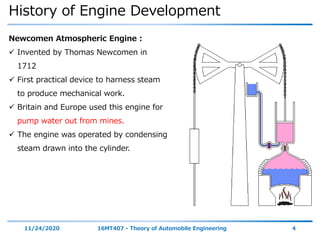
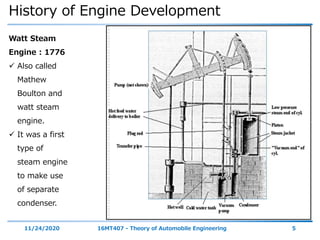
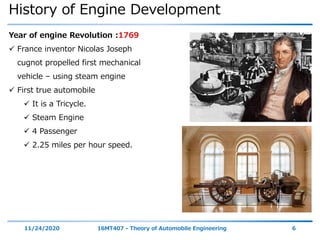
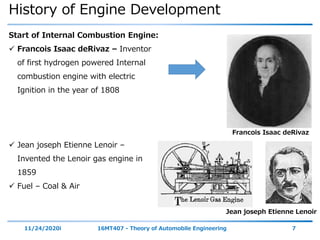
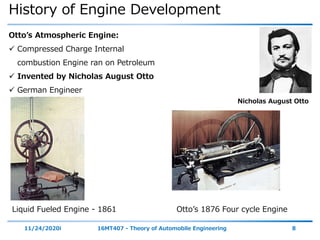
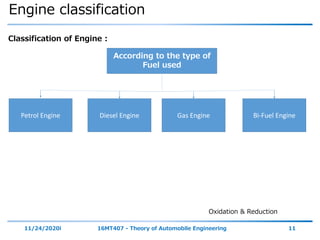
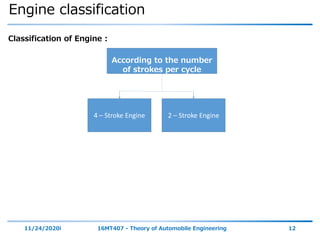
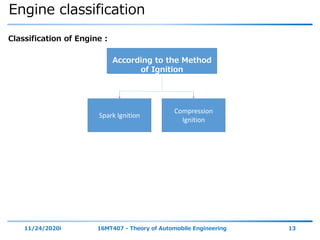
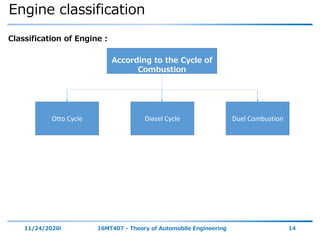
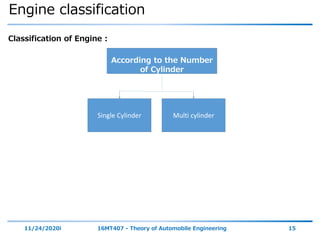
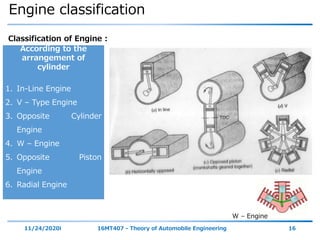
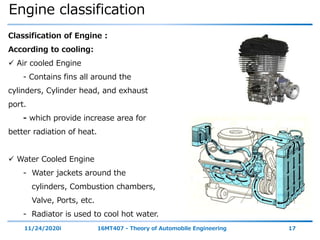
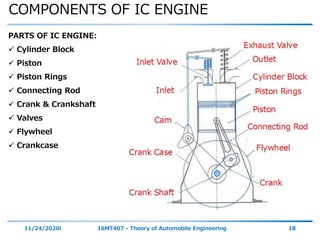
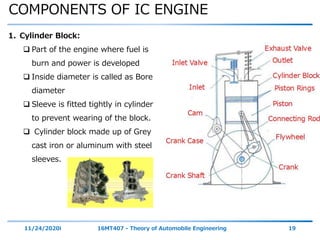
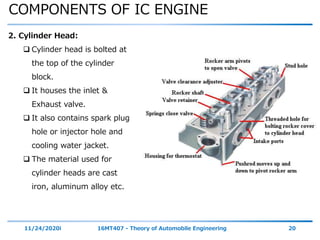
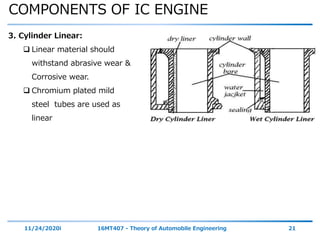
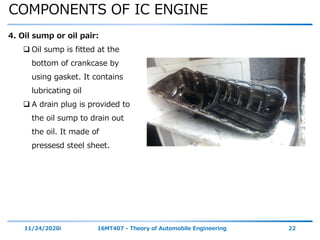
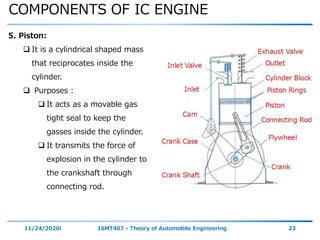
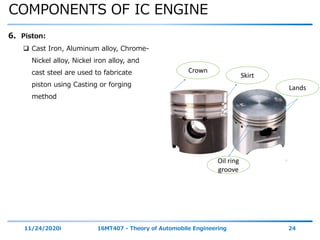
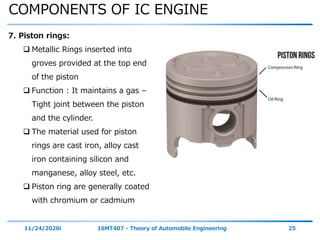
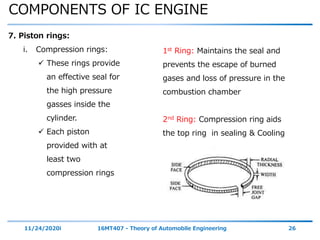
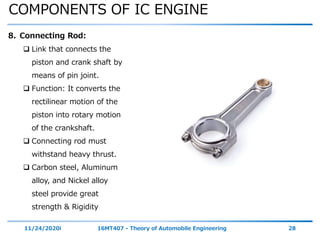
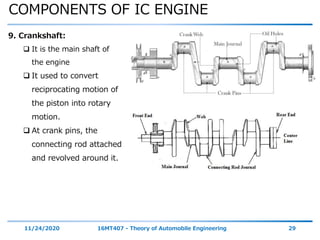
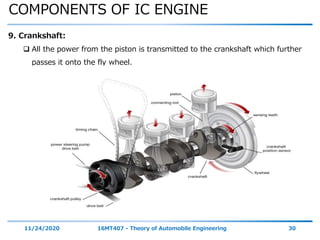
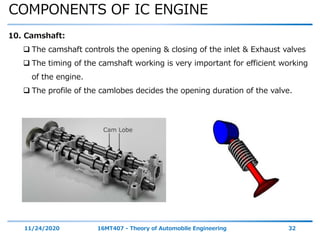
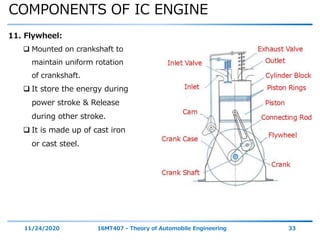
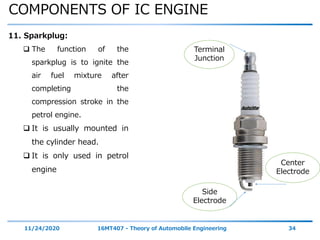
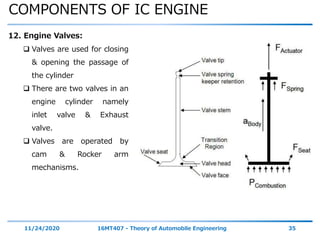
The document outlines the objectives and topics covered in a session about engine components and their materials, focusing on the history of engine development, combustion processes, and various classifications of internal combustion engines. It details the evolution from early steam engines to modern internal combustion engines, discussing significant inventions and classifications based on fuel type, engine strokes, and ignition methods. Additionally, it describes essential engine components such as the cylinder block, piston, and crankshaft along with their materials and functions.