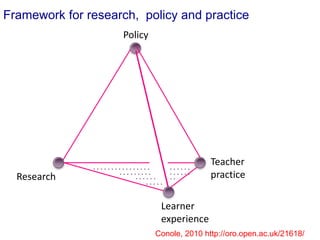
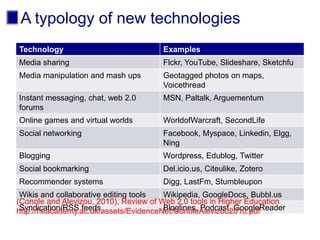
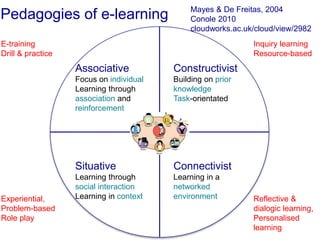
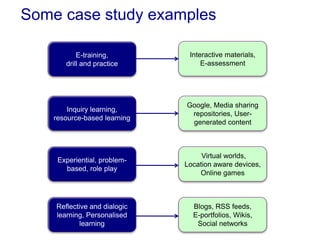
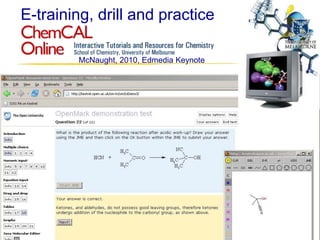
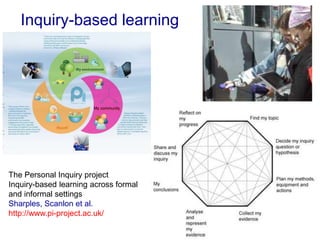
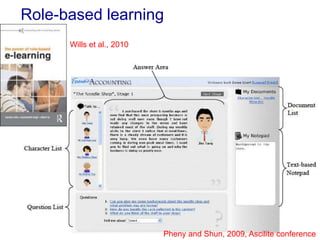
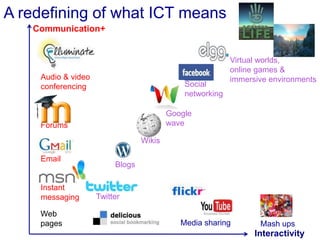
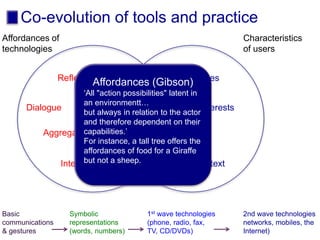
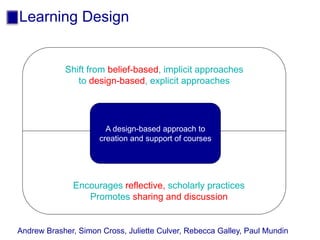
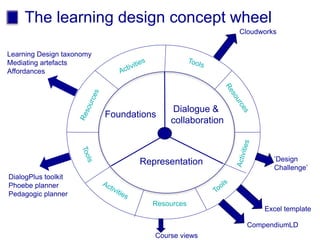
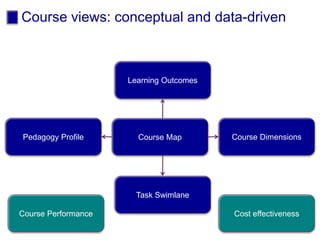
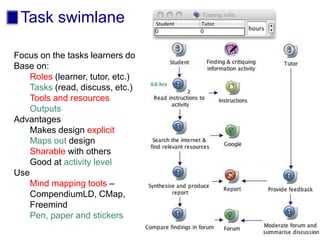
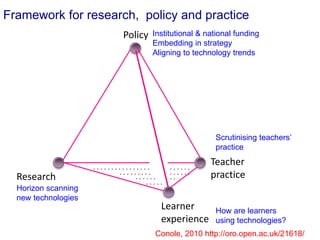
The document discusses connecting research, policy, and practice in e-learning. It provides a framework linking the four areas of research, policy, teacher practice, and learner experience. It then examines the history of e-learning and various technologies and pedagogical approaches. Key lessons include the need for new digital literacies and better linking research to policy and practice. The future will involve an ongoing evolution of technologies and their use in education.