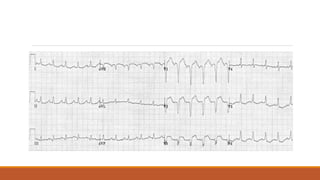
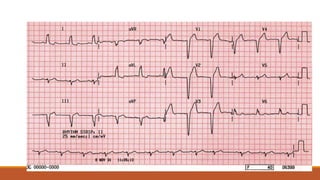
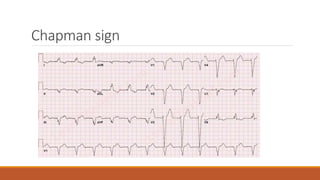
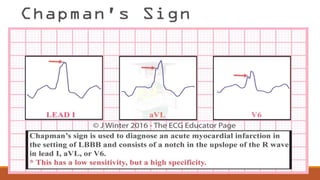
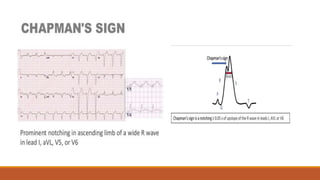
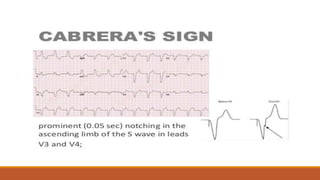
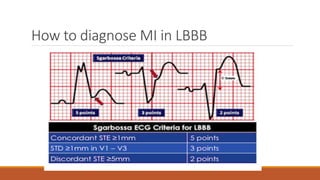
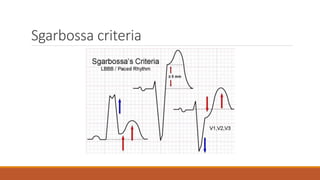
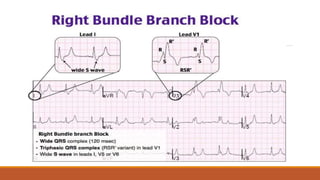
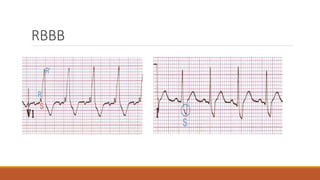
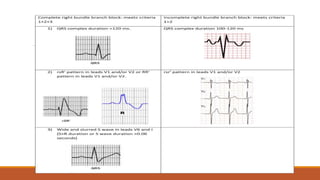
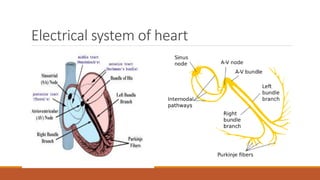
The document discusses the conduction system of the heart and bundle branch blocks. It notes that a bundle branch block is diagnosed when the QRS duration is over 120ms, there is a dominant S wave in V1, and a broad monophasic R wave in lateral leads. It lists causes of left bundle branch block such as aortic stenosis, dilated cardiomyopathy, and myocardial infarction. It explains how left bundle branch block leads to reversed septal activation and prolonged conduction time to the left ventricle. The document also discusses right bundle branch block and potential causes like pulmonary embolism, ischemic heart disease, and cardiomyopathy.

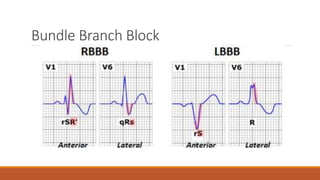

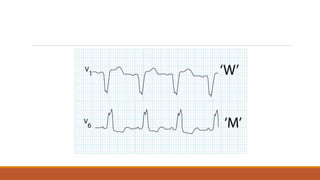
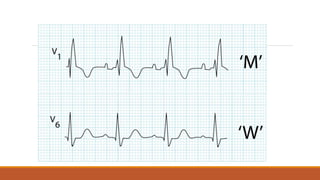
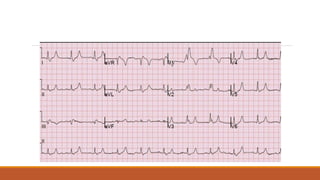
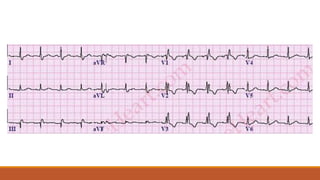
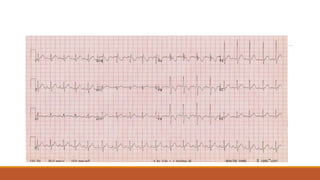
![The heart rhythm must be supraventricular in origin
The QRS duration must be ≥ 120 ms[2]
There should be a QS or rS complex in lead V1
There should be a notched ('M'-shaped) R wave in lead V6.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/conductionabnormalities-210126143702/85/Conduction-abnormalities-5-320.jpg)