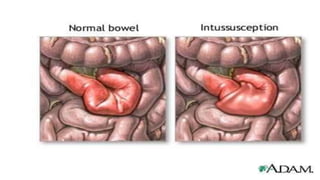
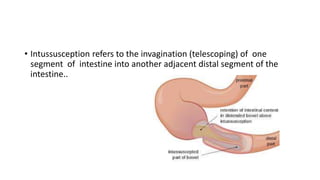
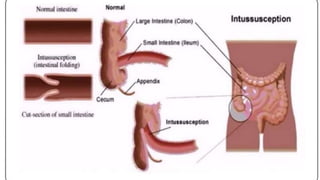
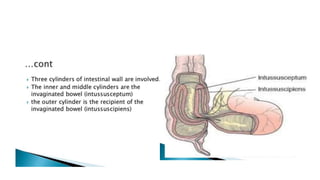
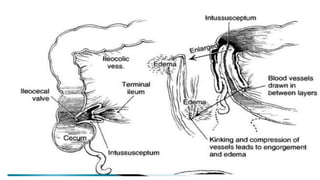
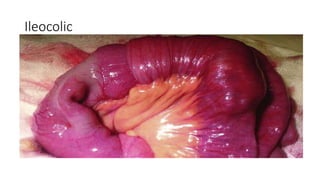
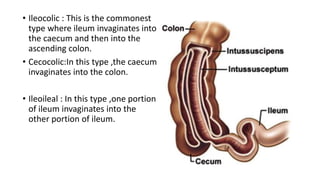
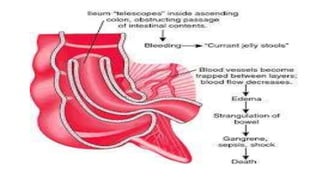
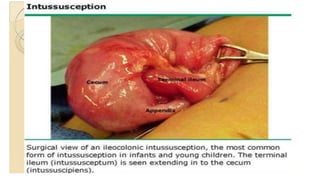
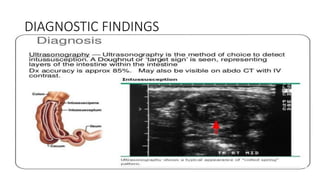
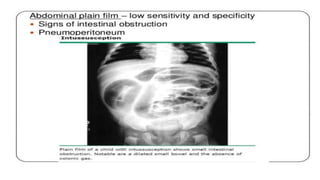
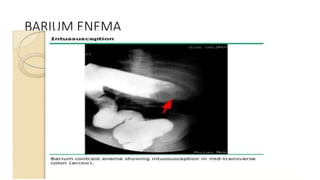
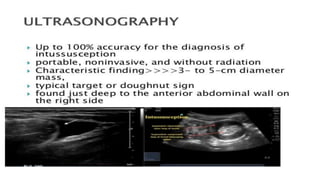
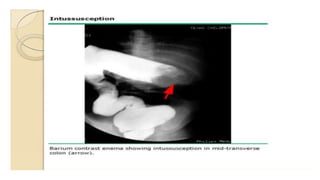
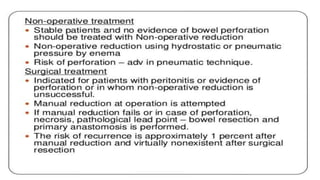
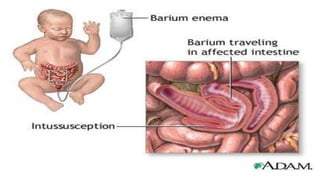
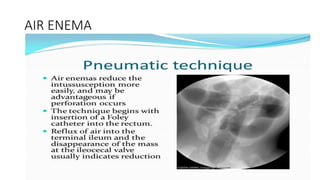
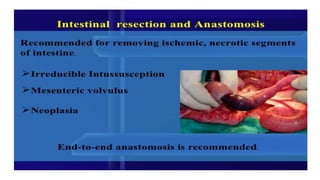
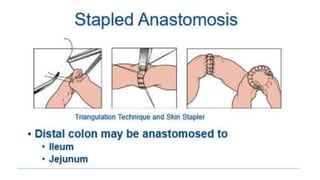
This document discusses intussusception, which refers to the telescoping of one part of the intestine inside another. The most common type is ileocolic, where the ileum invaginates into the caecum and ascending colon. Causes are often unknown but may include gastroenteritis or lesions. Diagnosis is usually via barium or air enema. Treatment involves non-surgical hydrostatic reduction using barium or air, while surgery is needed if reduction fails or tissue is non-viable. Nursing care focuses on pre-op preparation, monitoring for recurrence after attempted reduction, and supporting recovery after surgery through careful observation and gradual feeding/ambulation.