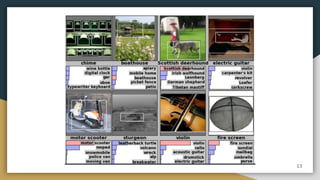
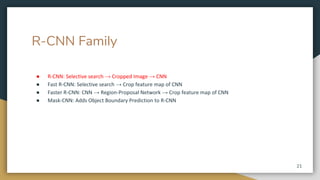
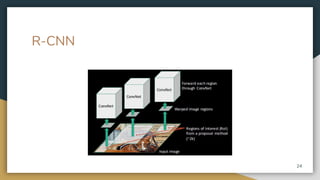
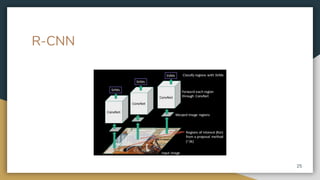
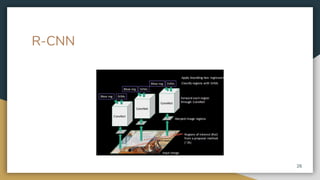
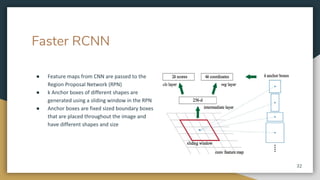
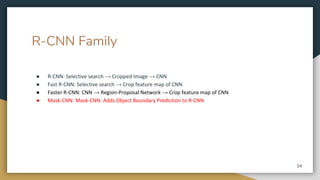
The document discusses object detection using the R-CNN deep learning framework, detailing concepts such as inductive bias, region proposals, and different iterations of R-CNN including Fast R-CNN, Faster R-CNN, and Mask R-CNN. It explains the machine learning processes involved in classification, localization, and segmentation, specifically how selective search is employed for region proposals. The paper emphasizes the challenges and improvements in the R-CNN family of algorithms for efficient object detection.