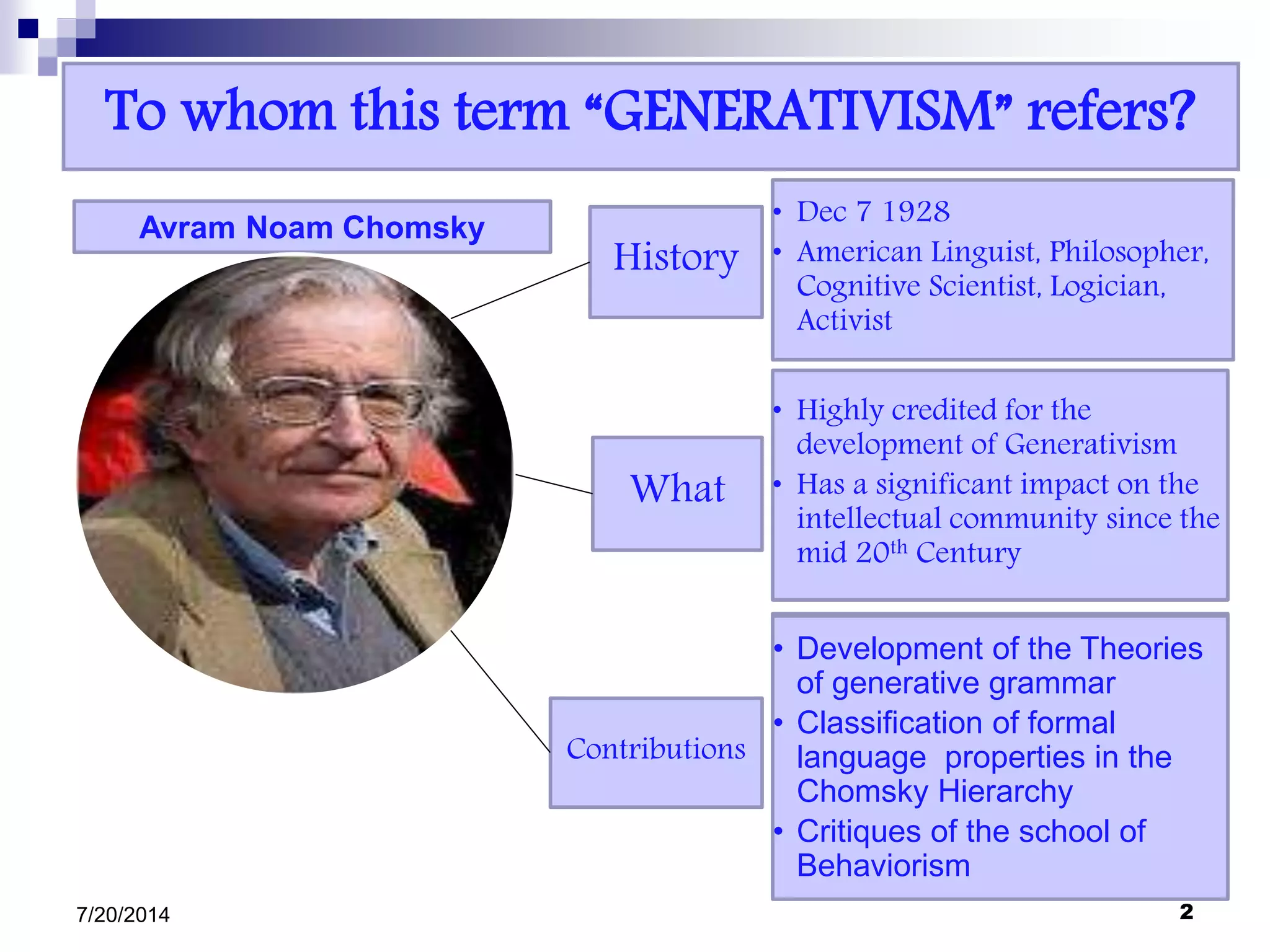
Generativism refers to the theory of language developed by Noam Chomsky and his followers. It rejects the behaviorist view that language is learned through external stimuli, and instead argues that humans possess an innate, internal language acquisition device. Generativism sees language as composed of rules that allow for creativity and an infinite number of sentences. It makes a distinction between competence (knowledge of language) and performance (actual use of language). This theory has been highly influential in linguistics and other fields.