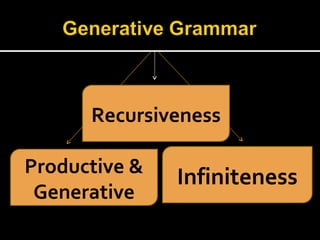
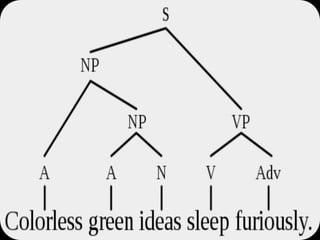
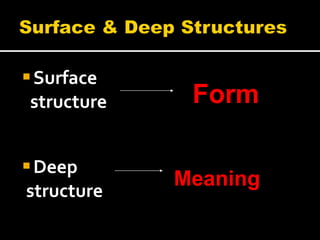
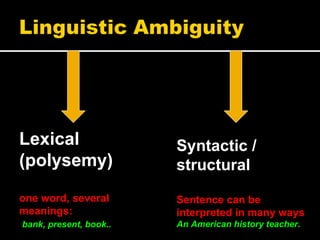
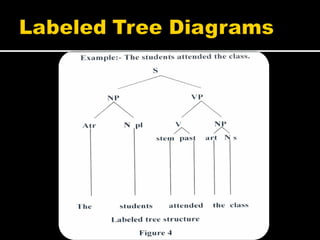
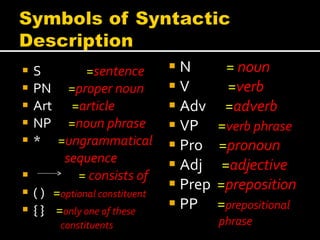
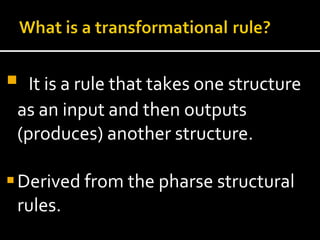
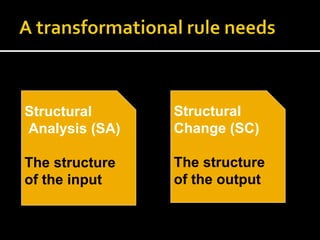
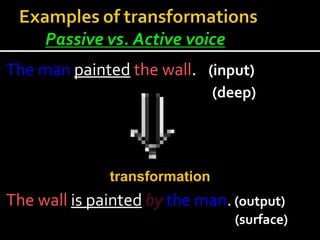
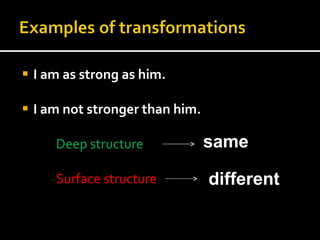
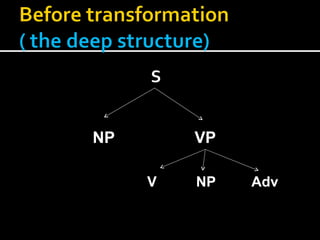
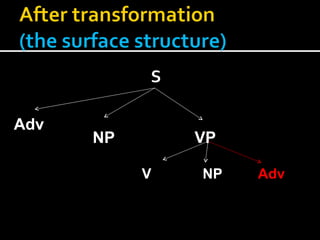
Noam Chomsky introduced the concept of generative grammar in the 1950s, which explores the relationship between surface structure and deep structure in language. The document discusses syntactic theories and transformation rules, illustrating how different sentence structures maintain the same underlying meaning. Additionally, it outlines various syntactic symbols and their meanings, emphasizing the mathematical nature of syntactic analysis.