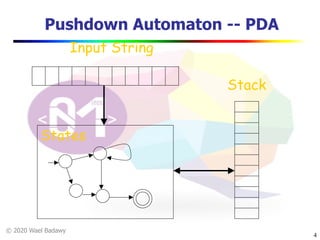
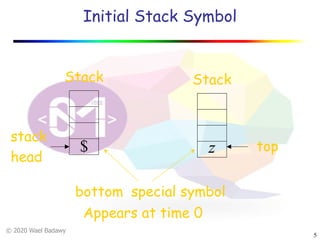
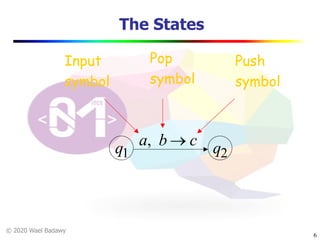
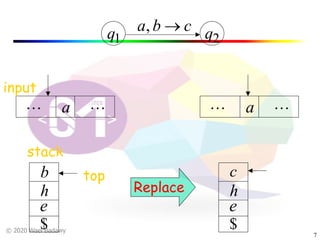
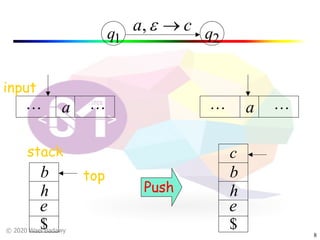
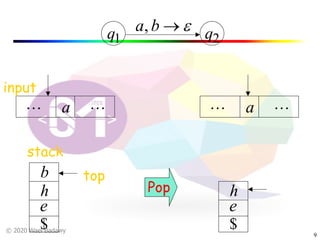
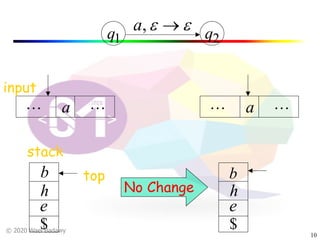
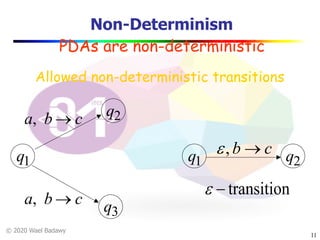
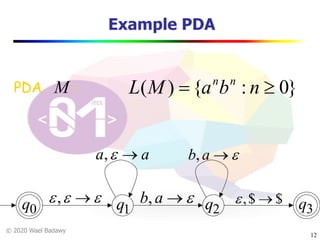
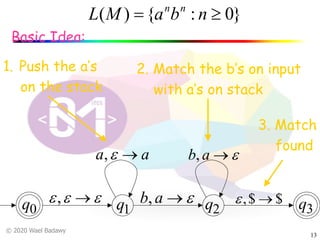
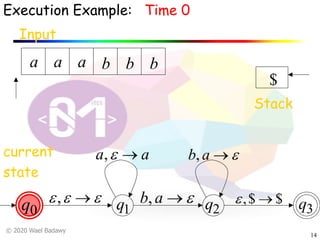
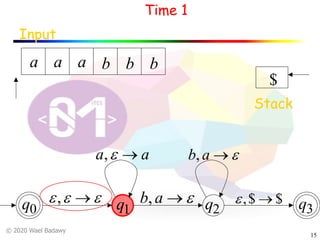
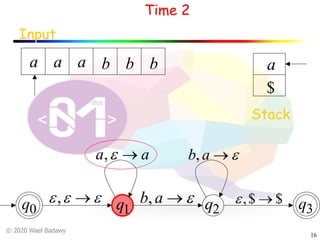
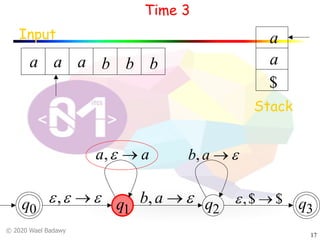
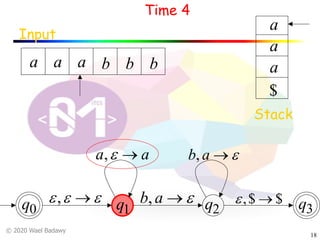
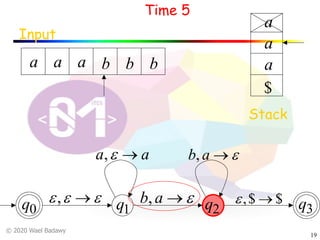
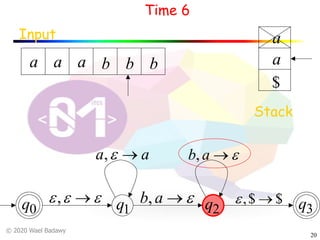
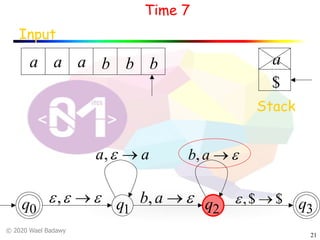
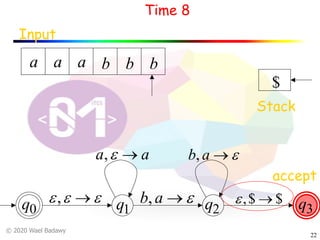
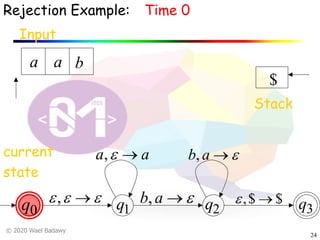
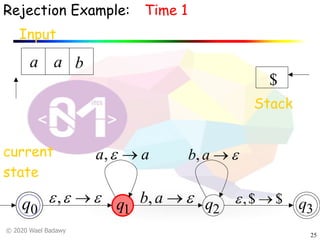
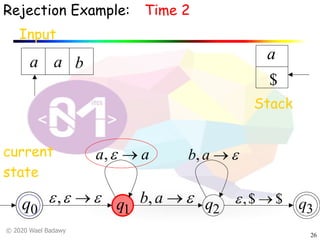
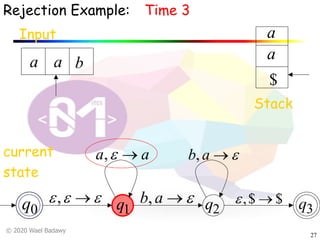
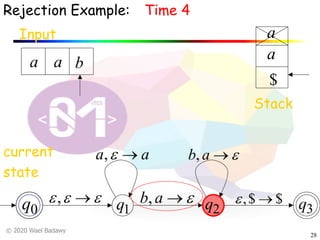
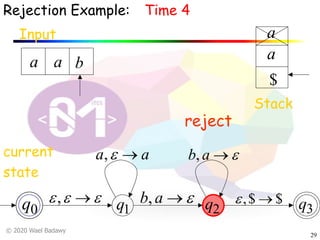
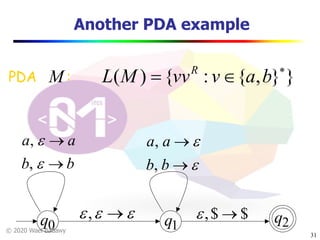
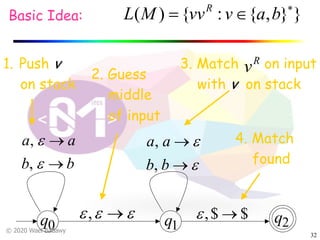
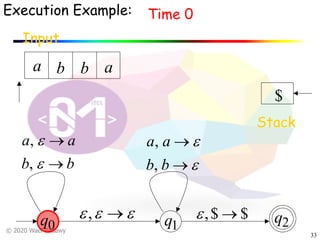
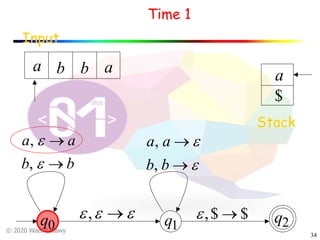
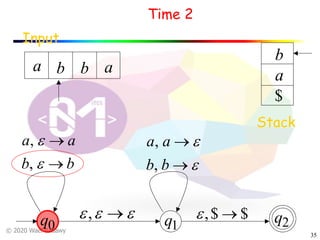
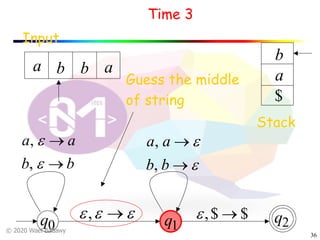
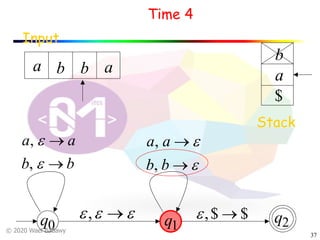
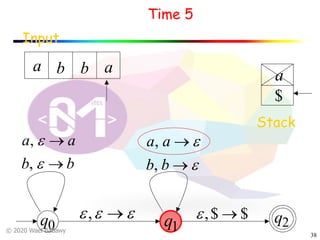
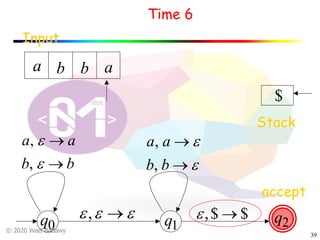
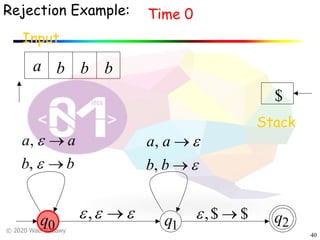
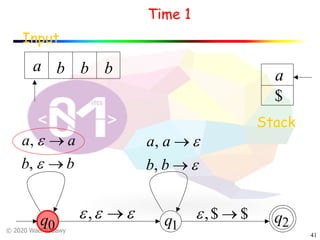
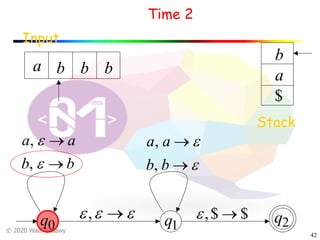
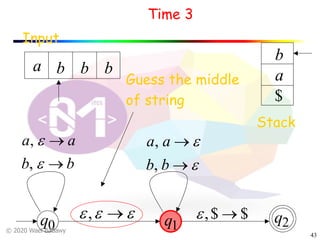
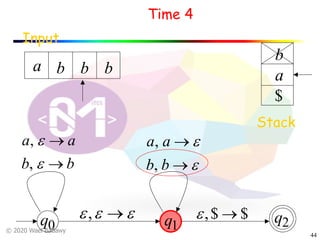
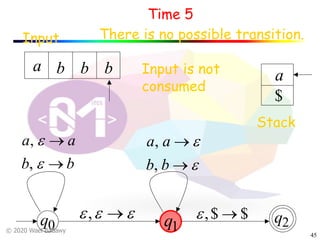
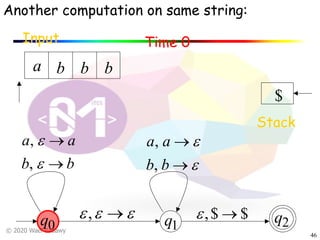
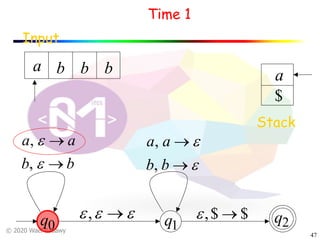
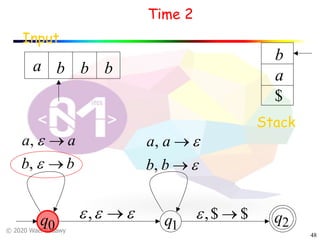
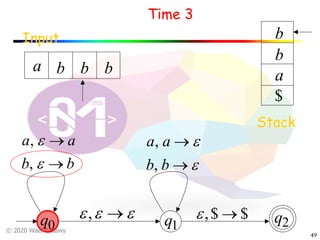
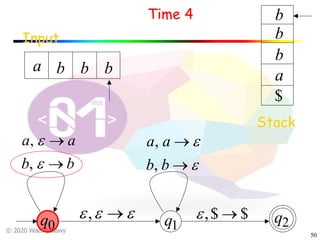
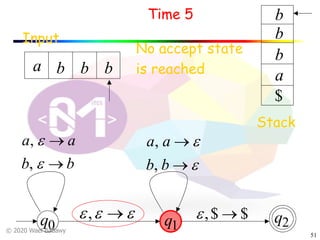
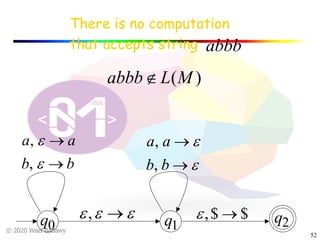
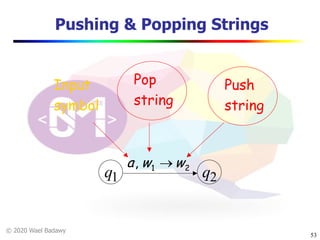
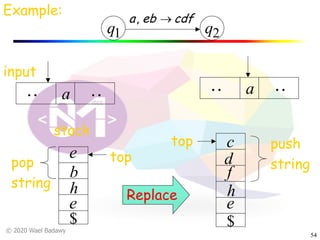
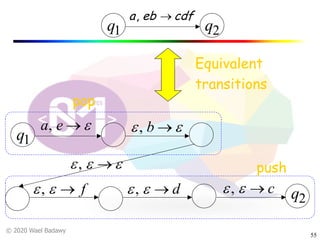
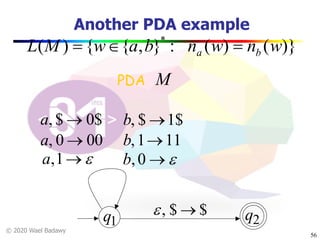
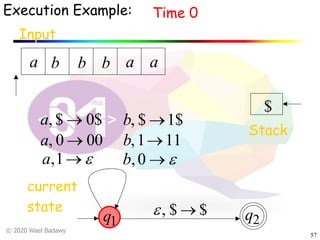
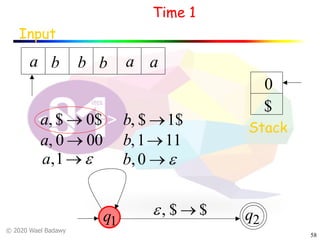
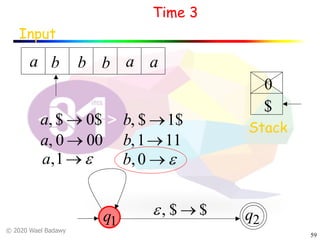
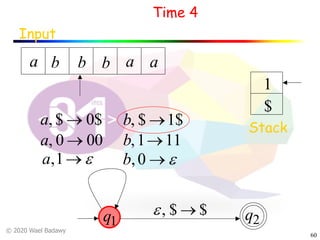
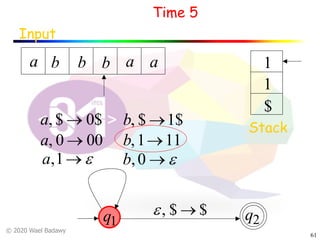
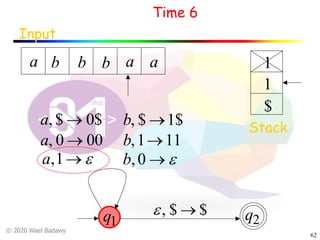
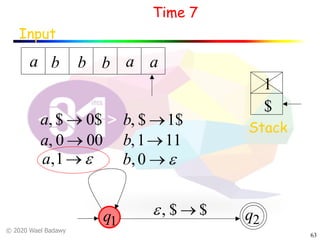
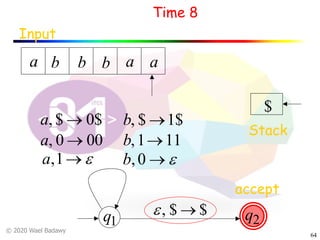
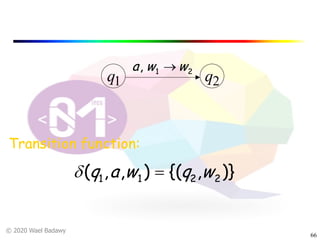
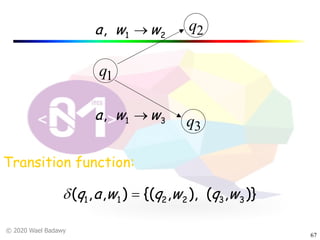
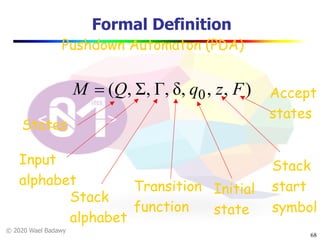
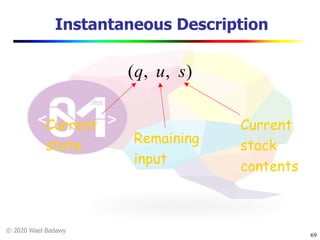
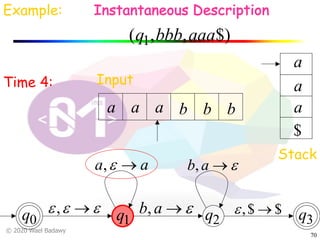
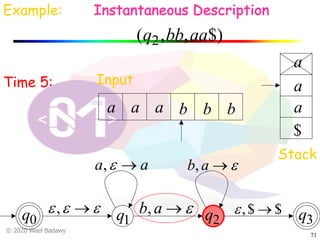
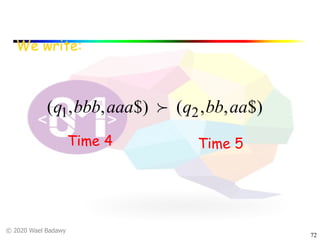
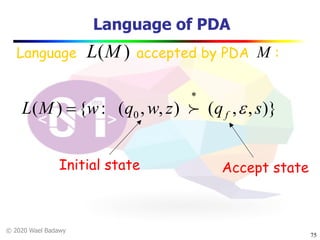
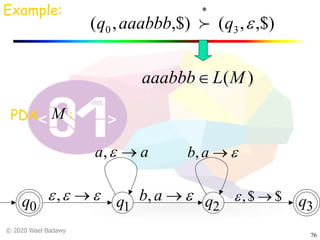
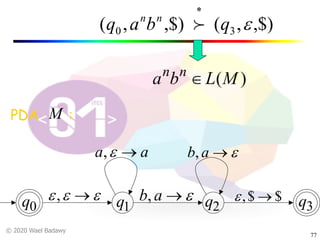
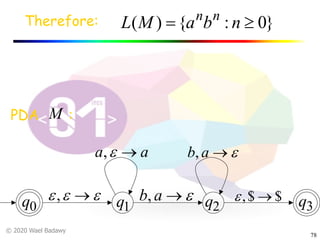
The document discusses pushdown automata (PDAs). It begins with an overview of the components of a PDA - the input string, stack, states, and transitions. It then provides examples of PDA configurations and computations for accepting and rejecting strings. Key points made include: PDAs are non-deterministic, a string is accepted if the entire input is consumed in an accepting state, and strings can be pushed and popped from the stack individually or as strings. The document uses several examples to demonstrate how PDAs work.