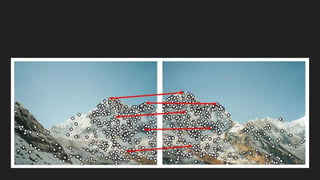
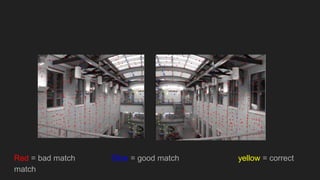
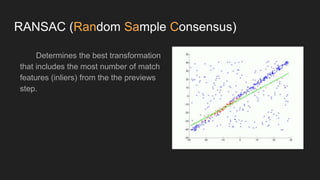
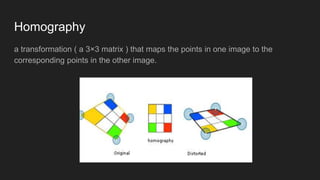
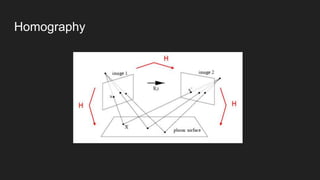
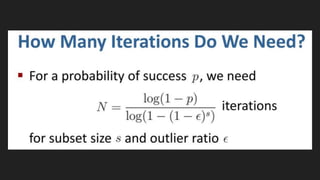
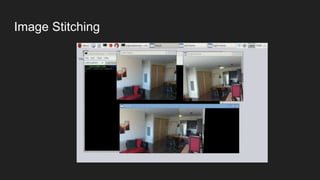
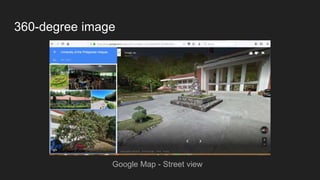
This document discusses feature matching and RANSAC algorithms. It begins by explaining feature matching, which determines correspondences between descriptors to identify good and bad matches. RANSAC is then introduced as a method to determine the best transformation that includes the most inlier feature matches. The document provides details on how RANSAC works including selecting random samples, computing transformations, and iteratively finding the best model. Applications like image stitching, panoramas, and video stabilization are mentioned.