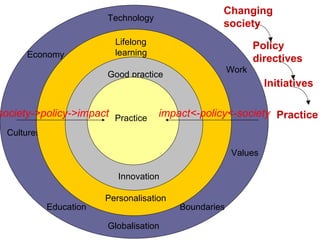
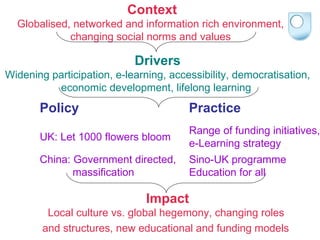
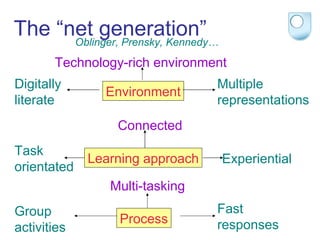
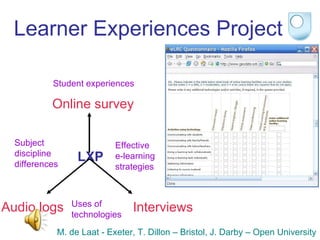
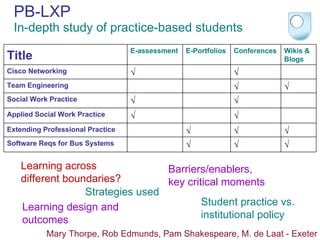
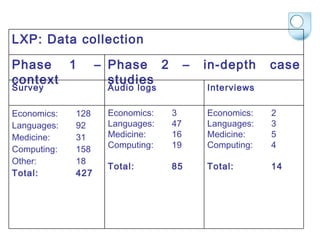
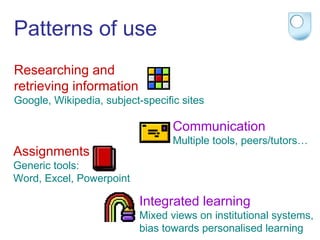
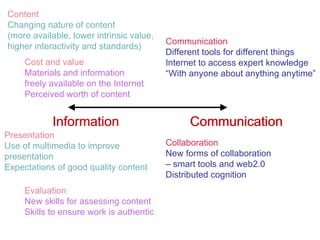
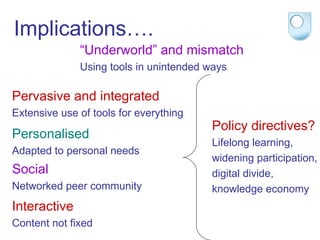
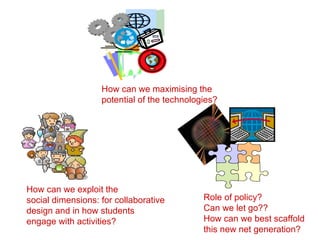
The document summarizes findings from the JISC Learner Experience Programme (LXP) regarding students' use of technology. The LXP studied students across different disciplines and found extensive use of various tools for tasks like researching, communicating, and completing assignments. Students had personalized approaches and used tools in unintended ways compared to institutional policies. This points to a mismatch between policy directives focused on lifelong learning and the realities of students' technology use in a rapidly changing social and educational context.
![The student experience How does it align with policy directives? Gráinne Conole [email_address] Eden Conference, Naples 15 th June 2007](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conole-110512062246-phpapp02/85/The-student-experience-How-does-it-align-with-policy-directives-1-320.jpg)