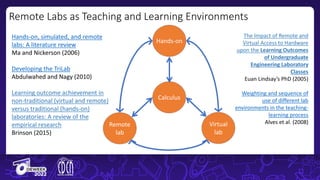
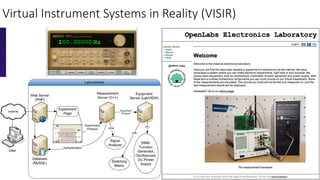
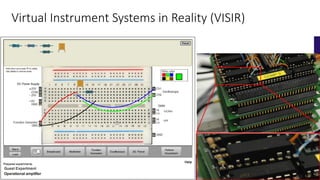
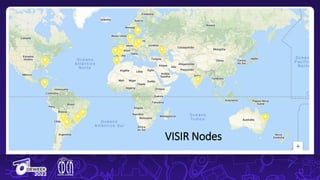
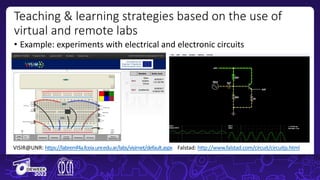
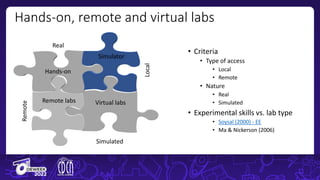
The document discusses the integration of remote and virtual labs in technical higher education, focusing on their role in enhancing instructional laboratories and engineering education. It outlines significant trends over the past century, such as the shift towards outcomes-based education and the integration of technology, while citing key challenges and developments in educational technology. Additionally, it emphasizes the impact of COVID-19 on accelerating the adoption of these technologies in educational settings.



![• Froyd, J.E.; Wankat, P.C., Smith, K.A.; Five Major Shifts in 100 Years of Engineering
Education, Proceedings of the IEEE, Vol. 100, pp. 1344-1360, May 13th, 2012
• Adams Becker, S., Cummins, M., Davis, A., Freeman, A., Hall Giesinger, C., and
Ananthanarayanan, V. (2017). NMC Horizon Report: 2017 Higher Education
Edition. Austin, Texas: The New Media Consortium. [online]
http://cdn.nmc.org/media/2017-nmc-horizon-report-he-EN.pdf
• Ruth Graham, The Global State of the Art in Engineering Education, MIT, March
2018. ISBN 13: 9780692089200
Trends in Engineering Education](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eden-oew-2022-ppt-gca-220310073202/85/Digital-experiences-in-technical-higher-education-5-320.jpg)