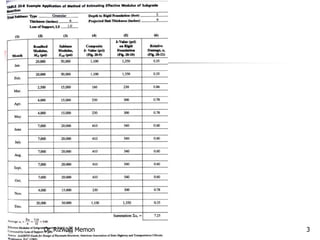
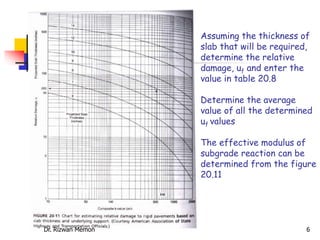
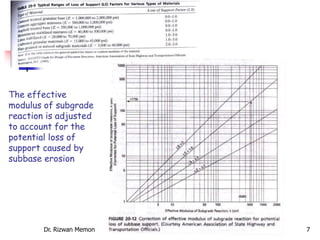
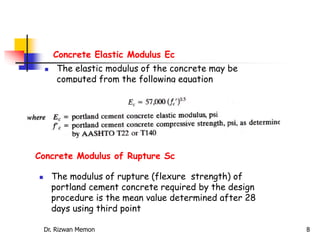
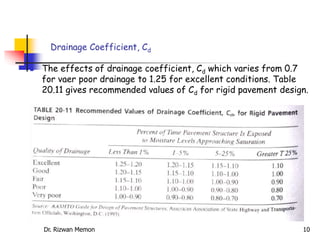
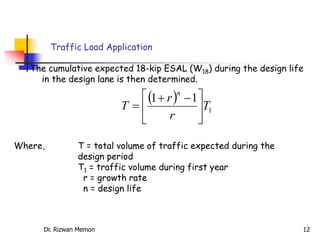
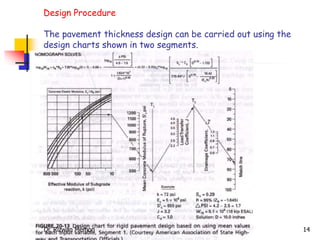
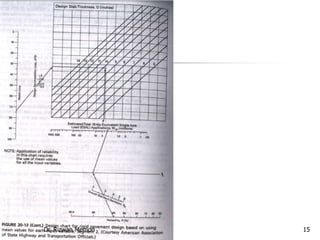
The AASHTO guide for designing rigid pavements considers several factors: the effective modulus of subgrade reaction, concrete elastic modulus and modulus of rupture, load transfer coefficient, reliability and standard deviation, traffic load application, and serviceability loss. The document then proceeds to describe the process for determining each of these factors to complete the pavement thickness design using design charts.