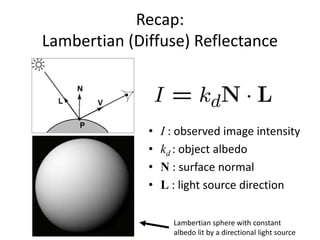
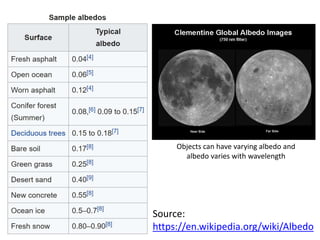
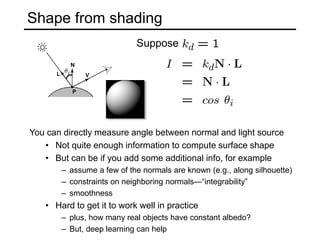
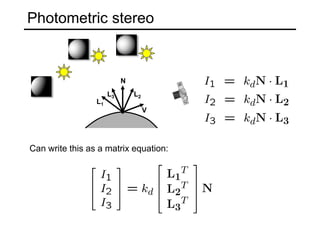
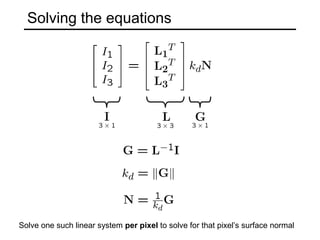
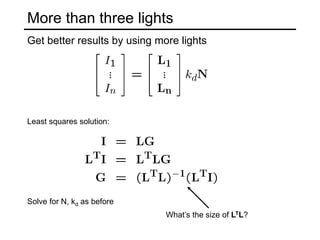
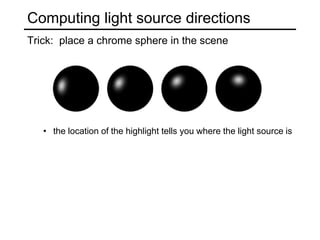
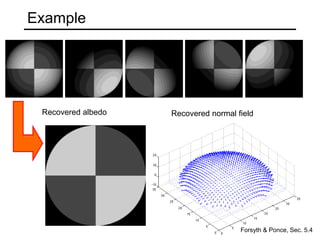
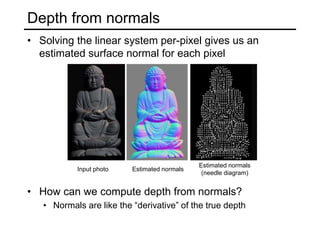
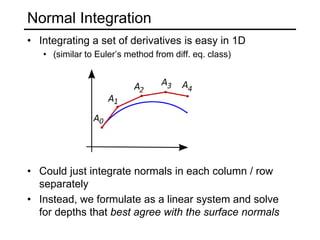
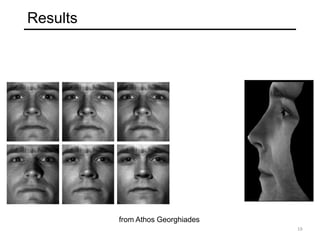
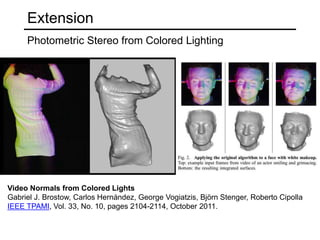
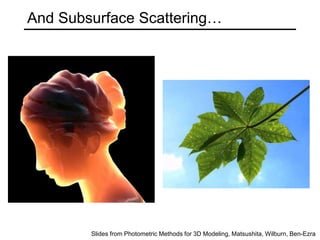
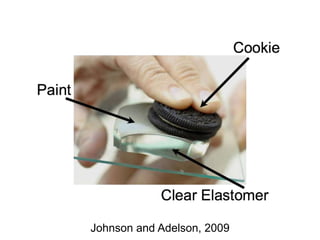
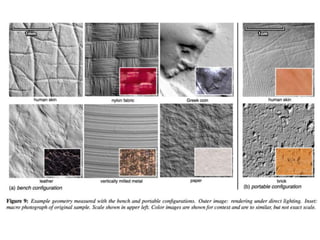
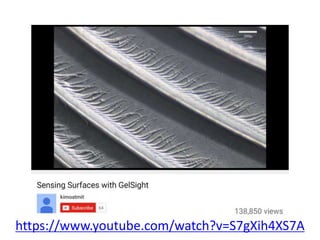
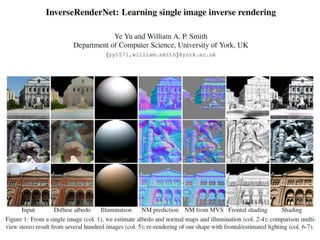
The document discusses the computer vision technique of photometric stereo, which uses images of an object lit by known light sources from different directions to determine the object's 3D shape and surface reflectance properties. It explains that photometric stereo solves a matrix equation per pixel to determine each pixel's surface normal from image intensities under different lighting. Integrating the surface normals can then yield a depth map. The technique works best for diffuse objects and makes assumptions such as constant albedo that may not always hold for real-world scenes.