1. Transistor biasing involves setting the proper zero signal collector current and maintaining the proper collector-emitter voltage during signal passage. This is done to ensure faithful amplification.
2. If a transistor is not properly biased, it will work inefficiently and distort the output signal. Biasing can be done with a battery or biasing circuit associated with the transistor.
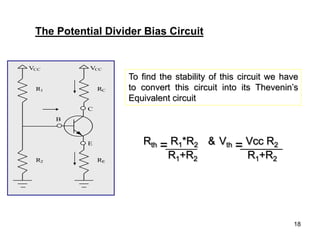
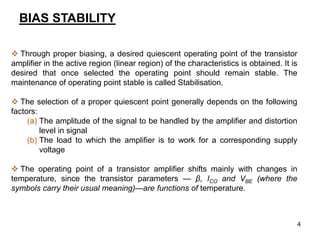
3. Proper biasing sets the operating point in the active region and aims to keep it stable despite temperature changes or other variations, through techniques like negative feedback. The potential divider bias circuit is commonly used due to its stability.










![15
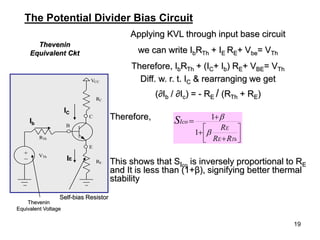
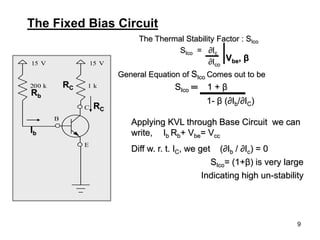
Applying KVL through base circuit
we can write (Ib+ IC) RC + Ib Rf+ Vbe= Vcc
Diff. w. r. t. IC we get
(∂Ib / ∂Ic) = - RC / (Rf + RC)
Therefore, SIco ═ (1+ β)
1+ [βRC/(RC+ Rf)]
Which is less than (1+β), signifying better thermal stability](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/transistorbiasing-230325173434-9a837522/85/Transistor_Biasing-pdf-15-320.jpg)