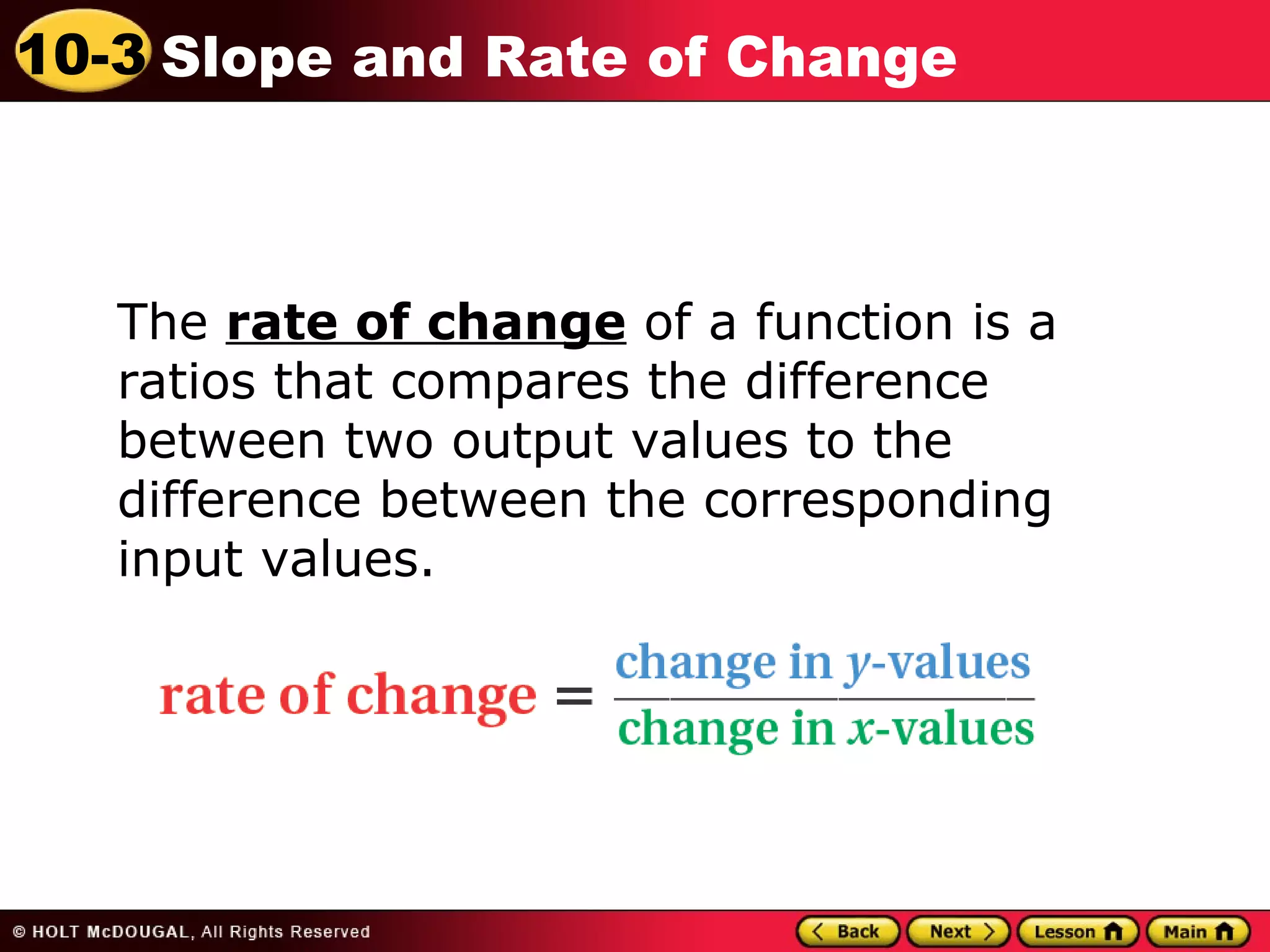
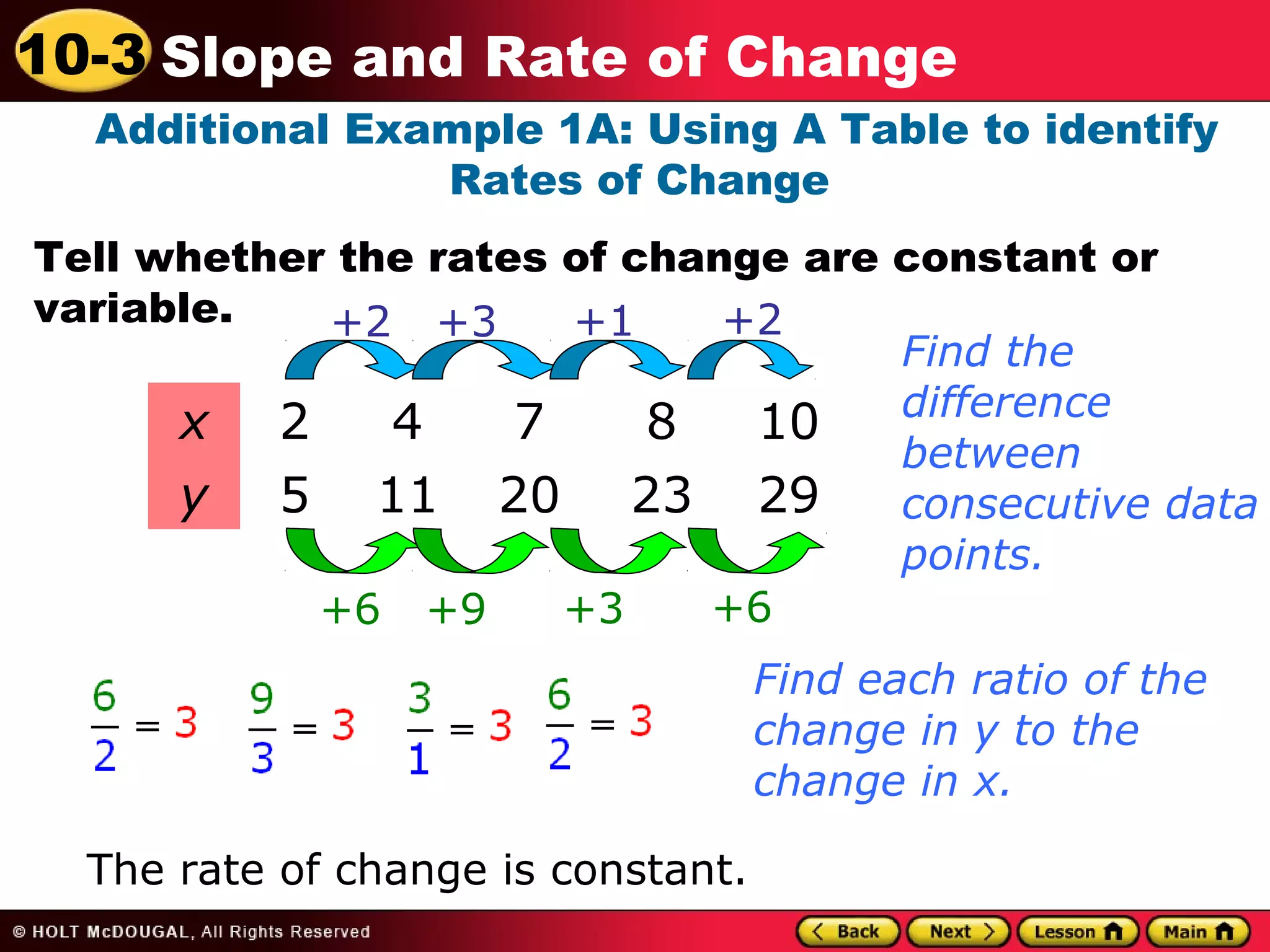
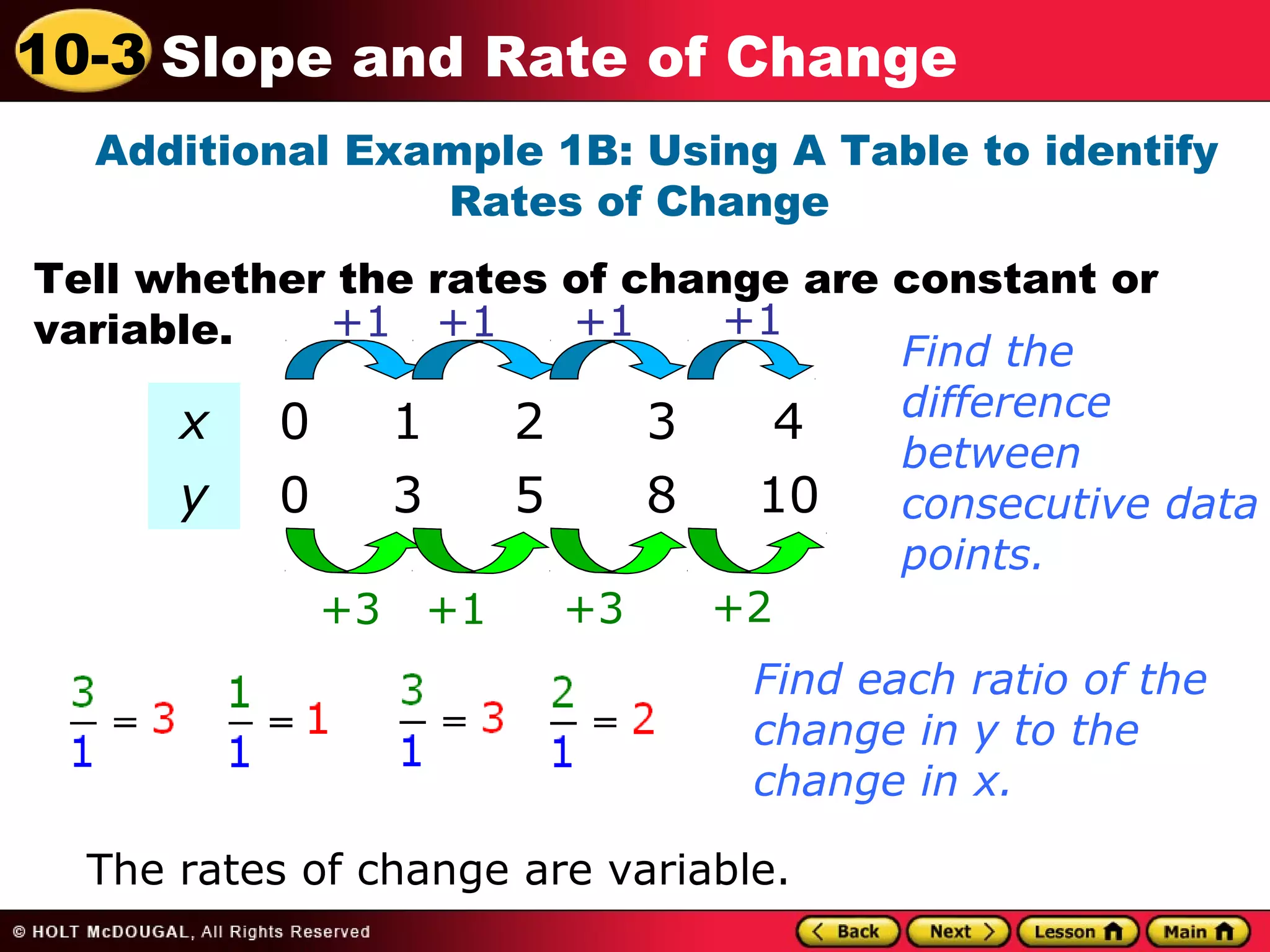
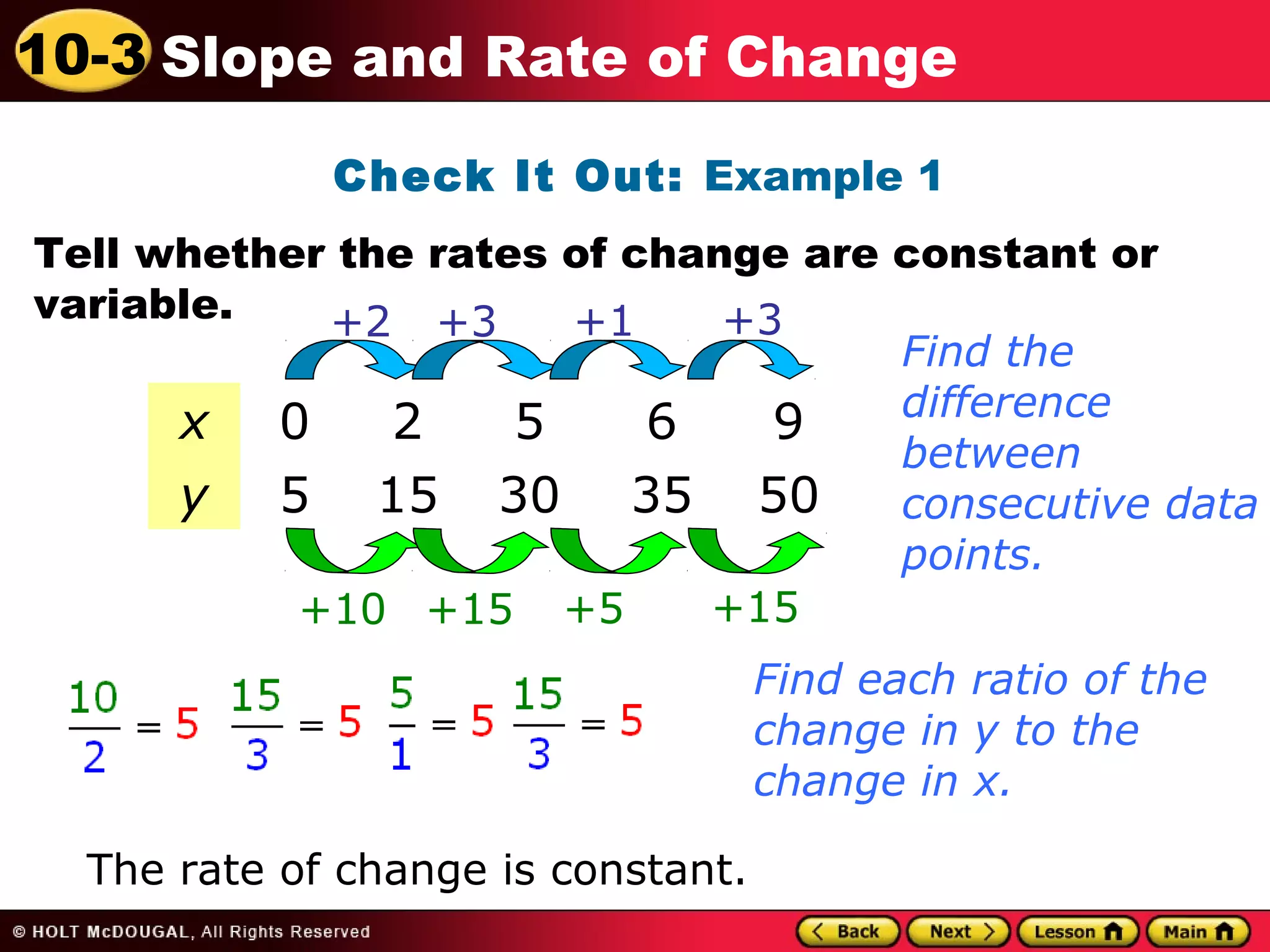
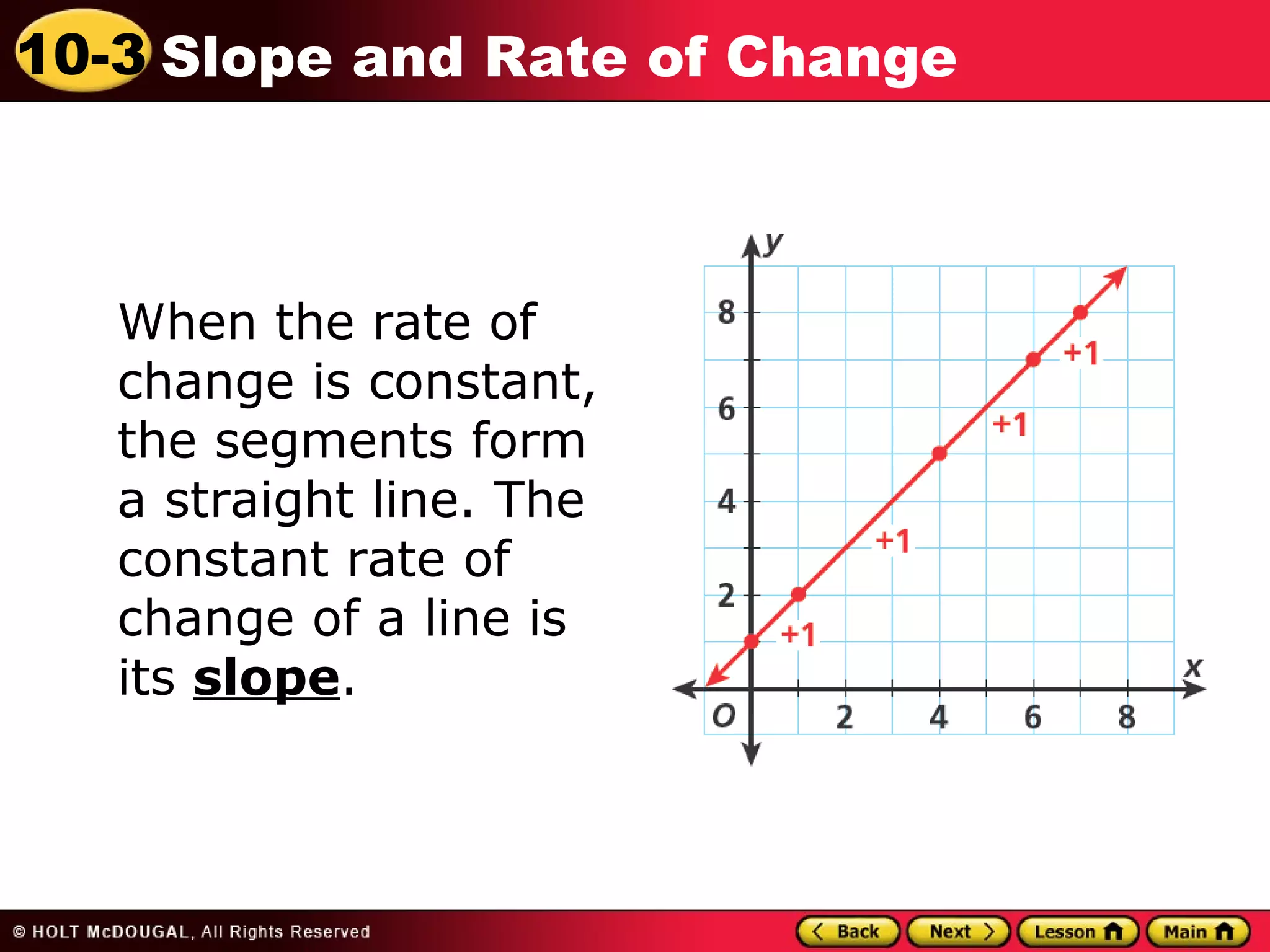
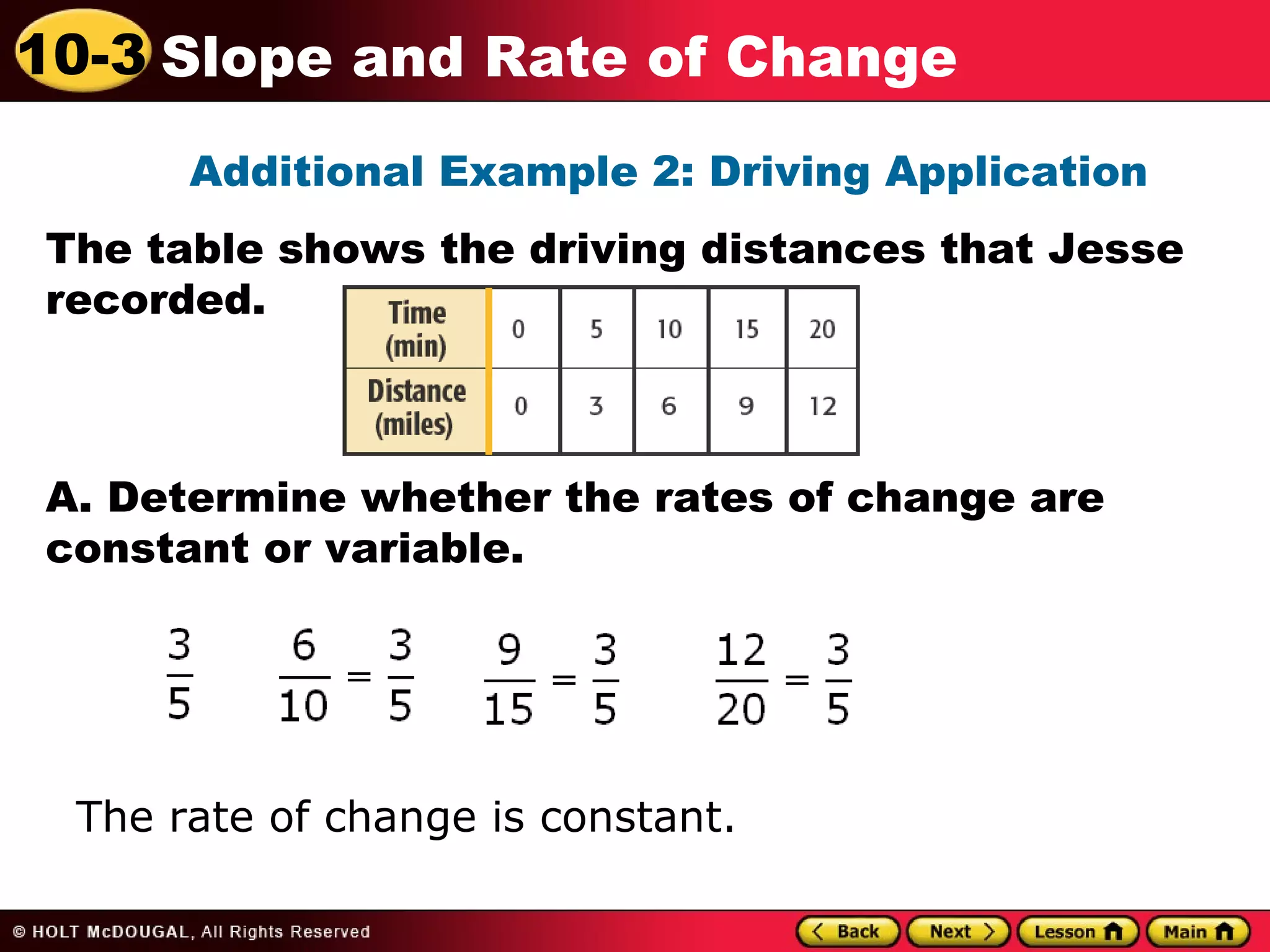
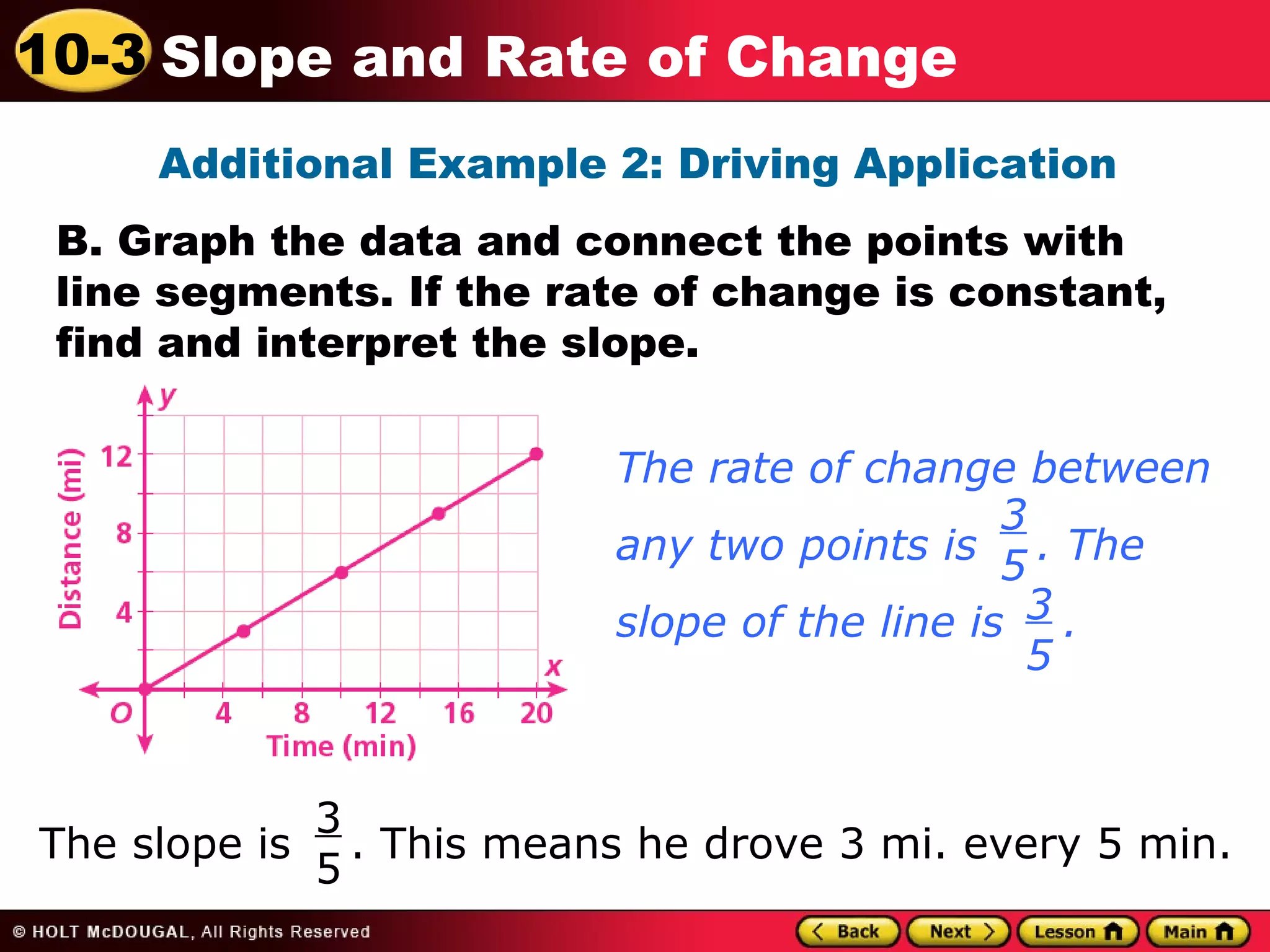
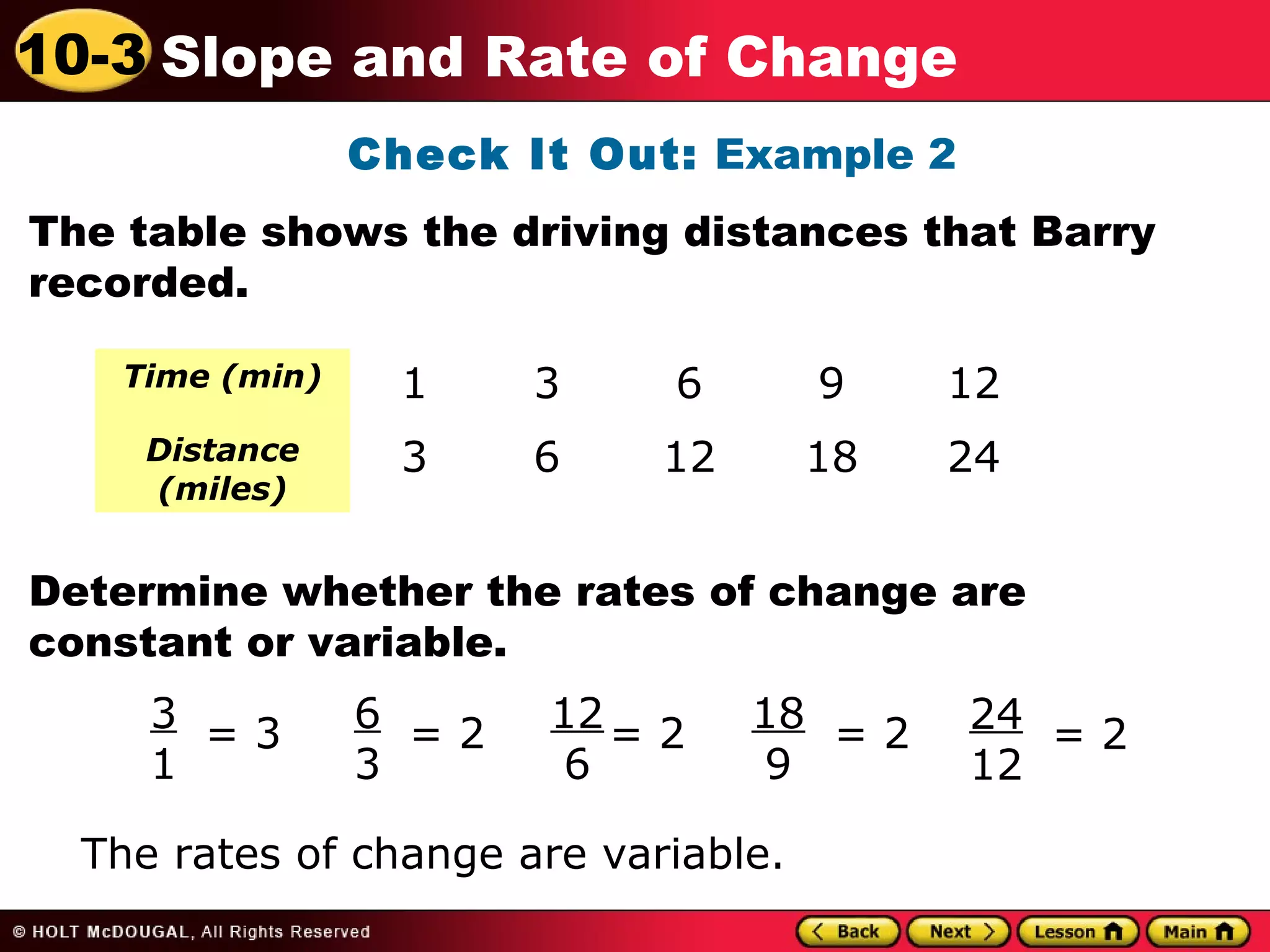
This document discusses slope and rate of change. It defines rate of change as a ratio that compares the difference in output values to the difference in input values. It provides examples of using tables of x-y data points to determine if the rates of change are constant or variable. When the rate of change is constant between data points, the graph will be a straight line, and the constant rate of change is defined as the slope.