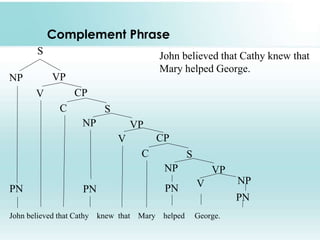
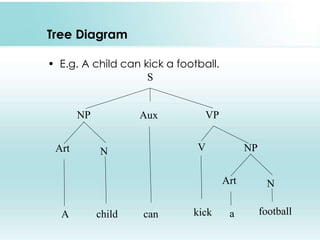
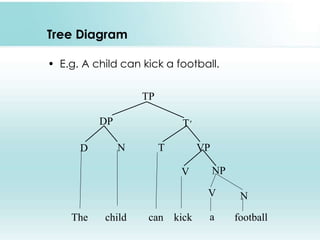
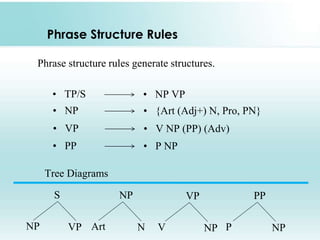
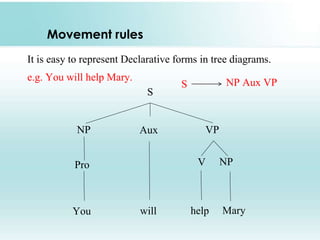
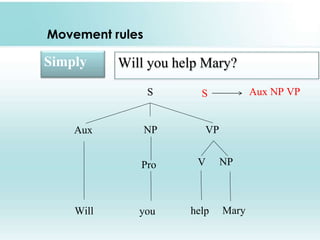
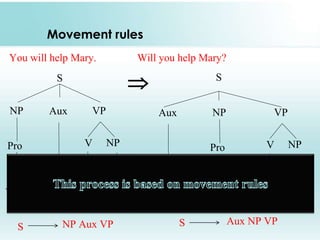
This document provides an overview of syntax and generative grammar. It defines syntax as the way words are arranged to show relationships of meaning within and between sentences. Grammar is defined as the art of writing, but is now used to study language. Generative grammar uses formal rules to generate an infinite set of grammatical sentences. It distinguishes between deep structure and surface structure. Tree diagrams are used to represent syntactic structures with symbols like S, NP, VP. Phrase structure rules, lexical rules, and movement rules are discussed. Complement phrases and recursion are also explained.














![Recursion
Examples:
• a. ab
• b. aabb
• c. aaabbb
• a. The man [who the girl saw is my friend
• b. The man [who the girl [who sneezed] saw] is my
friend.
• c. The man [who the girl [who Peter [who knows] met]
saw] is my friend.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complementphrase-140717093512-phpapp01/85/Complement-phrase-22-320.jpg)