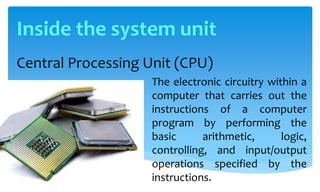
The document details a 10-day training workshop hosted by resource speaker Mark John Perez, focusing on the essentials of technology, including hardware, software, and networking. It outlines the objectives and history of computers, the classification of computer types, and the fundamental components of computer systems. Additionally, it provides insights into computer peripherals, internal components, and the relationship between hardware and software.