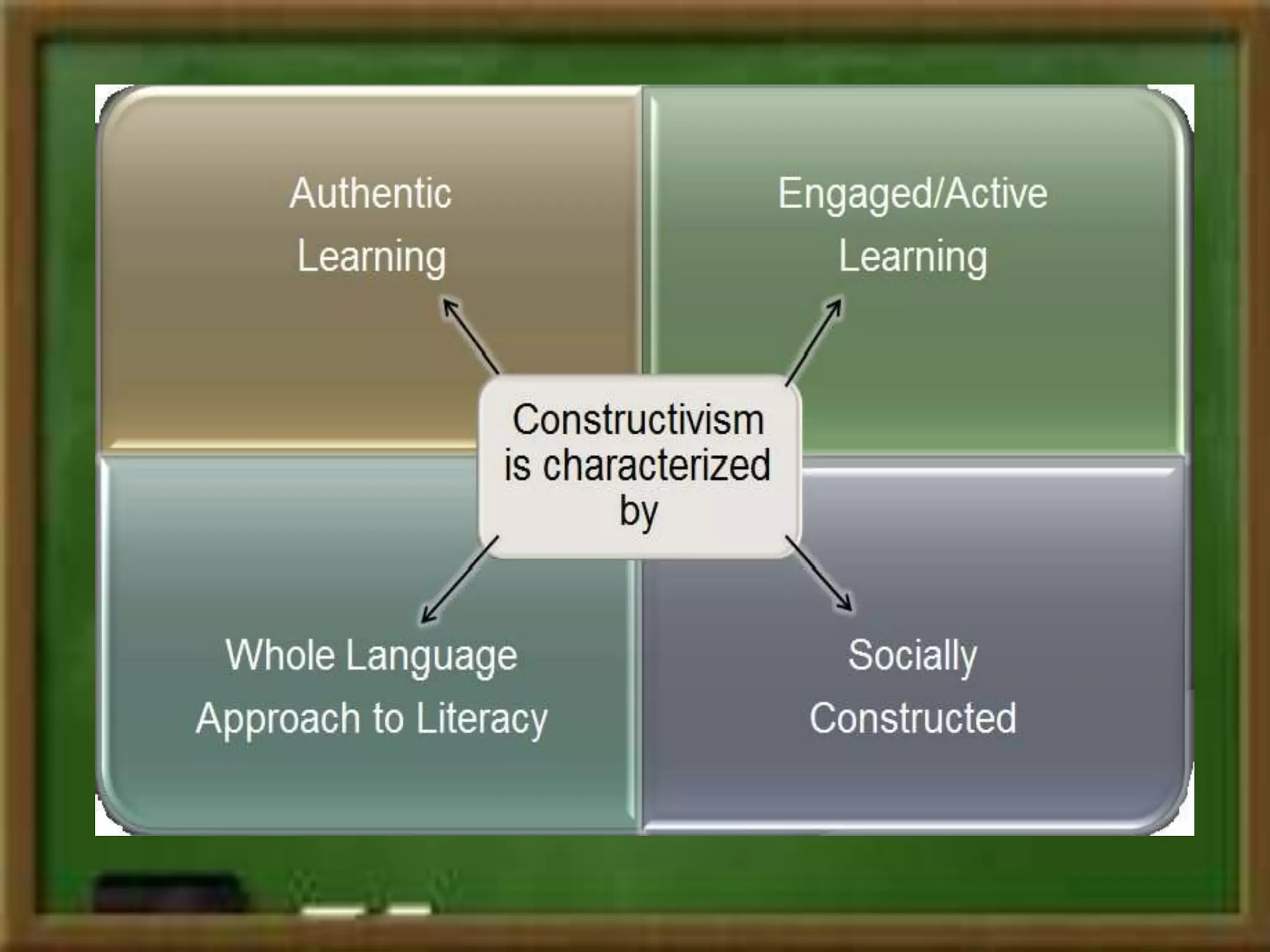
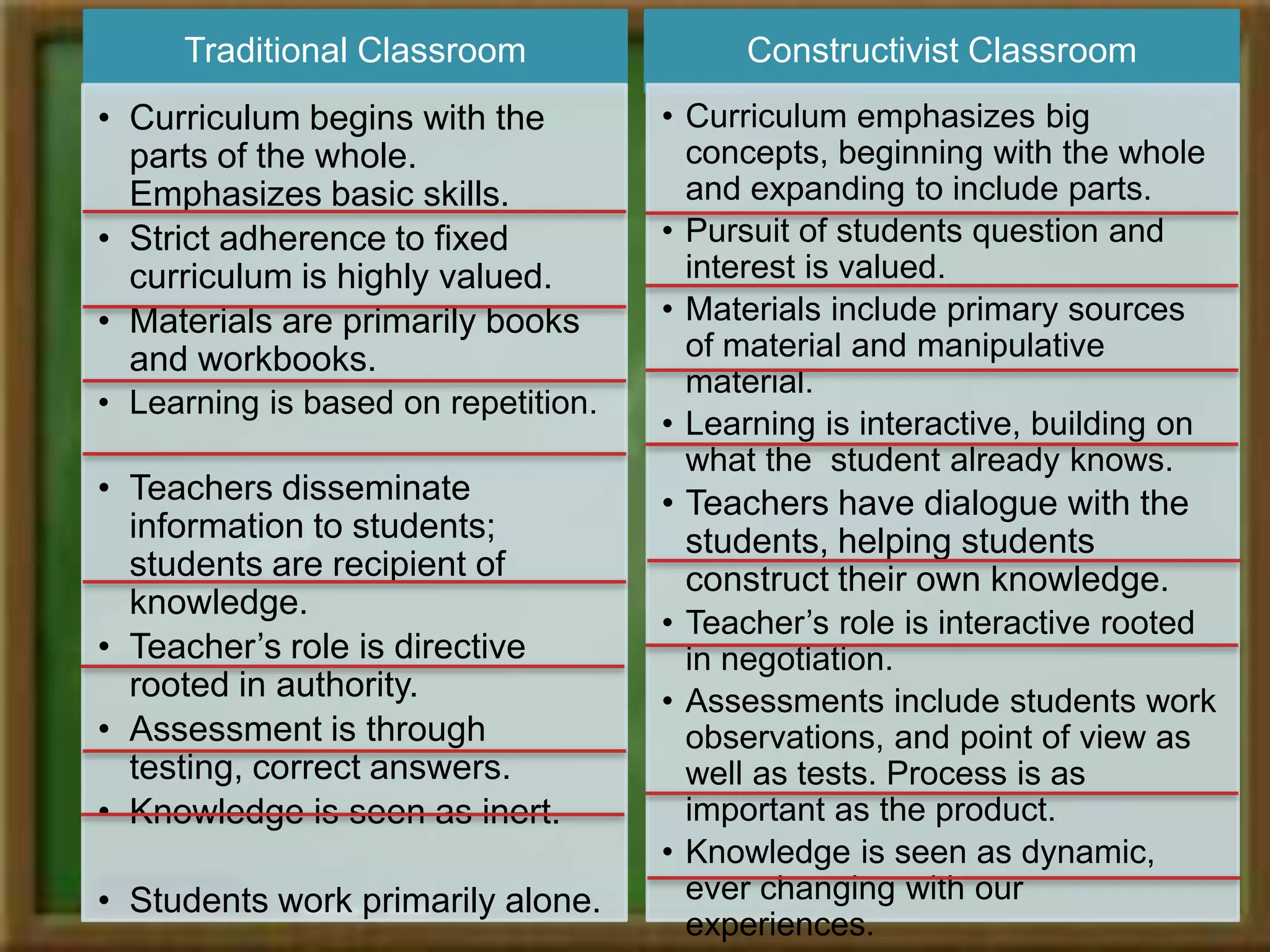
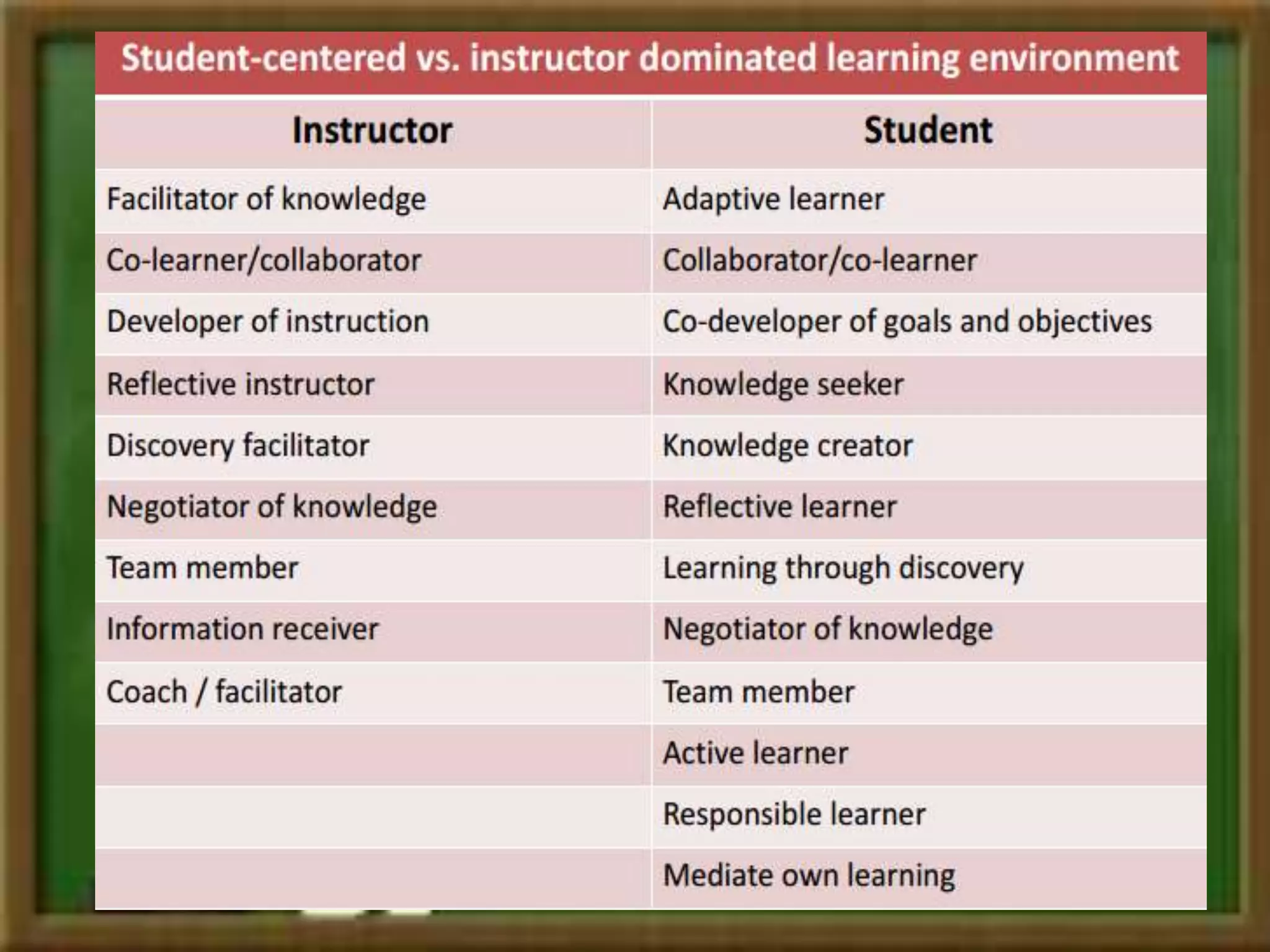
Constructivism is a learning theory that asserts learners construct knowledge individually and socially through experience and interaction with their surroundings, largely influenced by scholars like Piaget and Vygotsky. It emphasizes two views: individual constructivism, focusing on internal knowledge creation, and social constructivism, which highlights shared knowledge development. The approach advocates for interactive, experiential learning in contrast to traditional classrooms that prioritize rote memorization and passive learning.