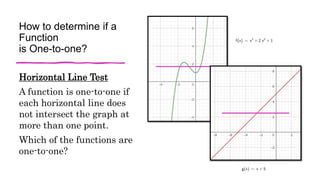
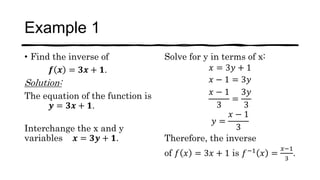
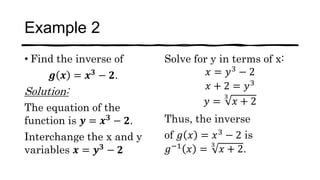
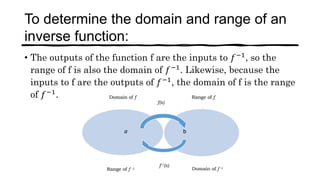
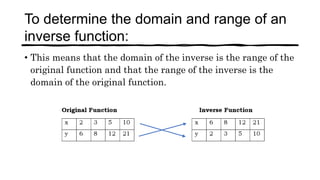
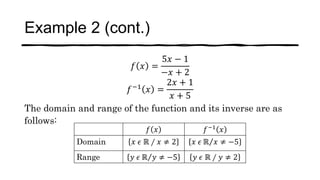
This document discusses one-to-one functions and their inverses. It defines a one-to-one function as a function where no two x-values are mapped to the same y-value. The inverse of a one-to-one function f is defined as f^-1 where the inputs and outputs are swapped. Examples are provided of finding the inverse of various functions by swapping variables and solving for y in terms of x. The domain of an inverse function is the range of the original function, and the range of the inverse is the domain of the original function.