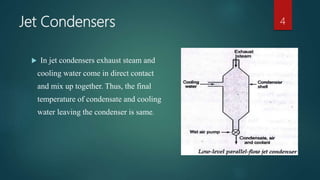
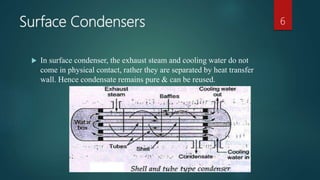
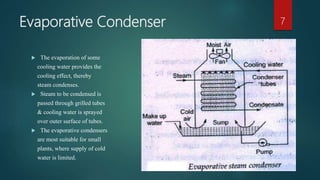
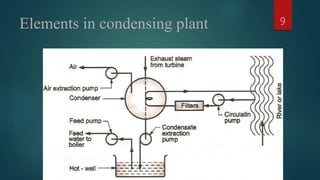
The document discusses different types of condensers. It begins by explaining that a condenser is a heat exchanger that converts a working fluid from a gas to a liquid state using a coolant like water. It then describes jet condensers which directly mix exhaust steam and cooling water, surface condensers which separate steam and water with a heat transfer wall, and evaporative condensers which use evaporating cooling water to provide cooling. The document also compares jet and surface condensers and classifies condensers based on their external cooling fluid, such as air, water, or evaporative cooling.