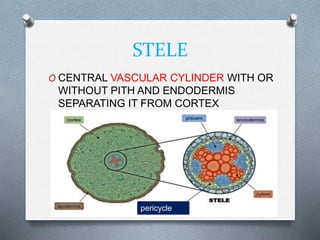
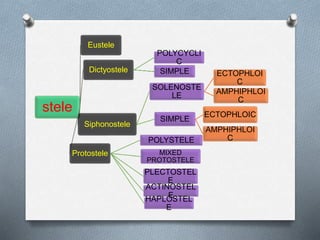
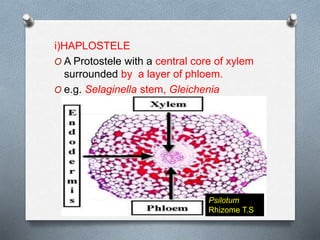
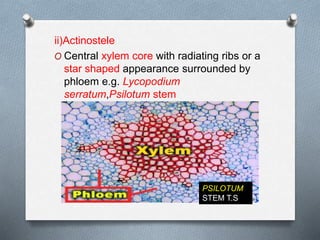
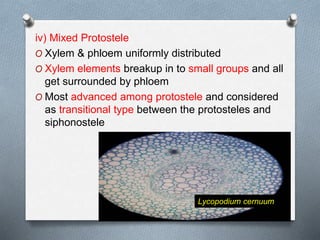
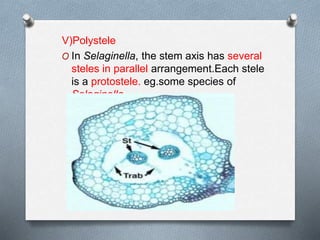
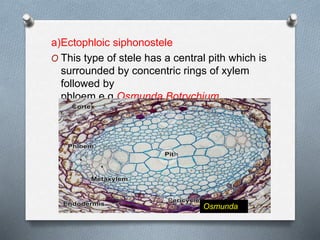
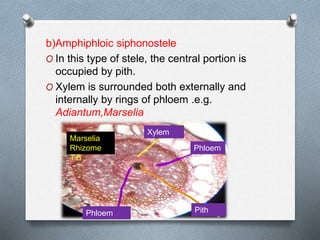
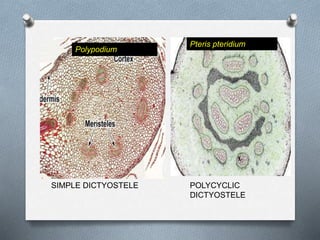
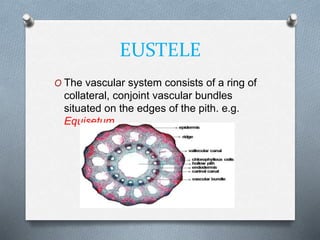
Pteridophytes are vascular plants that reproduce via spores. They have a number of shared characteristics including lignified cell walls, tracheary elements, and an independent sporophyte generation. The stele, or central vascular cylinder, of pteridophytes can take several forms. The protostele is the simplest form, with a central xylem core surrounded by phloem. More advanced forms include the siphonostele, with a central pith, and the dictyostele, with overlapping leaf gaps. The eustele features a ring of vascular bundles around the edge of the pith.