This document discusses feedback amplifiers and provides details on:
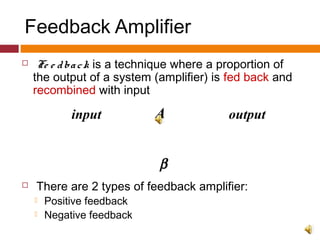
1. Feedback amplifiers can be positive or negative, with negative feedback reducing gain and improving performance. Negative feedback subtracts part of the output from the input.
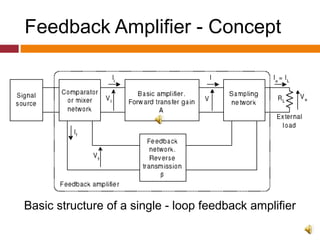
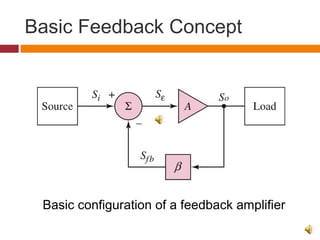
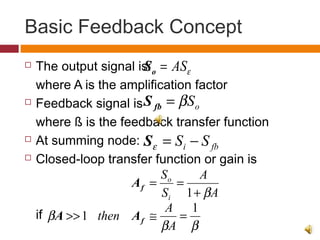
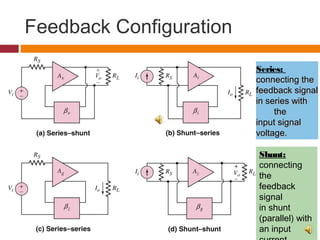
2. The basic structure of a single-loop feedback amplifier feeds part of the output back to the input. This reduces gain but improves stability, bandwidth, noise, and distortion compared to a basic amplifier.
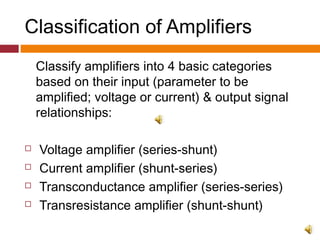
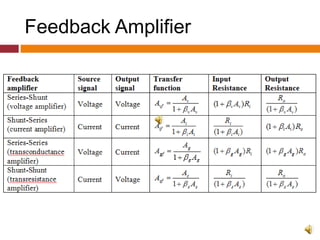
3. Amplifiers are classified based on their input and output signals as voltage, current, transconductance, or transresistance amplifiers depending on whether the input is voltage or current and the output relationship.