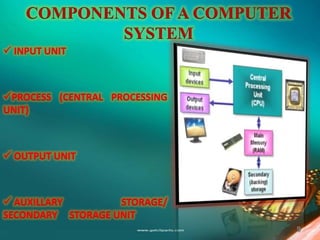
The document provides an overview of information technology, focusing on computer systems, communication technology, and software types. It discusses the components of a computer, various types of memory, storage devices, networking technologies, and the role of operating systems. Additionally, it highlights specific applications such as word processing and presentation graphics.