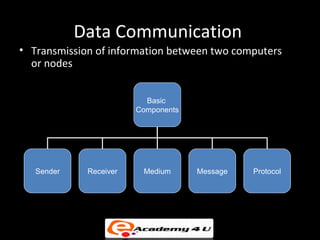
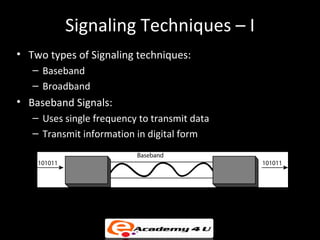
1. Communication between computers uses transmission of digital data over a network medium using defined protocols.
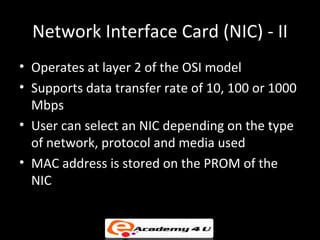
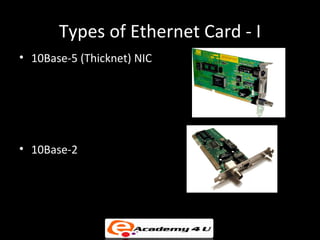
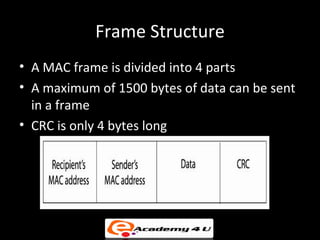
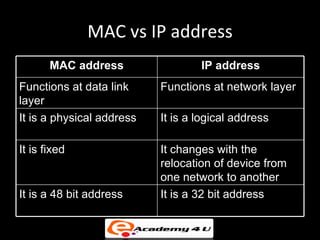
2. Network interface cards connect devices to networks and operate at the data link layer, using hardware addresses and frame structures to transfer data.
3. Tools like volt-ohm meters, tone generators, and optical testers can be used to diagnose and repair physical cabling issues on a network.