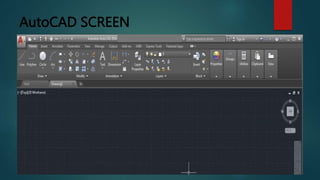
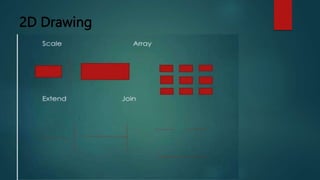
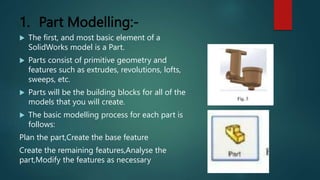
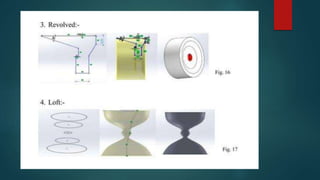
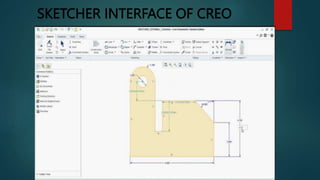
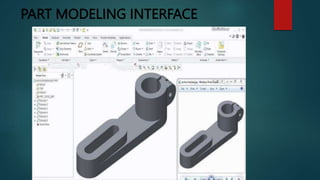
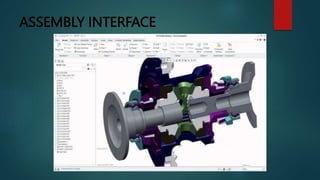
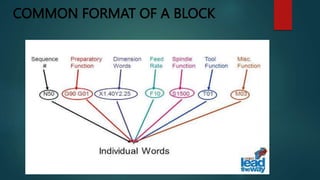
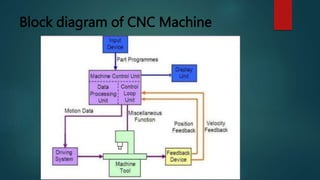
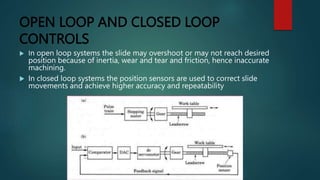
This document provides an overview of Dipak Chauhan's internship at Indo German Tool Room in Ahmedabad. It discusses the importance of computer-aided design (CAD) software like AutoCAD, SolidWorks, Creo, and CNC machines in modern manufacturing. CAD software allows designers to digitally create 2D drawings and 3D models, while CNC machines use numerical control codes to automate manufacturing processes and improve precision and productivity. The internship will provide Dipak hands-on experience using these tools to support engineering industries in designing and machining complex parts.