Embed presentation
Downloaded 12 times


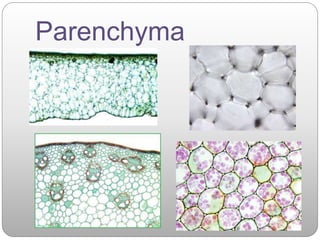
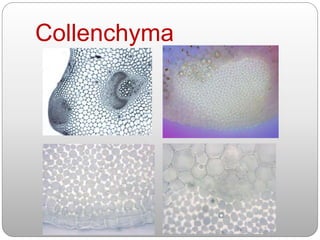
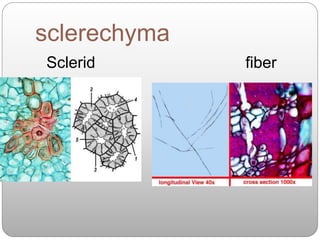

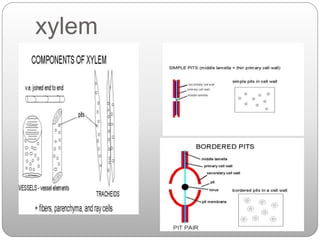

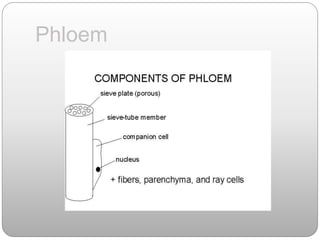
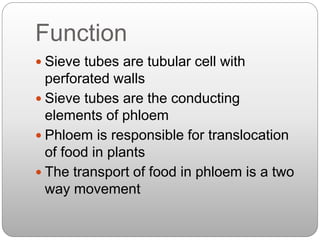
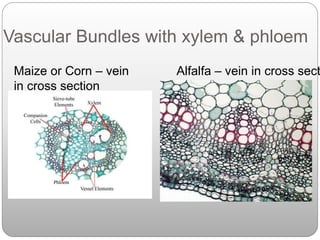
This document summarizes different types of plant tissue. It describes simple tissues like parenchyma, collenchyma, and sclerenchyma. It also describes complex tissues like xylem and phloem. Xylem is responsible for water conduction and consists of vessels, tracheids, fibers and parenchyma. Phloem transports food and consists of sieve tubes, companion cells, fibers and parenchyma. The document outlines the key functions of xylem, which is to conduct water and minerals, and phloem, which facilitates two-way translocation of food in plants.










