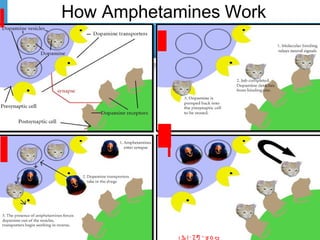
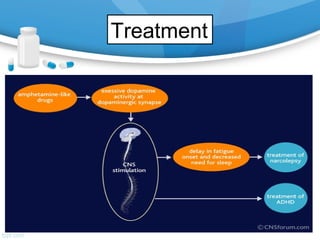
Amphetamines are central nervous system stimulants first synthesized in 1887, with various therapeutic uses such as treating narcolepsy and ADHD. While effective, they can lead to significant psychological and physiological side effects, particularly with high doses or prolonged use, including addiction and severe health issues. Treatment for acute overdose involves measures to increase elimination of the drug and may require long-term rehabilitation efforts.