Embed presentation
Downloaded 25 times

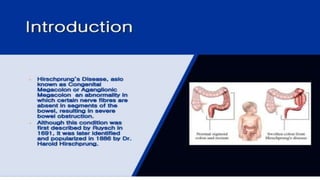
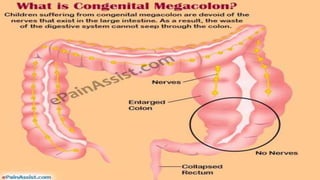

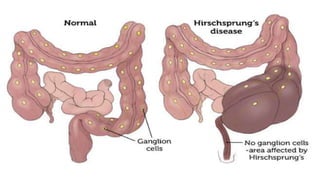

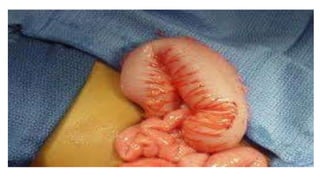


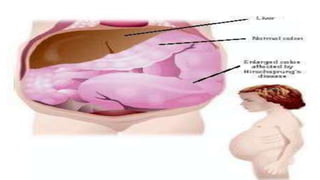



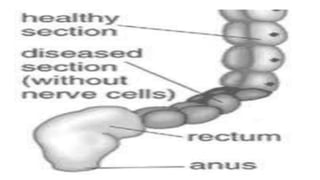


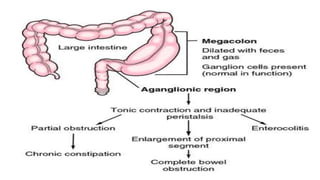
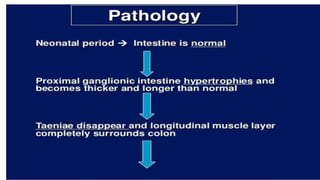
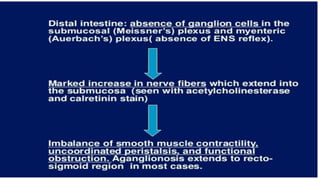

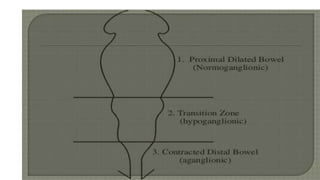











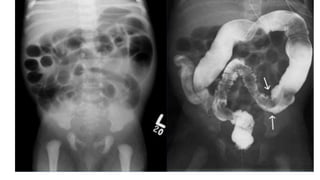

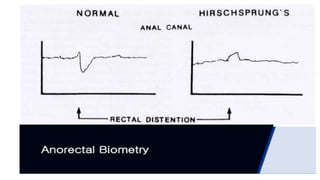
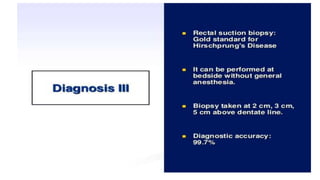
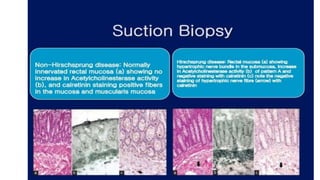





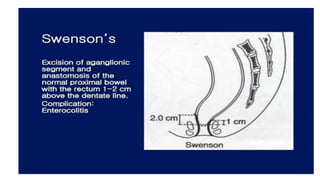
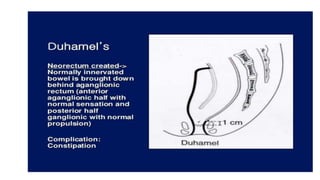
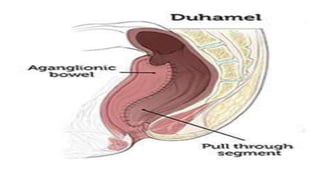
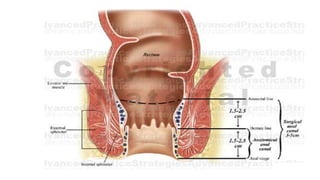
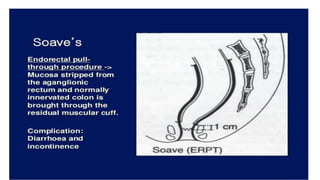


Hirschsprung's disease is a disorder of the gut caused by the congenital absence of ganglion cells in the submucosal and myentric plexus of the intestine, also known as megacolon or congenital aganglionic megacolon. It is caused by the congenital absence of autonomic parasympathetic ganglion cells. Surgical management involves removing the aganglionic bowel followed by anastomosis of the remaining portion, done in two stages - a temporary colostomy followed later by a pull through procedure to excise the aganglionic segment and connect the bowel.


















































