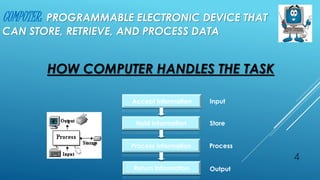
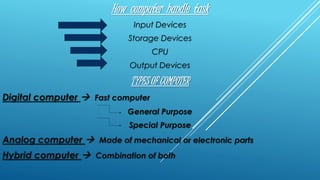
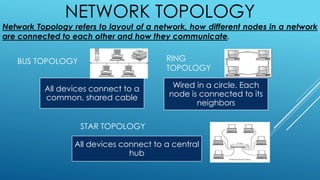
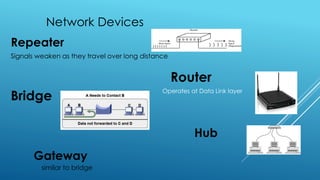
The document provides information about five group members working on a computer applications project. It then discusses various topics related to computers including bits, bytes, ASCII, file storage units, computer hardware components, input/output devices, storage devices, network topologies, and cable media types.