This document discusses automated systems, including what they are, where they are used, and why companies use them. Some key points:
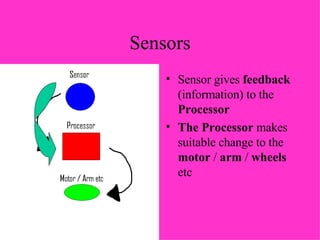
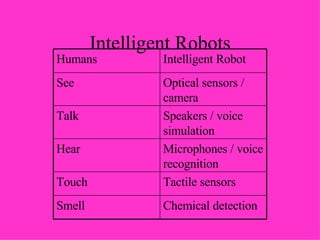
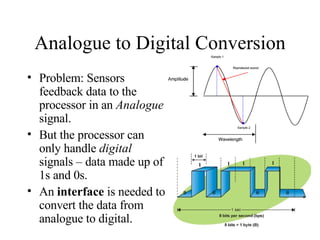
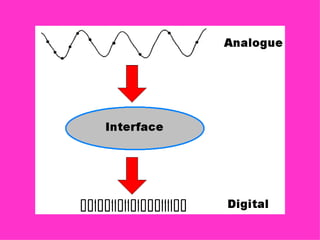
- Automated systems use computers to control machinery like robots in factories. They can operate at high speeds and in dangerous environments.
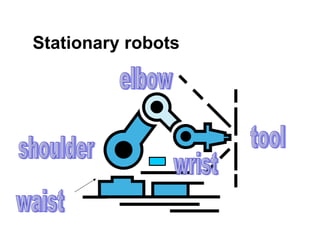
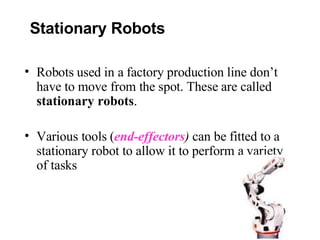
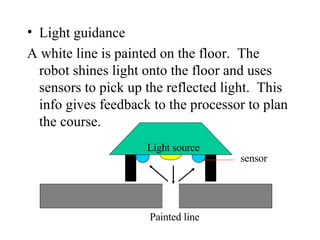
- Factories, oil rigs, and traffic lights all use automated systems. Robots can be stationary or mobile, using magnetic or light guidance systems.
- Companies invest in automated systems because while the initial costs are high, they eventually save money through increased production, quality control, and reduced labor costs.