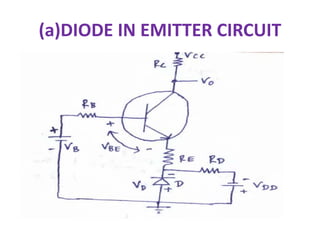
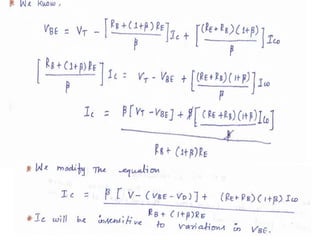
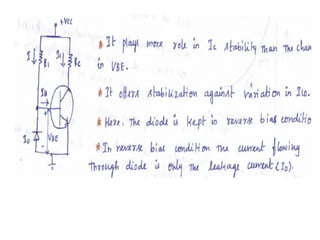
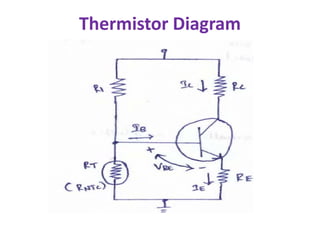
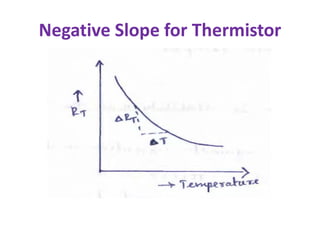
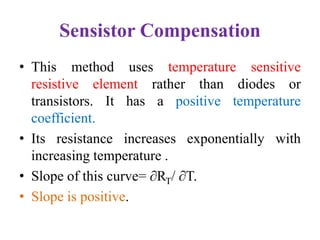
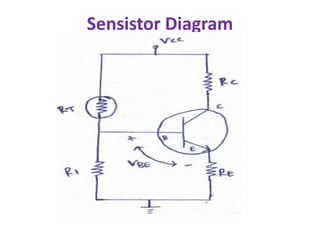
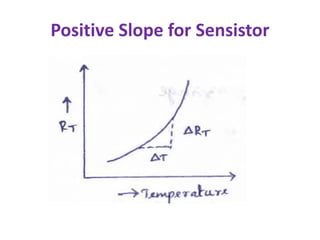
This document discusses various bias compensation techniques used to stabilize the operating point of transistors against temperature variations. It describes how diode compensation can be used to compensate for instability due to variations in VBE or ICO with temperature. A diode is placed in the emitter or collector circuit such that its temperature dependence matches that of the transistor. Thermistor and sensistor compensation are also discussed, where a thermistor or sensistor with a negative or positive temperature coefficient respectively is used to maintain a constant voltage at the transistor base against temperature changes.