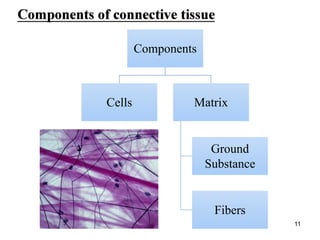
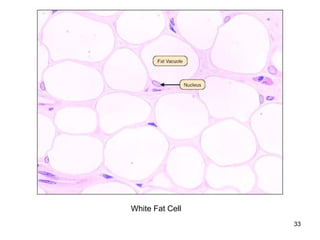
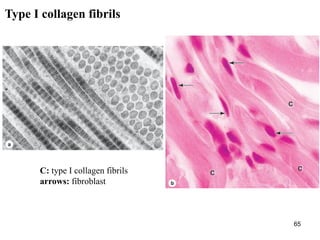
This document provides an overview of connective tissue. It discusses the main cells found in connective tissue, including fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells, plasma cells, and leukocytes. It also describes the main fibers - collagen, reticular, and elastic fibers - and ground substance. Finally, it outlines the main types of connective tissue, including connective tissue proper (loose and dense connective tissue), supporting connective tissue (cartilage and bone), and fluid connective tissue (blood). Loose connective tissue, also called areolar tissue, is characterized as having cells, fibers and ground substance in roughly equal parts and serving to bind organs and fill spaces between tissues.