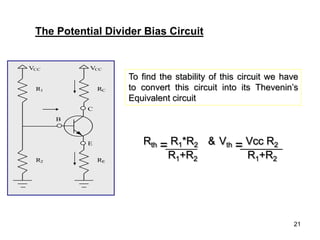
The potential divider bias circuit provides the most stable operating point (Q-point) for a transistor. It uses two resistors (R1 and R2) in a potential divider configuration to set the base voltage, and a third resistor (RE) connected from the emitter to ground introduces negative feedback. This feedback makes the Q-point nearly independent of temperature variations and transistor parameter changes, providing the highest stability of any biasing circuit.












![18
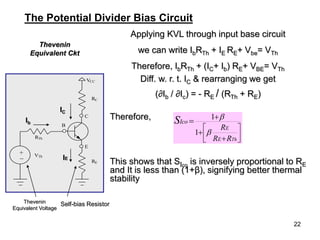
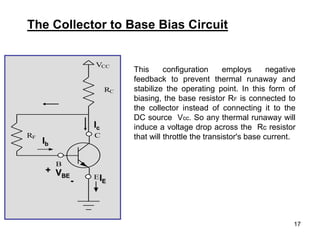
Applying KVL through base circuit
we can write (Ib+ IC) RC + Ib Rf+ Vbe= Vcc
Diff. w. r. t. IC we get
(∂Ib / ∂Ic) = - RC / (Rf + RC)
Therefore, SIco ═ (1+ β)
1+ [βRC/(RC+ Rf)]
Which is less than (1+β), signifying better thermal stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter32-220718153948-caff3b59/85/Chapter-3-2-ppt-18-320.jpg)