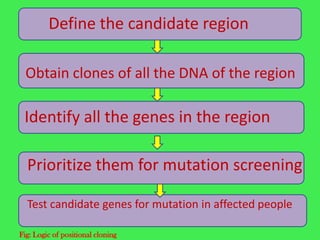
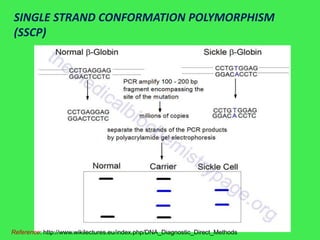
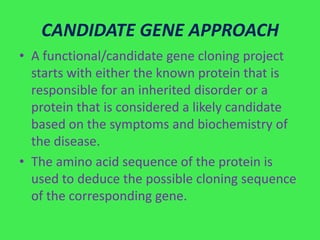
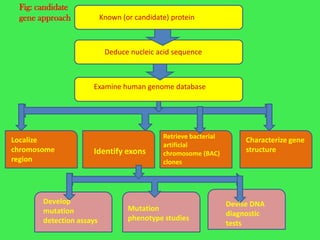
This document discusses various strategies for identifying disease genes, including position-dependent and position-independent approaches. Position-independent strategies include identifying a disease gene through knowledge of the protein product, using an animal model of the disease, or DNA sequence knowledge. Positional cloning involves mapping a disease to a chromosomal region and then identifying candidate genes within that region. Techniques like SSCP analysis and heteroduplex analysis are used to identify mutations in candidate genes. The candidate gene approach starts with a known or suspected protein involved in a disease.