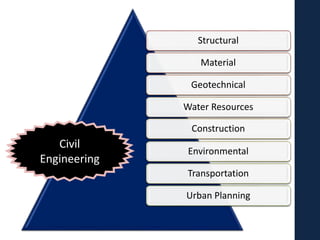
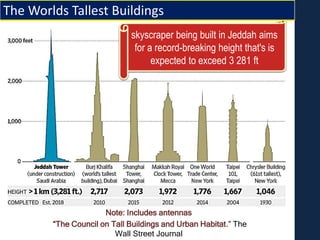
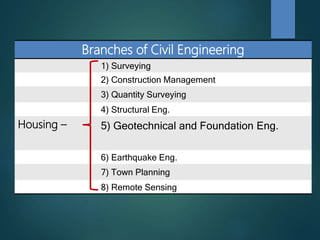
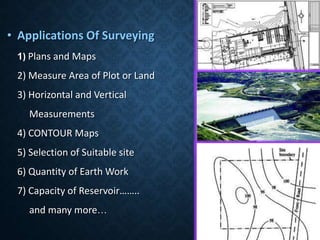
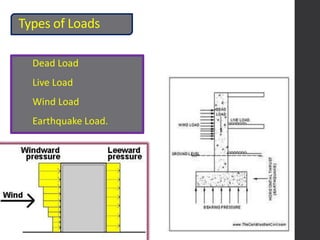
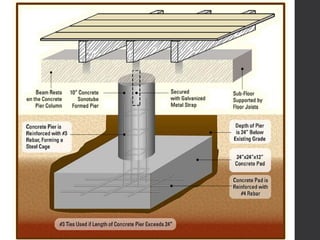
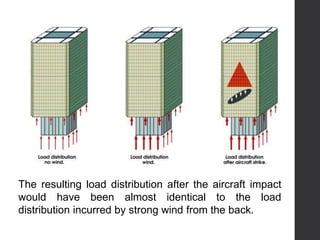
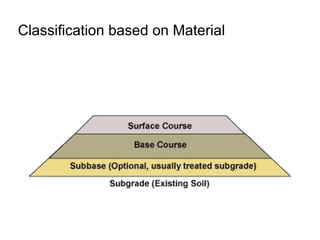
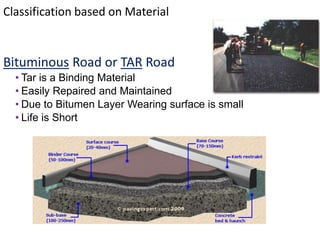
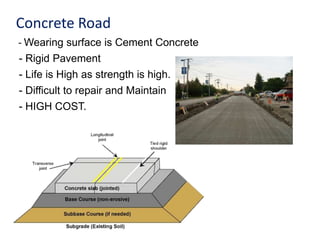
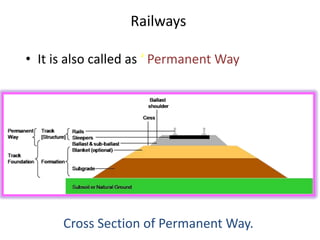
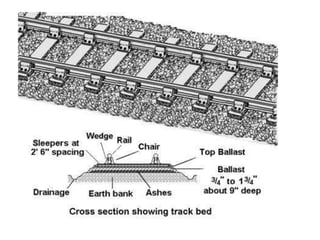
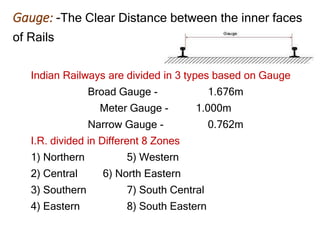
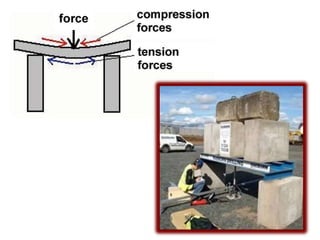
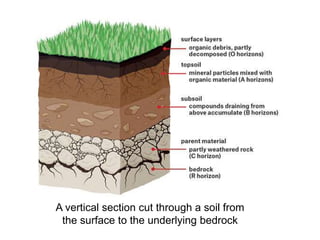
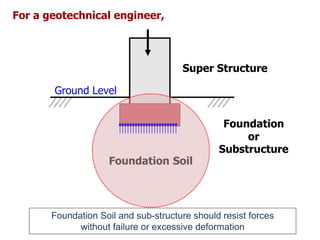
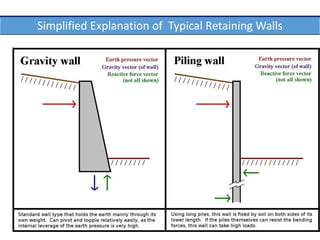
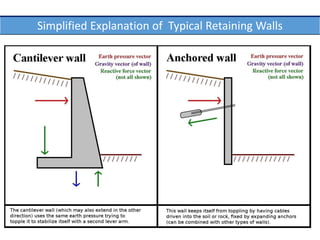
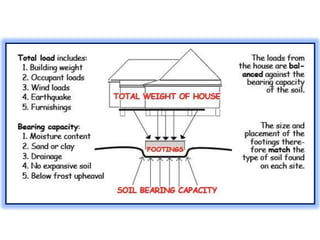
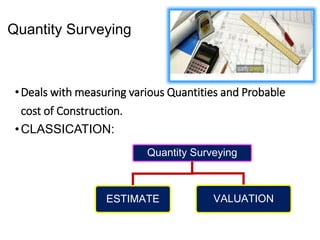
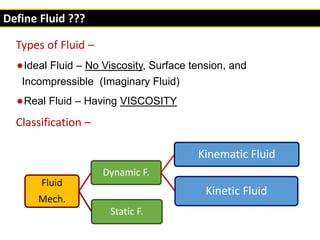
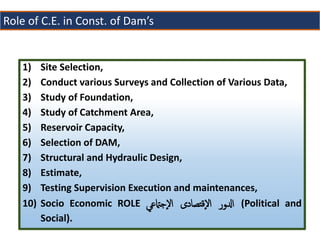
This document provides an overview of various branches of civil engineering including structural engineering, transportation engineering, geotechnical engineering, environmental engineering, construction management, quantity surveying, irrigation engineering, and earthquake engineering. It also discusses related topics like surveying, roads, railways, soil mechanics, fluid mechanics, and the roles of civil engineers in different construction projects. The key branches covered are structural design of buildings and bridges, transportation infrastructure like roads and railways, foundation design and geotechnical soil testing, water and wastewater management, construction planning and management, and disaster mitigation.