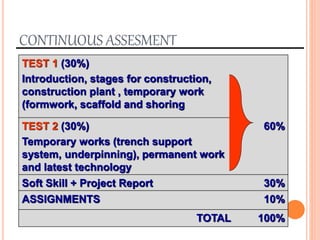
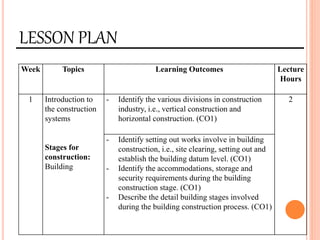
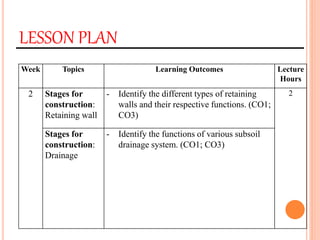
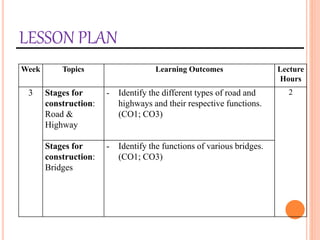
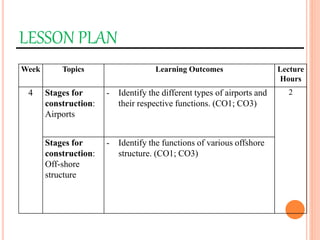
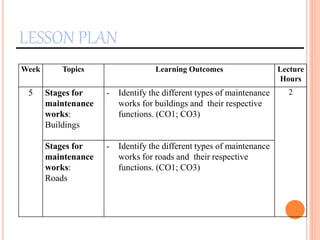
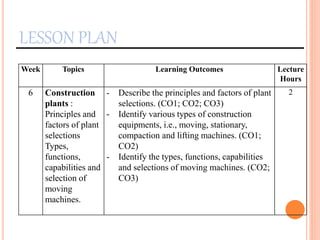
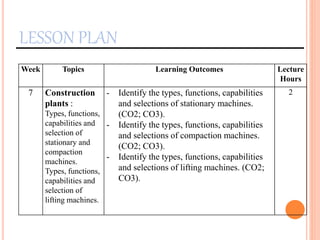
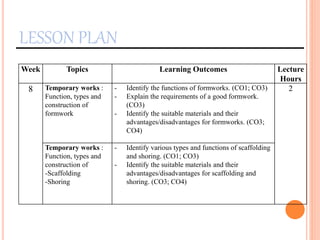
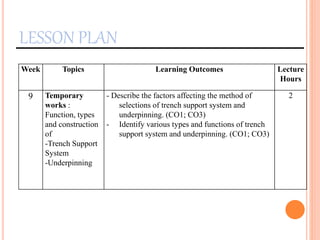
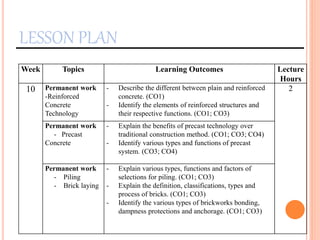
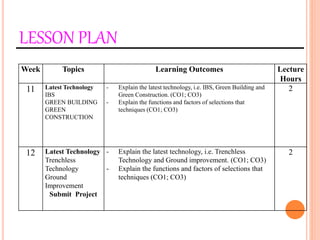
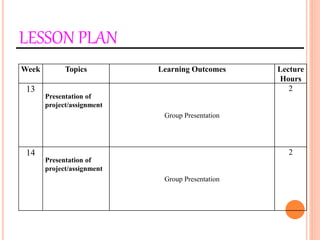
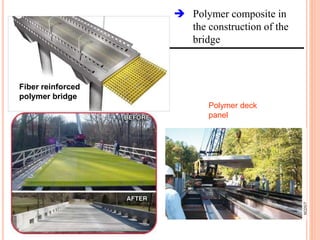
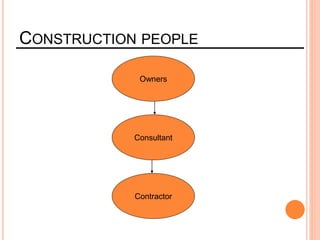
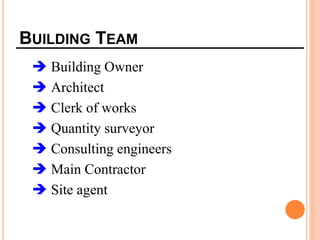
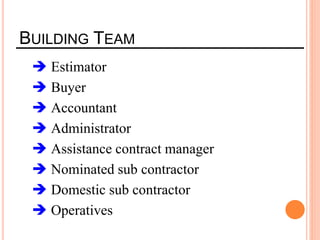
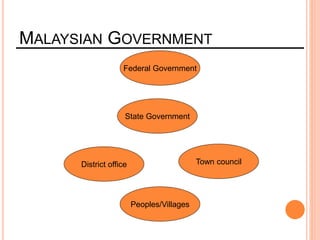
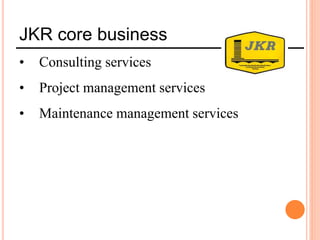
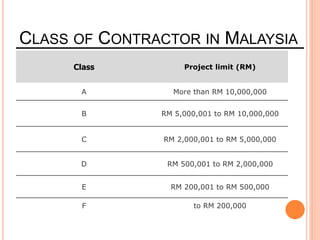
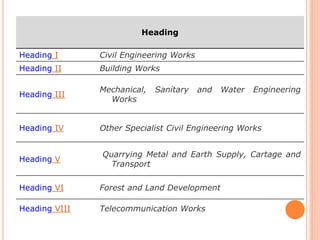
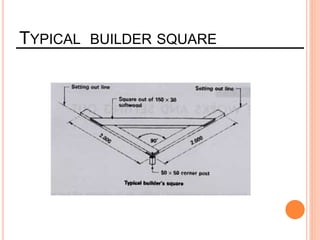
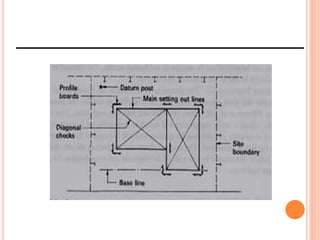
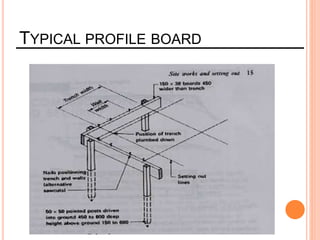
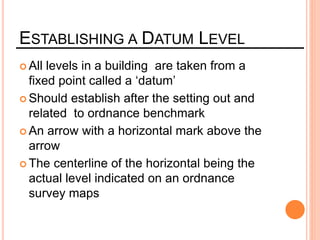
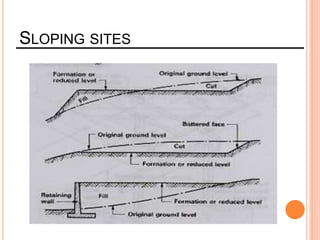
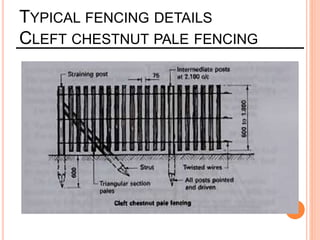
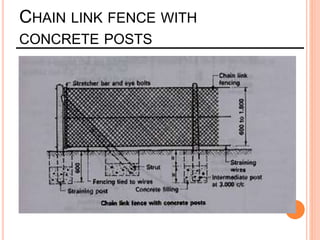
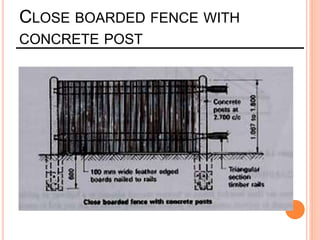
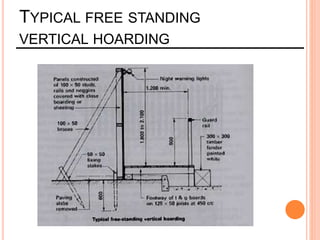
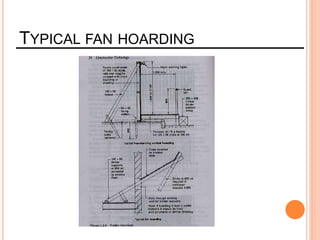
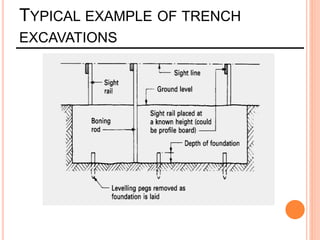
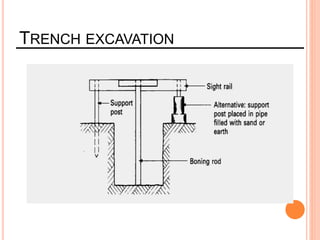
This document provides information about a construction technology and maintenance course, including its code, credit units, contact hours, assessment structure, and lesson plan. The course aims to help students understand construction methods, techniques, and equipment used on construction sites. It covers topics like building, infrastructure, and maintenance stages; temporary and permanent works; construction plants; and latest technologies. The lesson plan lists weekly topics, learning outcomes, and lecture hours across 14 weeks. Students will learn about construction processes, equipment selection, and sustainable development techniques. The course assessments include two tests, assignments, a project report, and group presentations.