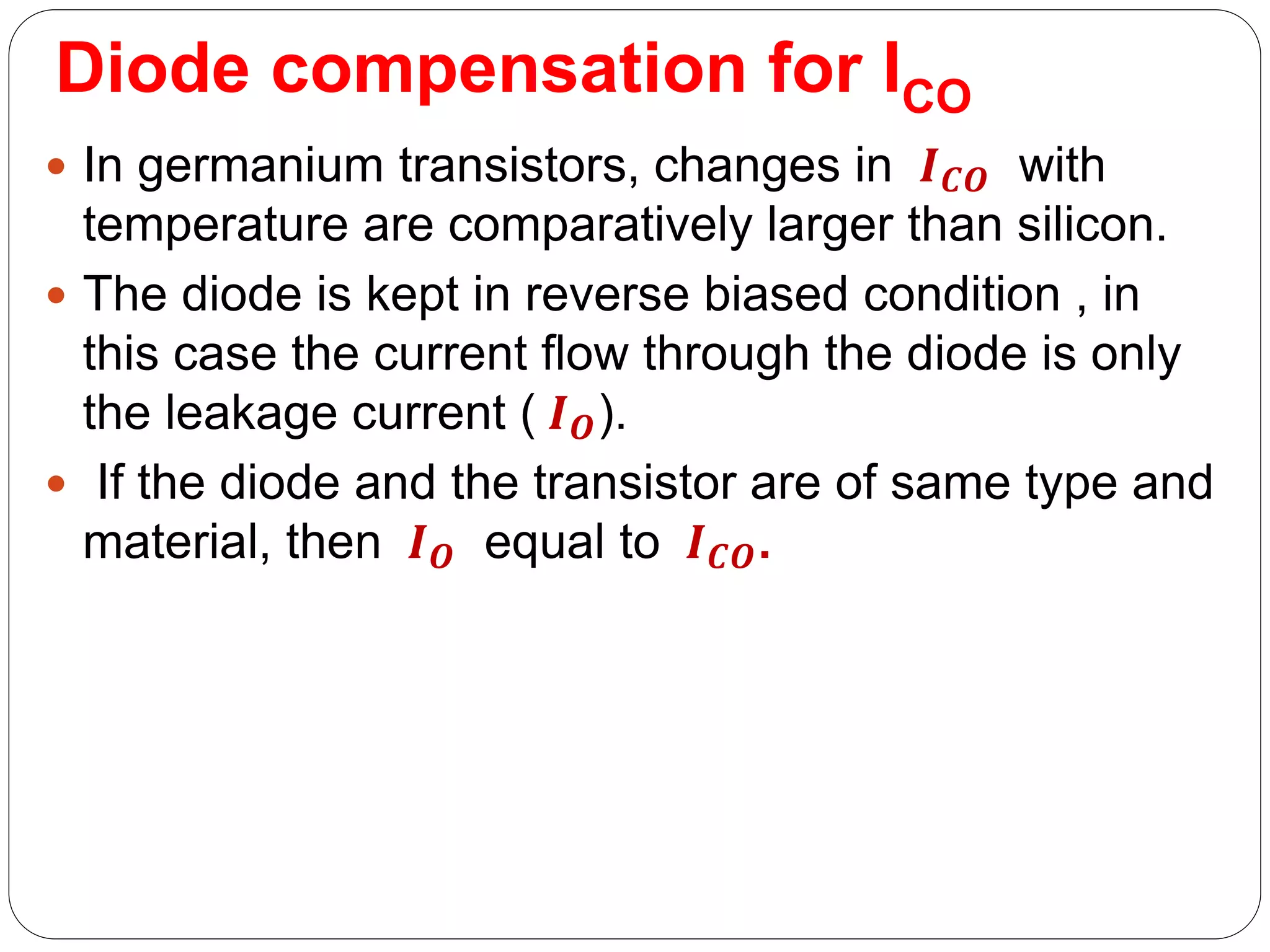
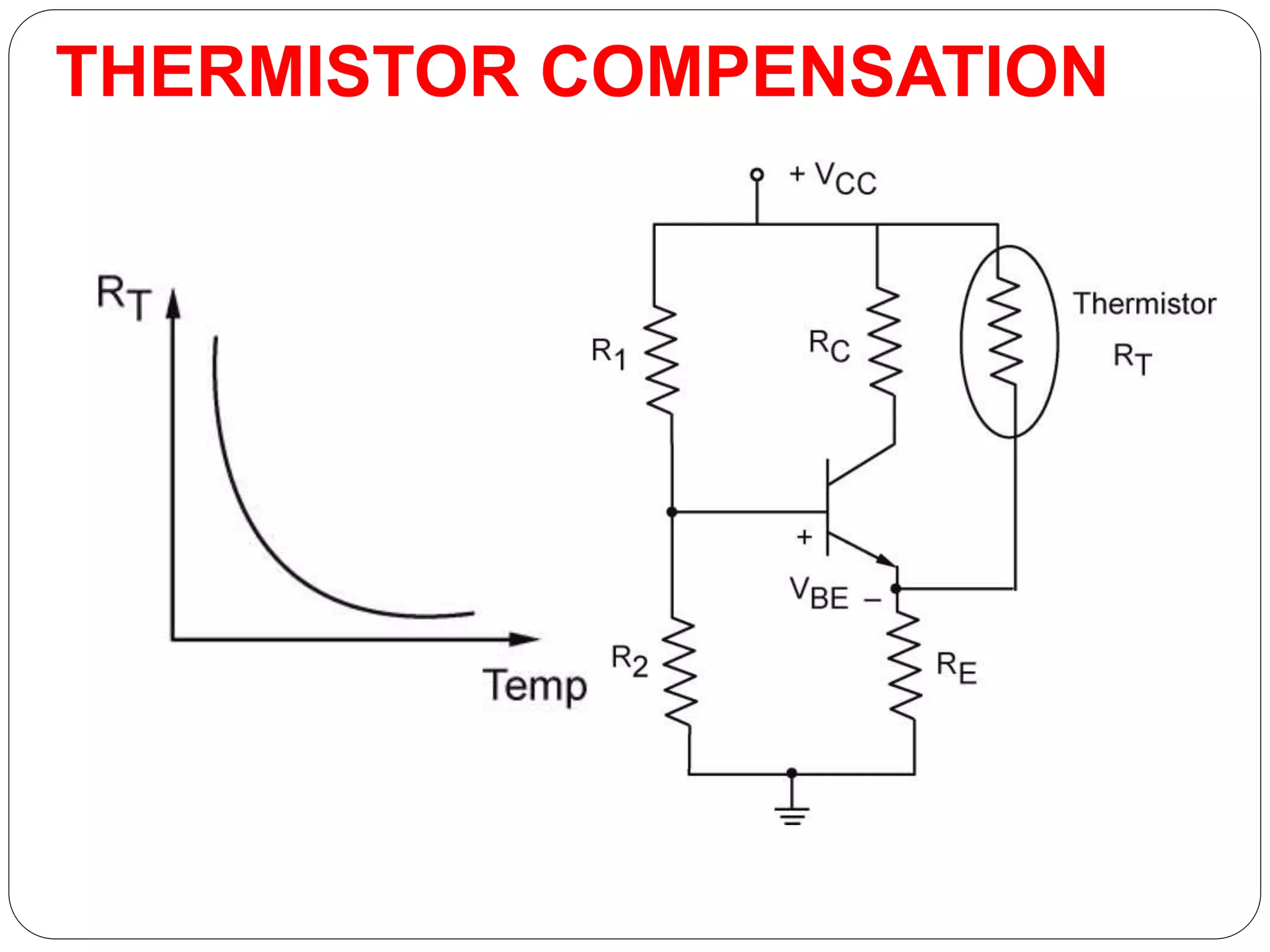
This document discusses different compensation techniques used to stabilize the operating point of transistors against temperature variations. It describes diode compensation, thermistor compensation, and sensistor compensation. Diode compensation can compensate for changes in base-emitter voltage or collector current with temperature. It works by using a diode that produces an opposing temperature-dependent voltage to the transistor's base-emitter junction. Thermistor compensation uses a negative temperature coefficient thermistor to reduce the collector current as temperature increases. Sensistor compensation uses a positive temperature coefficient resistor to decrease the base current as temperature rises.




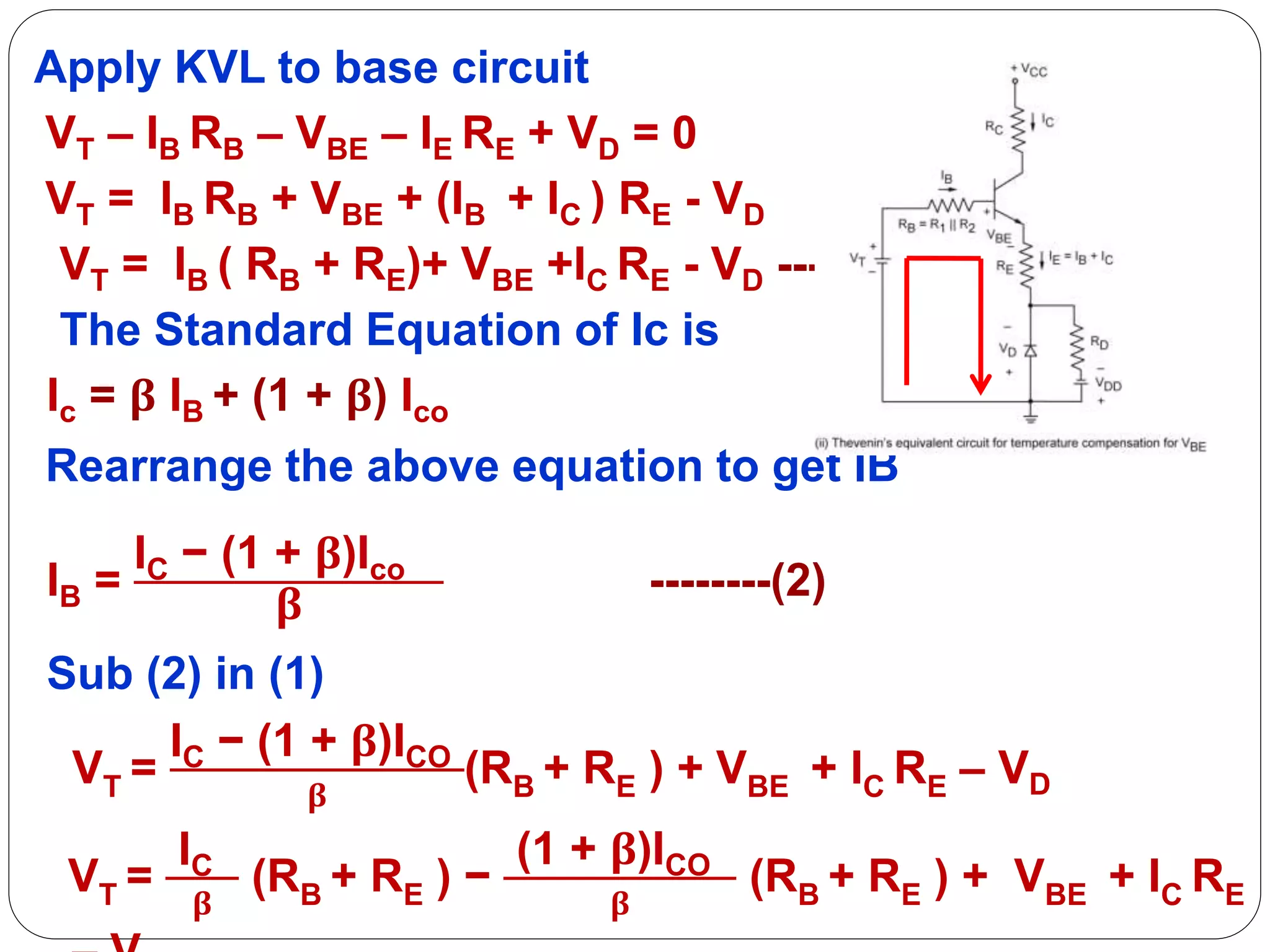
![VT =
IC
𝛃
(RB + RE )−
(1 + β)ICO
𝛃
(RB + RE )+ VBE+IC RE
– VD
VT =
IC
𝛃
[RB +(1+β) RE] −
(1 + β)ICO
𝛃
(RB + RE ) + VBE
– VD
VT =
IC[RB+ (1+β)RE] −(1 + β)ICO(RB+RE )+β(VBE –VD)
β
β VT = IC [RB +(1+β) RE] - (1 + β)ICO (RB + RE ) +β(VBE –VD)
IC [RB +(1+β) RE] = (1 + β)ICO (RB + RE ) +β(VT–VBE+VD)
IC =
(1 + β)ICO(RB+RE ) +β (VT–VBE+VD)
[RB+(1+β)RE]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/compensationtechniques-210831170214/75/Compensation-Techniques-7-2048.jpg)