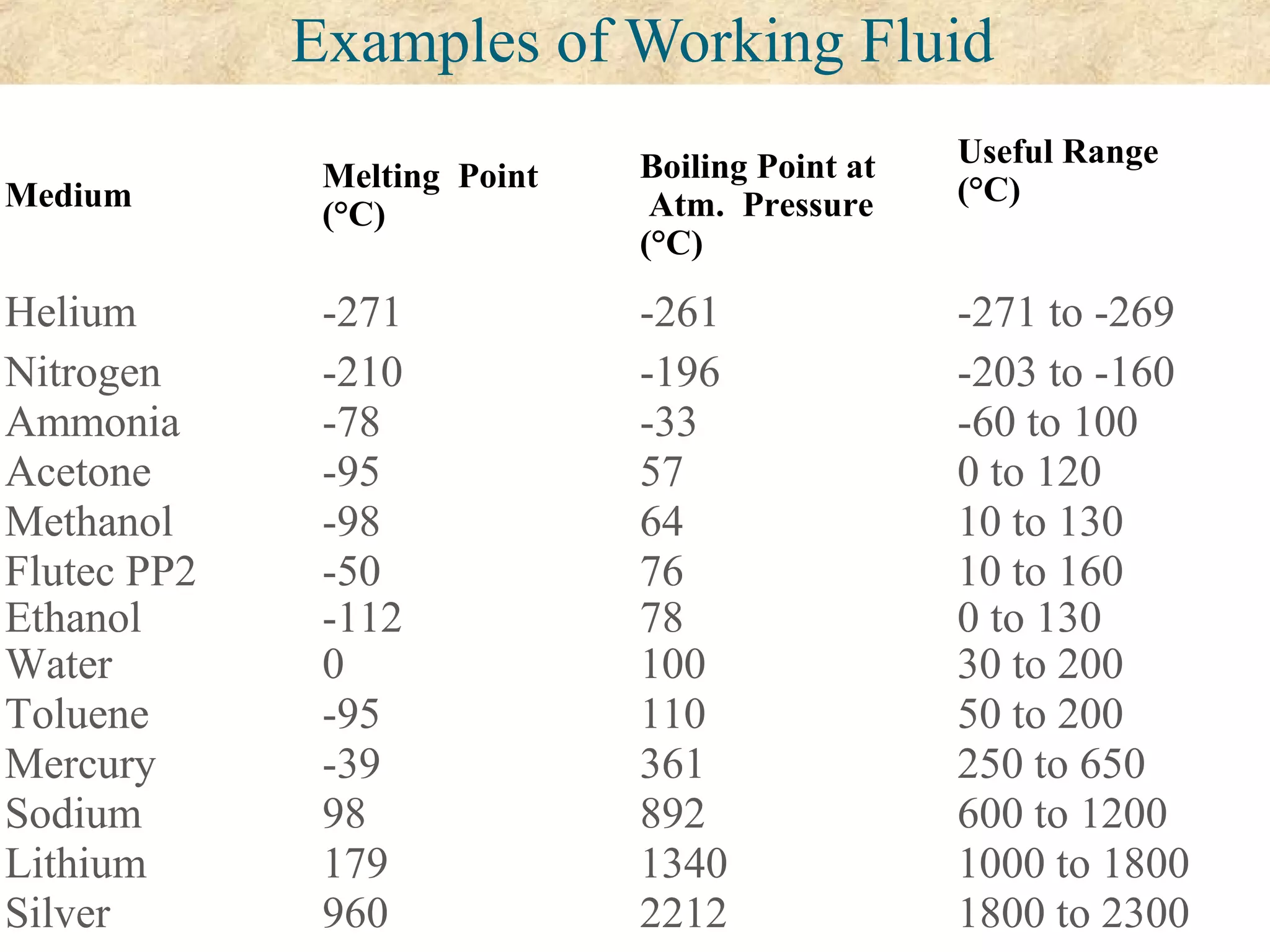
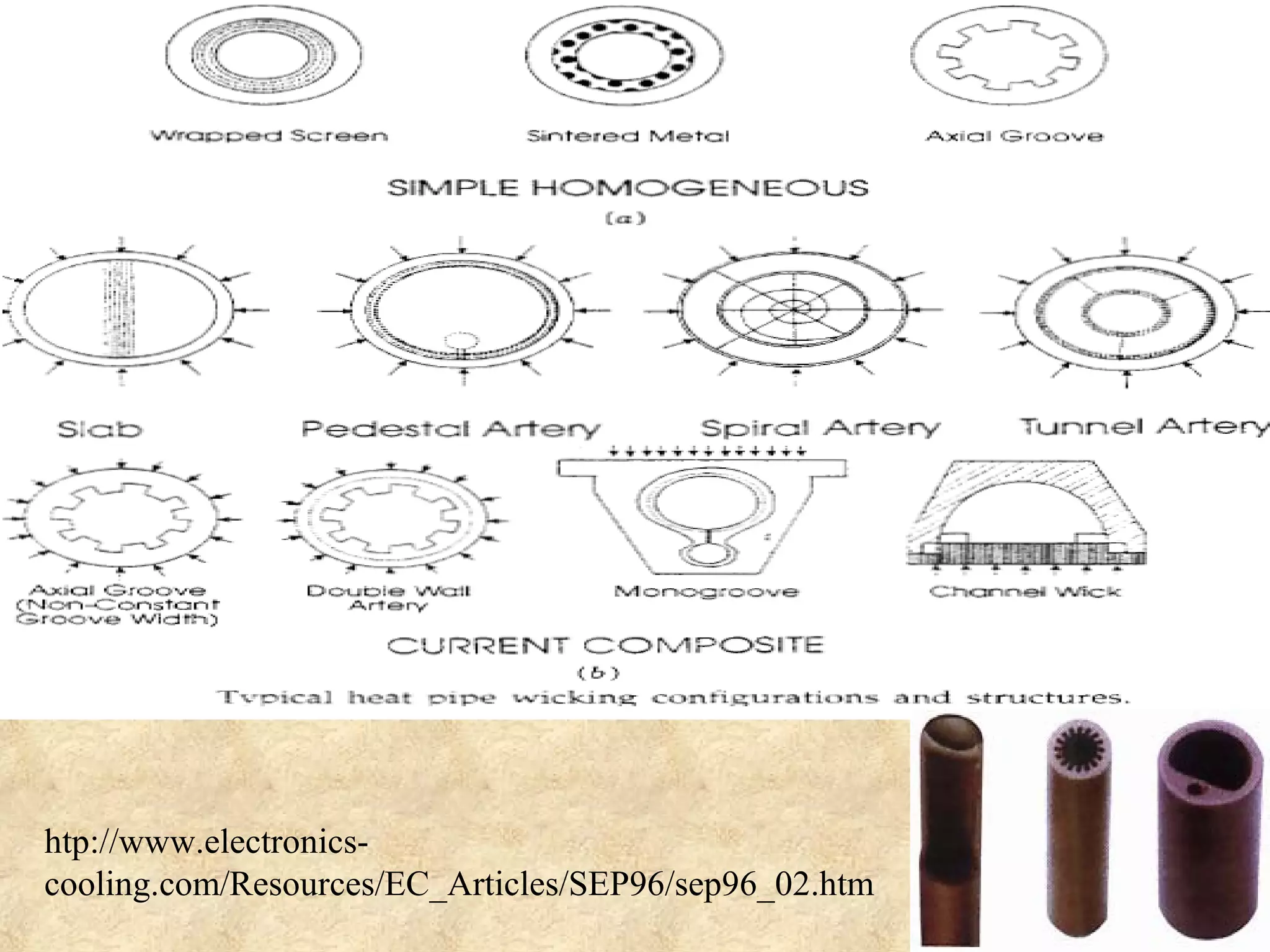
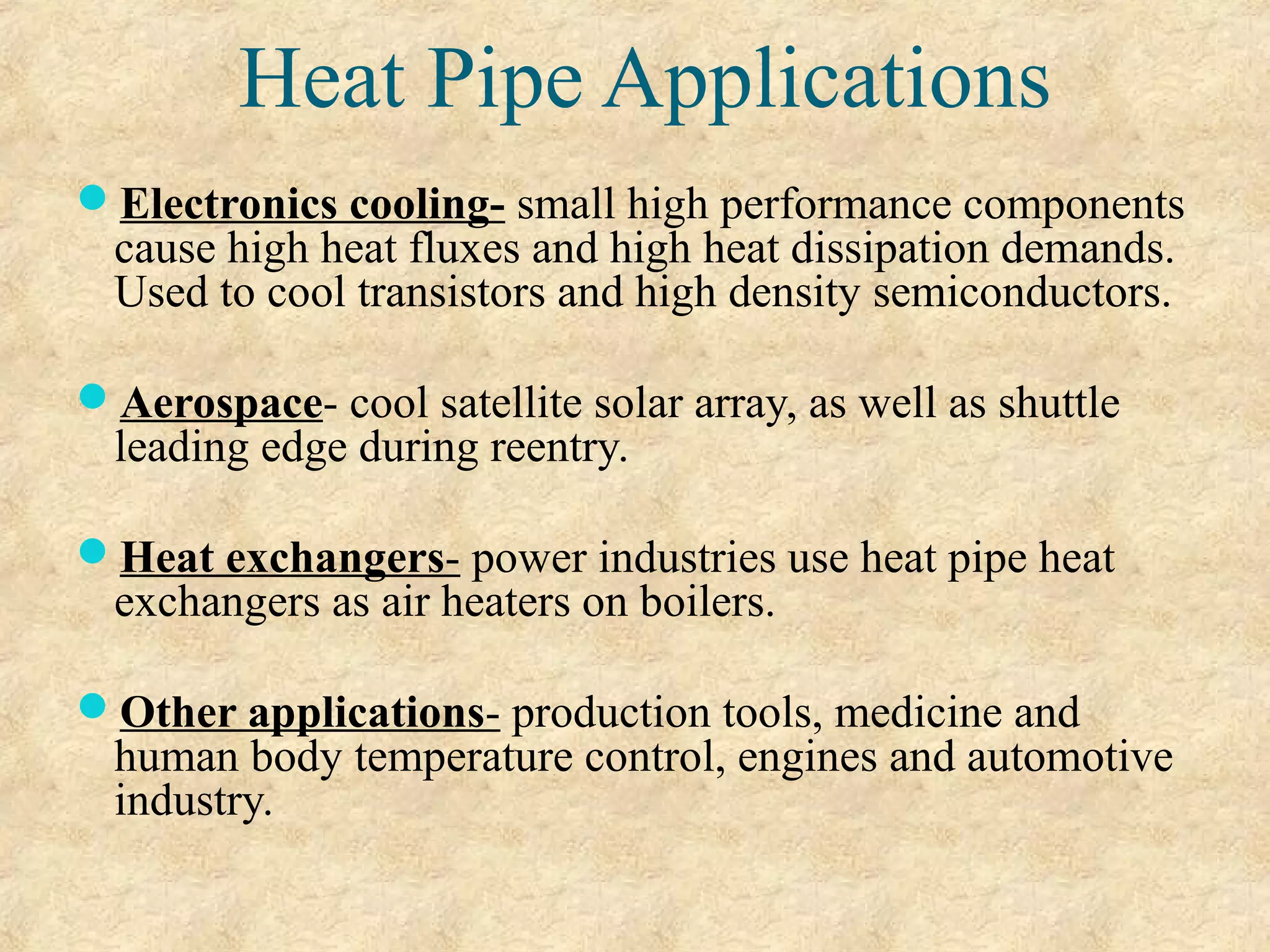
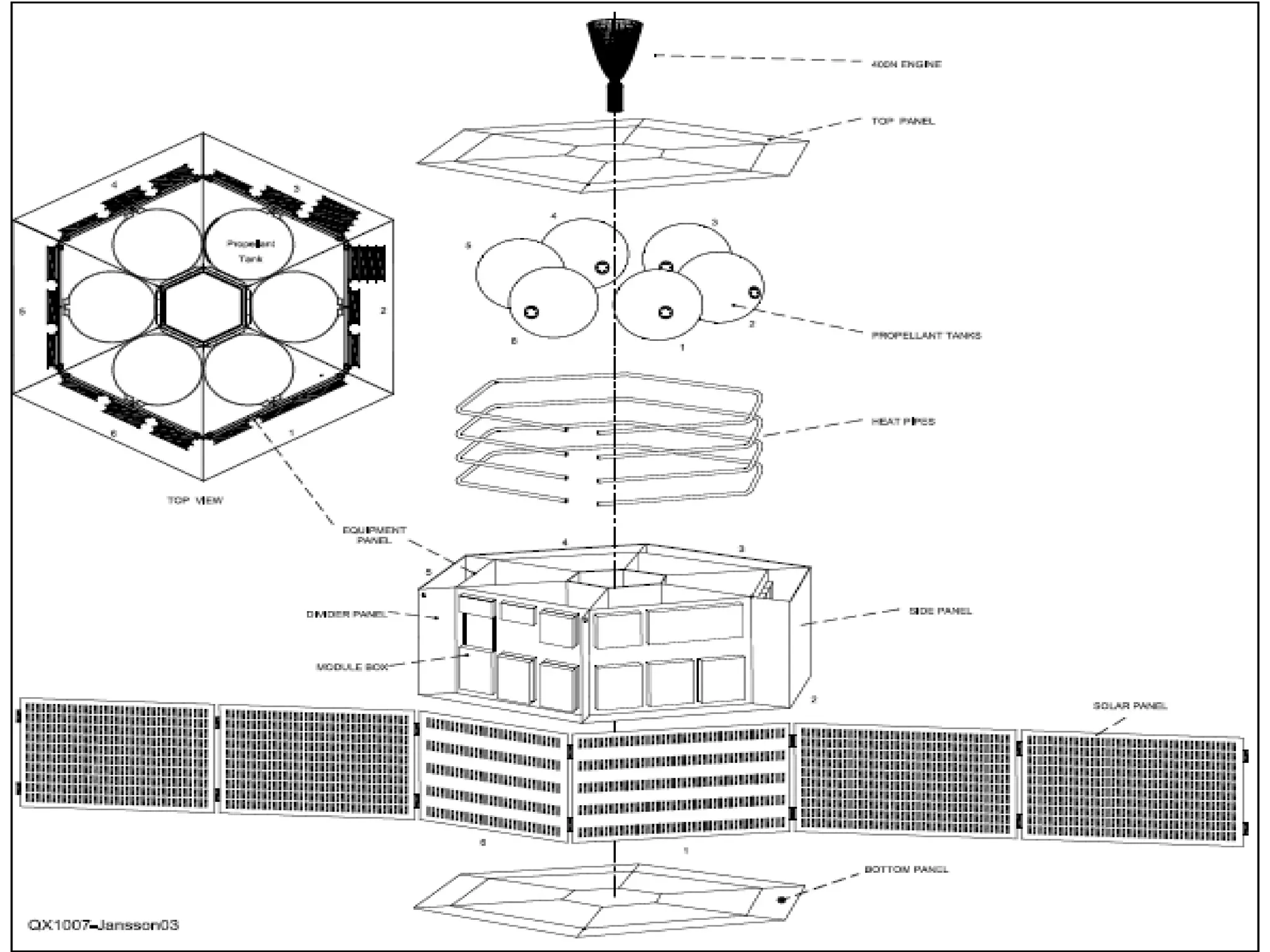
This document provides an overview of heat pipes, including their working principle and key components. A heat pipe is a device that transfers heat using a vaporization-condensation cycle with very high efficiency. It contains a container, working fluid, and wick structure. As heat is applied at the evaporator end, the fluid vaporizes and moves through the container to the condenser end where it condenses and is pumped back to the evaporator by the wick, transferring heat in the process. Common working fluids, wick designs, and applications of heat pipes are discussed. Heat pipes can be used to efficiently transfer heat in electronics, aerospace, and other industrial applications.