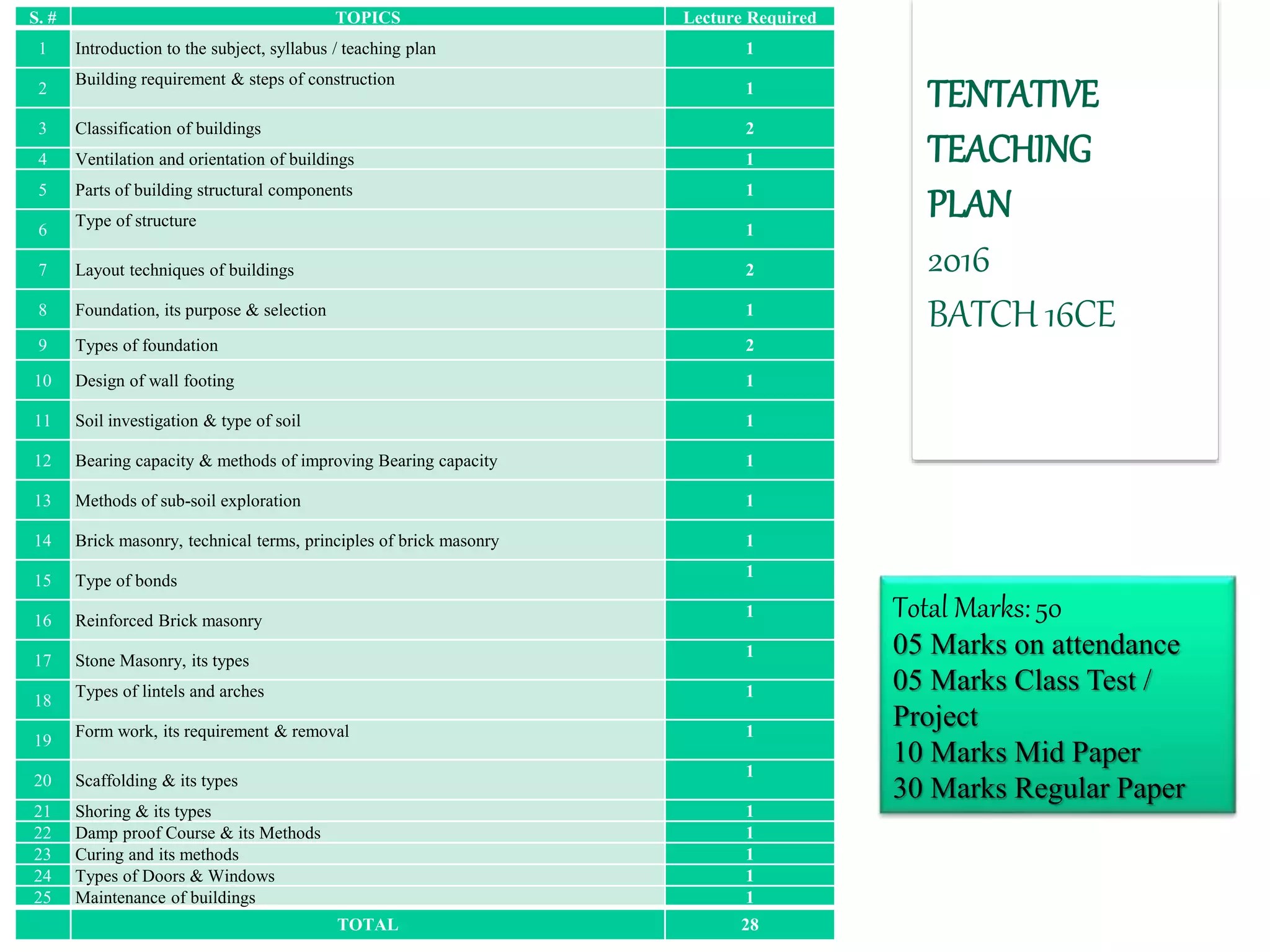
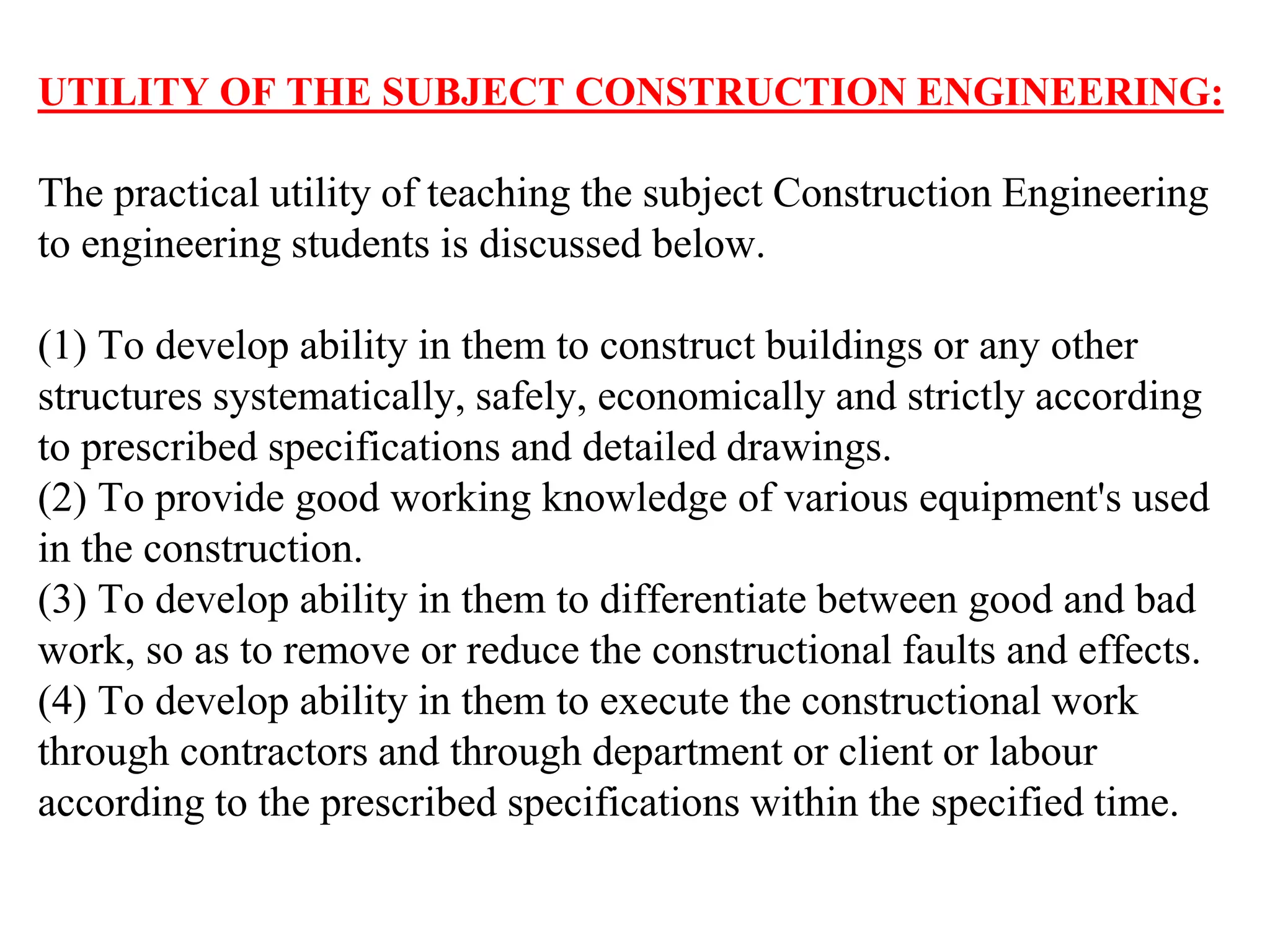
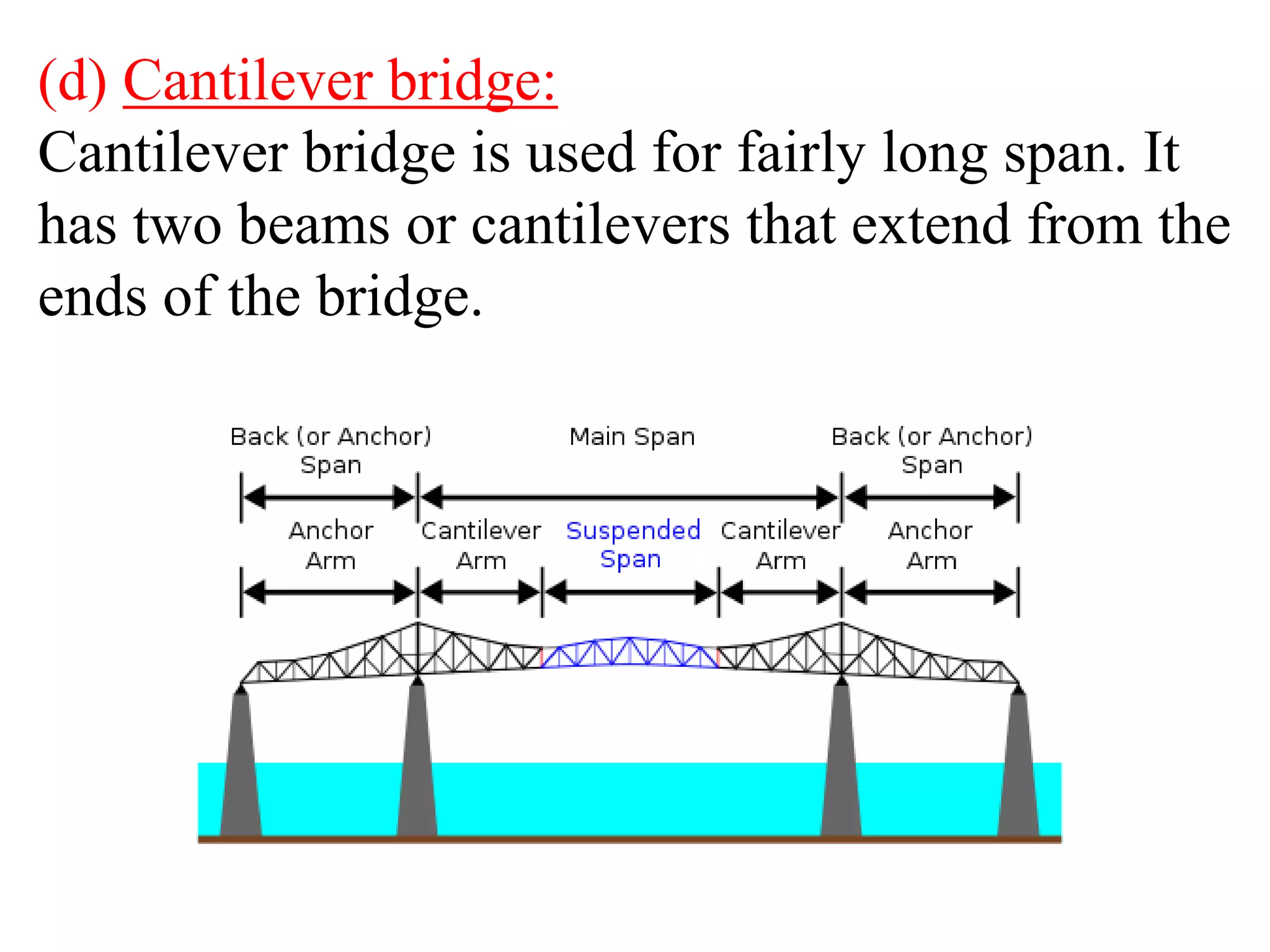
This document provides an overview of the Construction Engineering course taught by Prof. Dr. Kanya Lal Khatri. It outlines 28 topics that will be covered in the course, including building requirements, types of structures and foundations, masonry, doors and windows, and maintenance of buildings. It also discusses the importance of construction in society by providing shelter, opportunities, and infrastructure like highways, bridges, and dams. Finally, it highlights some key engineering projects from a construction point of view, such as buildings, airports, tunnels, bridges, and dams.