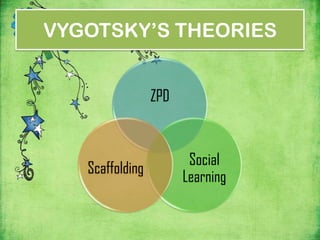
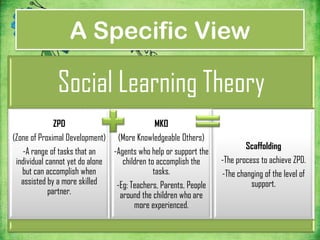
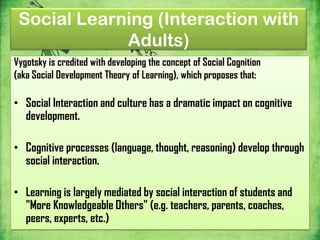
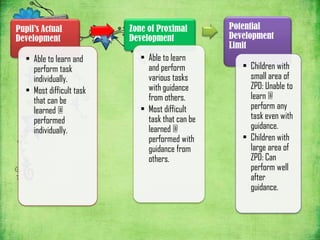
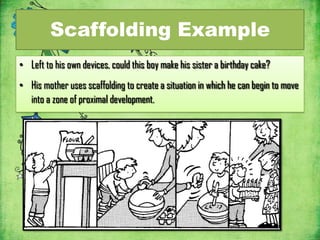
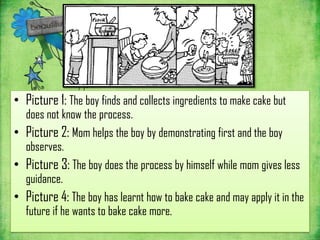
Vygotsky's theories focus on social learning and the zone of proximal development (ZPD). The ZPD refers to tasks that a child cannot complete alone but can complete with guidance from more knowledgeable others (MKO), such as teachers or parents. Scaffolding is the process of providing support to help a child achieve tasks within their ZPD. Vygotsky argued that social interaction and culture impact cognitive development, and that learning occurs through social interactions where children are assisted by more skilled partners within their ZPD.