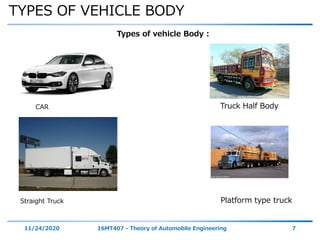
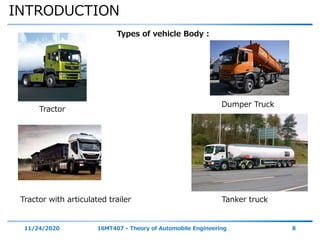
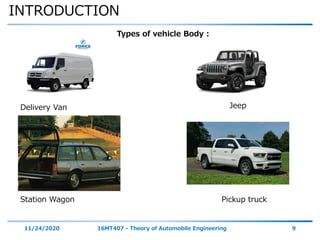
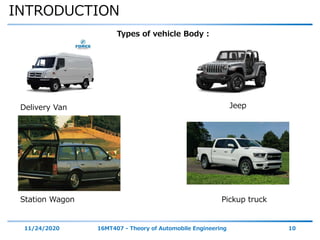
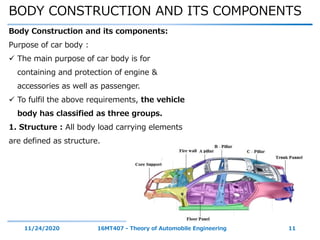
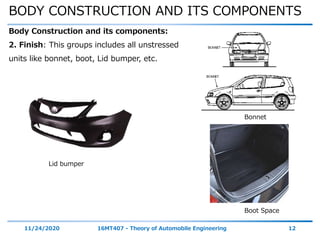
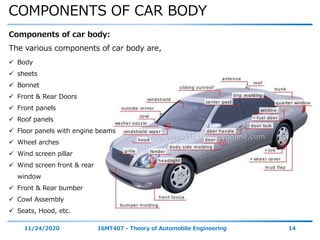
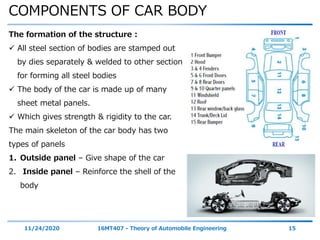
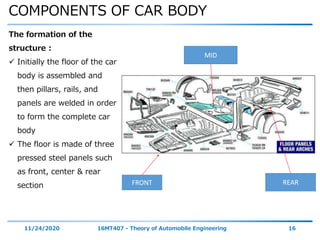
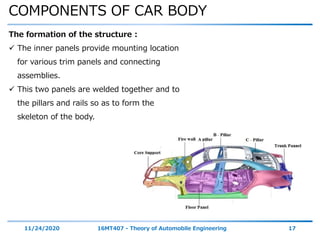
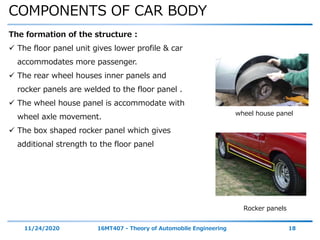
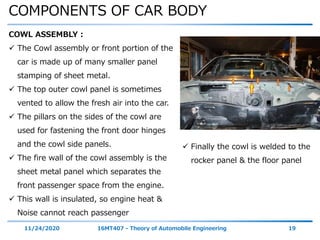
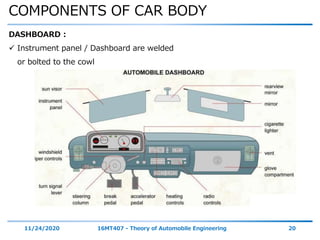
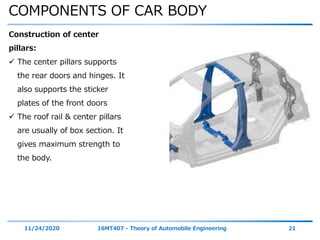
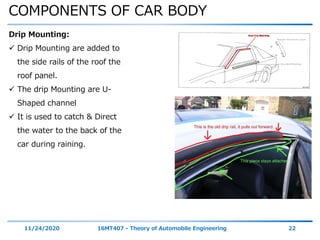
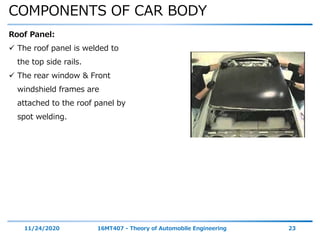
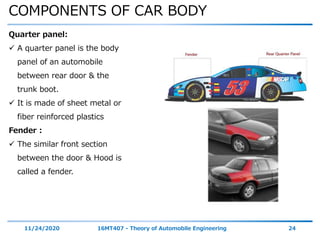
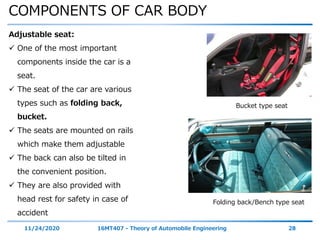
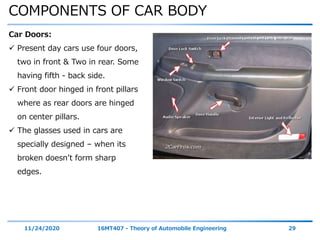
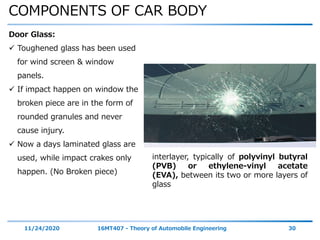
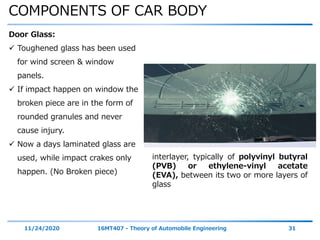
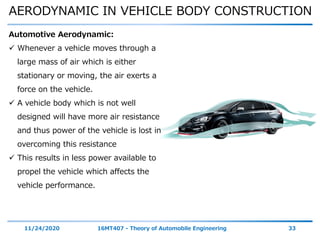
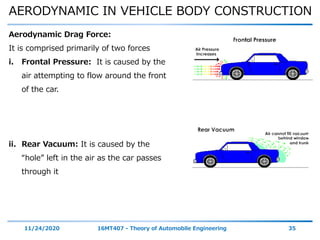
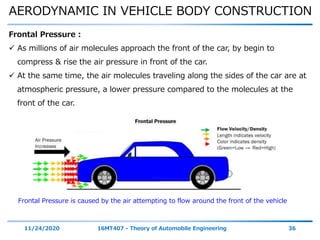
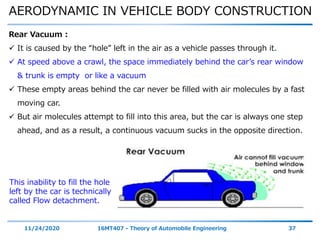
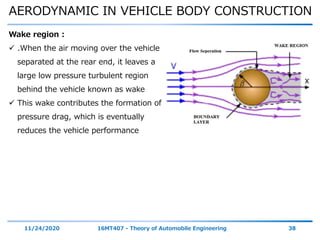
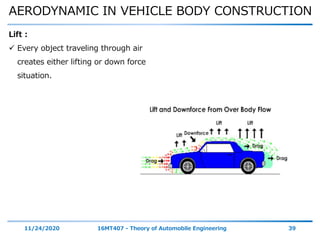
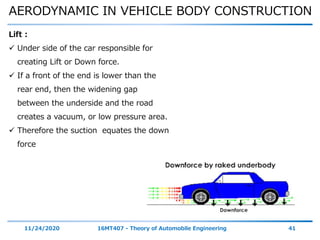
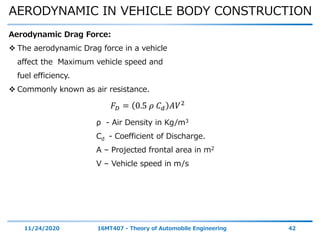
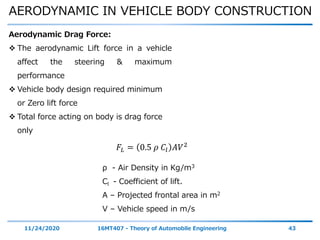
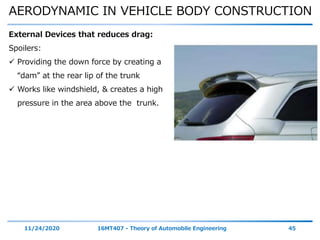
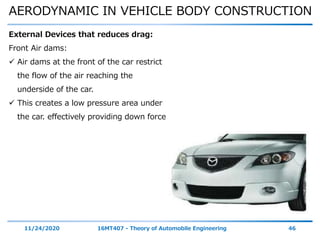
The document discusses the vehicle body construction. It begins by introducing the objectives of the session which are to understand how vehicle parts form the body and give an aesthetic view to consumers. It then covers various topics related to vehicle body design including the importance of design, types of bodies, body construction components, body materials, and aerodynamics. The document focuses on the components that make up the vehicle body, how the body is constructed, and the purpose of key parts like doors, hood, seats, and other interior and exterior parts.