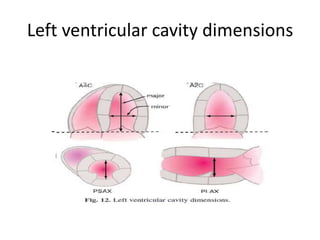
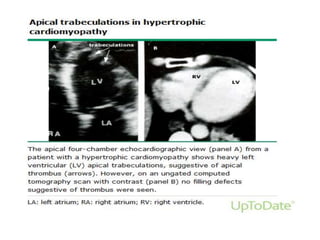
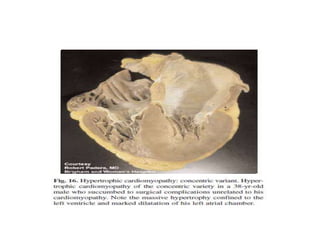
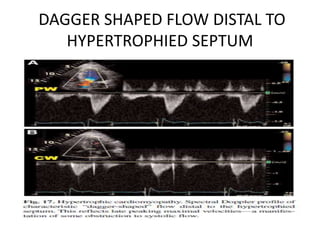
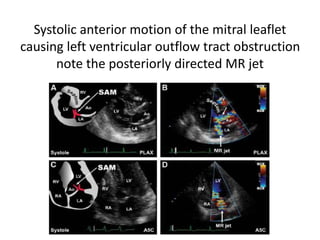
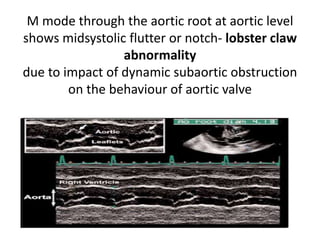
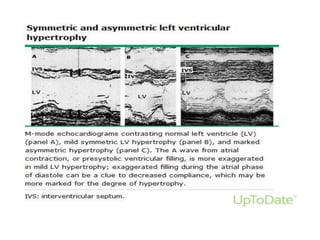
This document discusses the echocardiographic evaluation of hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HCM). Key points include:
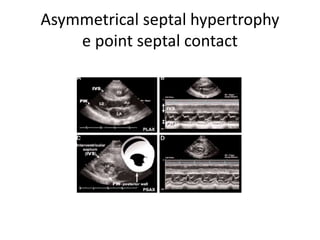
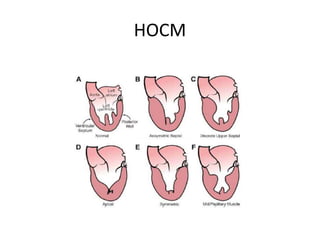
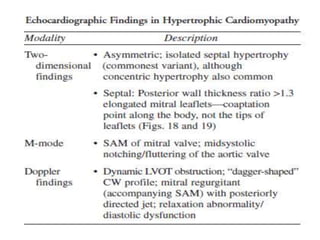
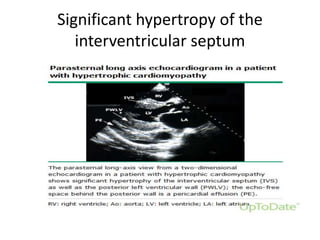
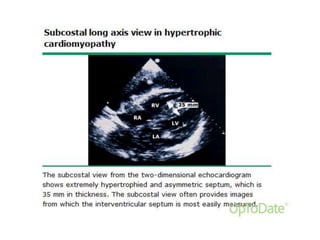
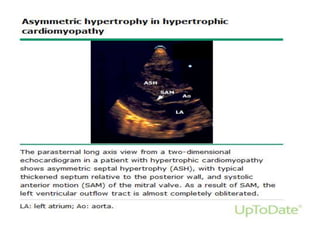
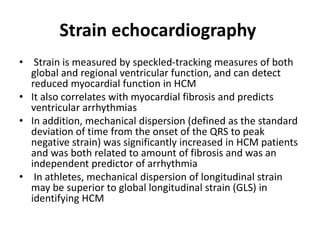
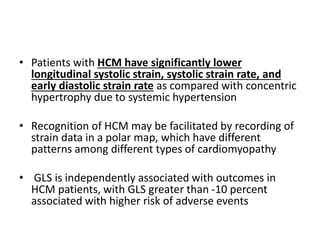
- Echocardiography is used to diagnose HCM based on unexplained left ventricular hypertrophy and rule out other causes. Asymmetric septal hypertrophy is a characteristic pattern.
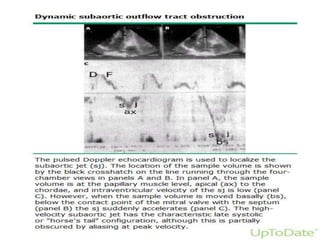
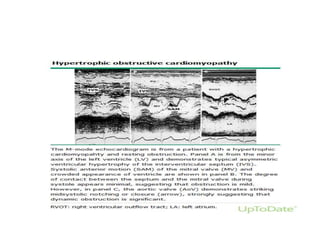
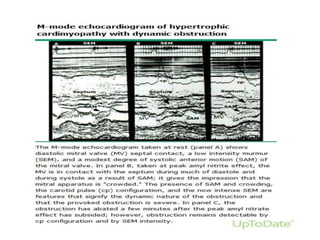
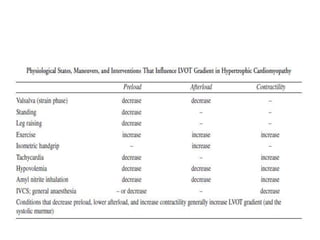
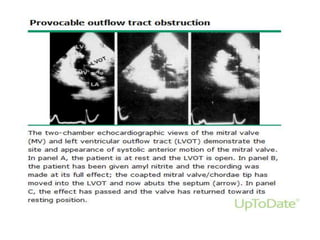
- Doppler echocardiography is used to detect left ventricular outflow tract obstruction at rest and with provocative maneuvers like Valsalva.
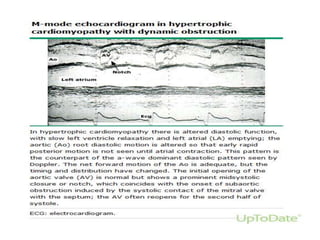
- Features like systolic anterior motion of the mitral valve indicate dynamic obstruction and need to be monitored with maneuvers.
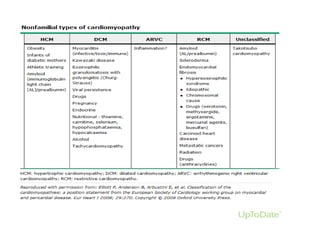
- Differential diagnosis includes secondary causes of left ventricular hypertrophy from things like hypertension which present differently on echocard