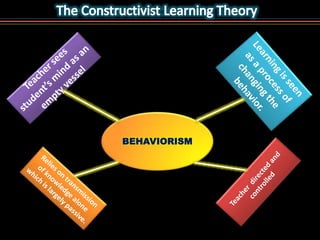
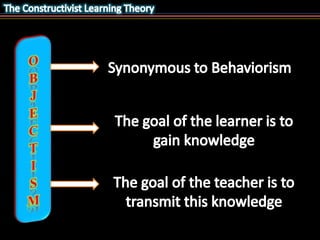
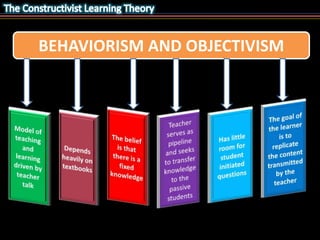
This document outlines the key objectives and concepts of constructivism. It defines constructivism as a philosophy of learning where learners actively construct their own understanding and knowledge based on reflection on their experiences. The document then discusses several philosophers who contributed ideas to constructivism, including the ideas that learning involves constructing one's own concepts, interacting with the environment, discovery, and constructing new ideas based on past knowledge. Finally, it lists 7 underlying ideas of constructivism, such as learning being a social and active process, the importance of experience and reflection in learning, and focusing on understanding and application to life.