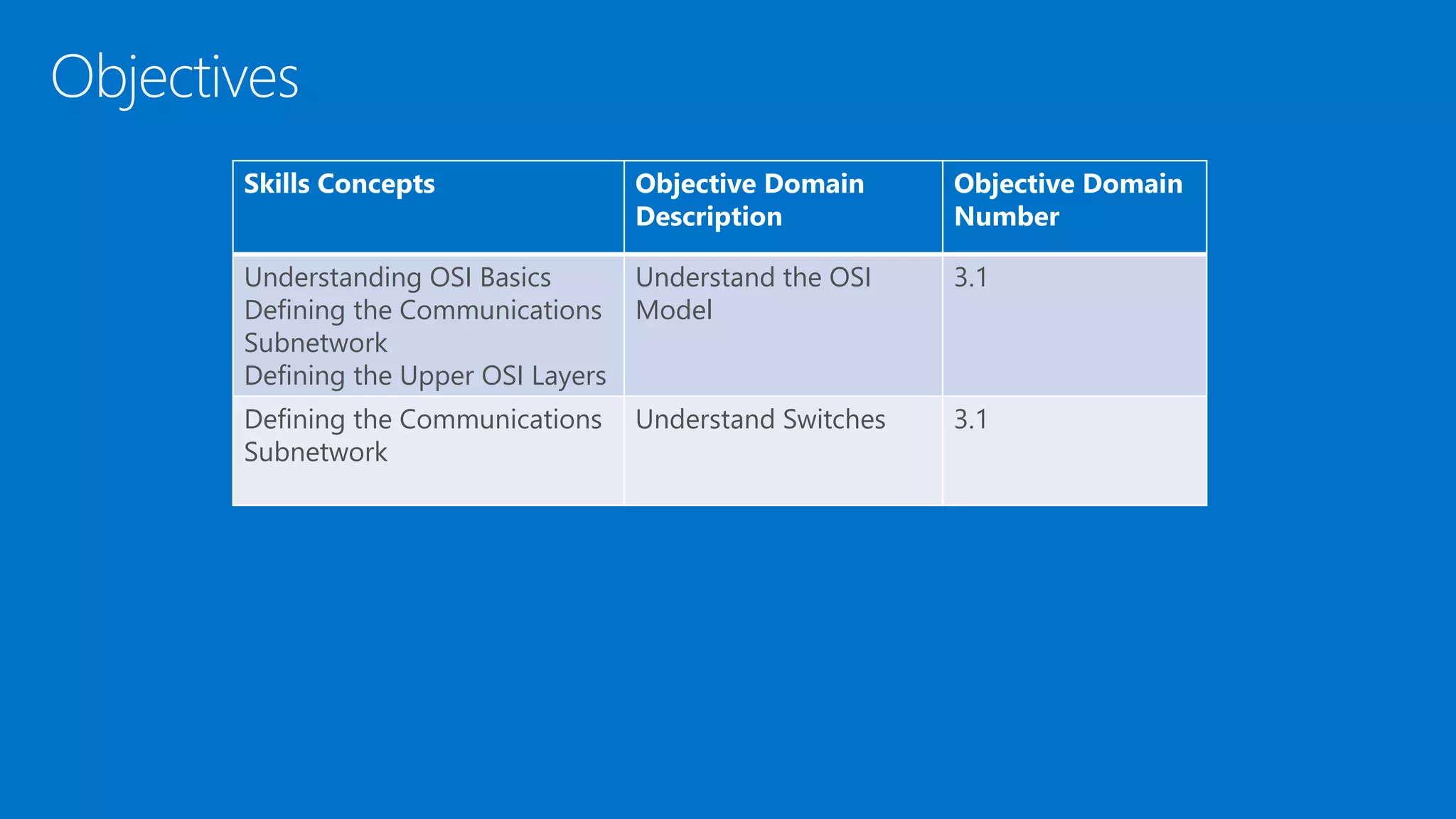
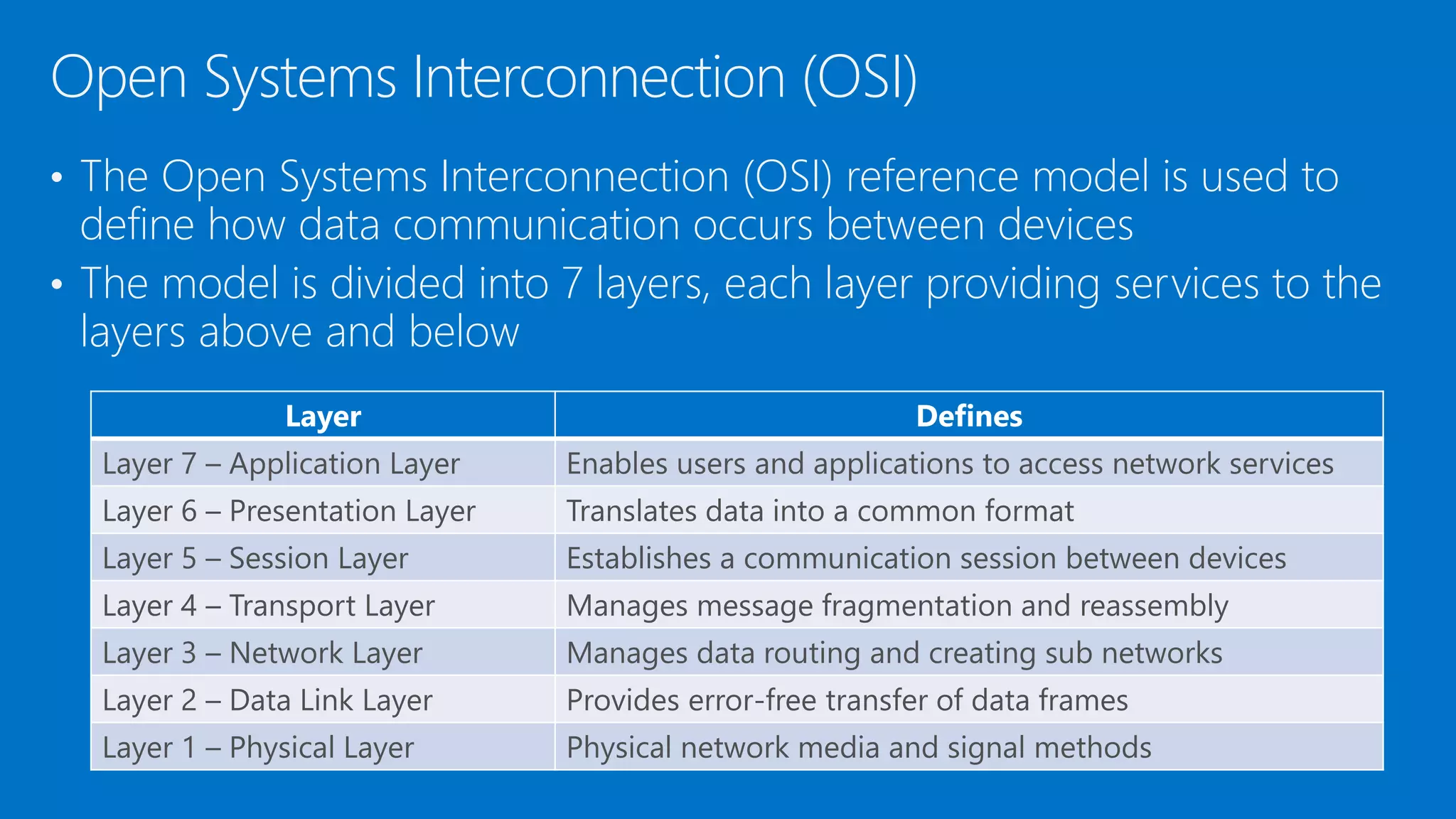
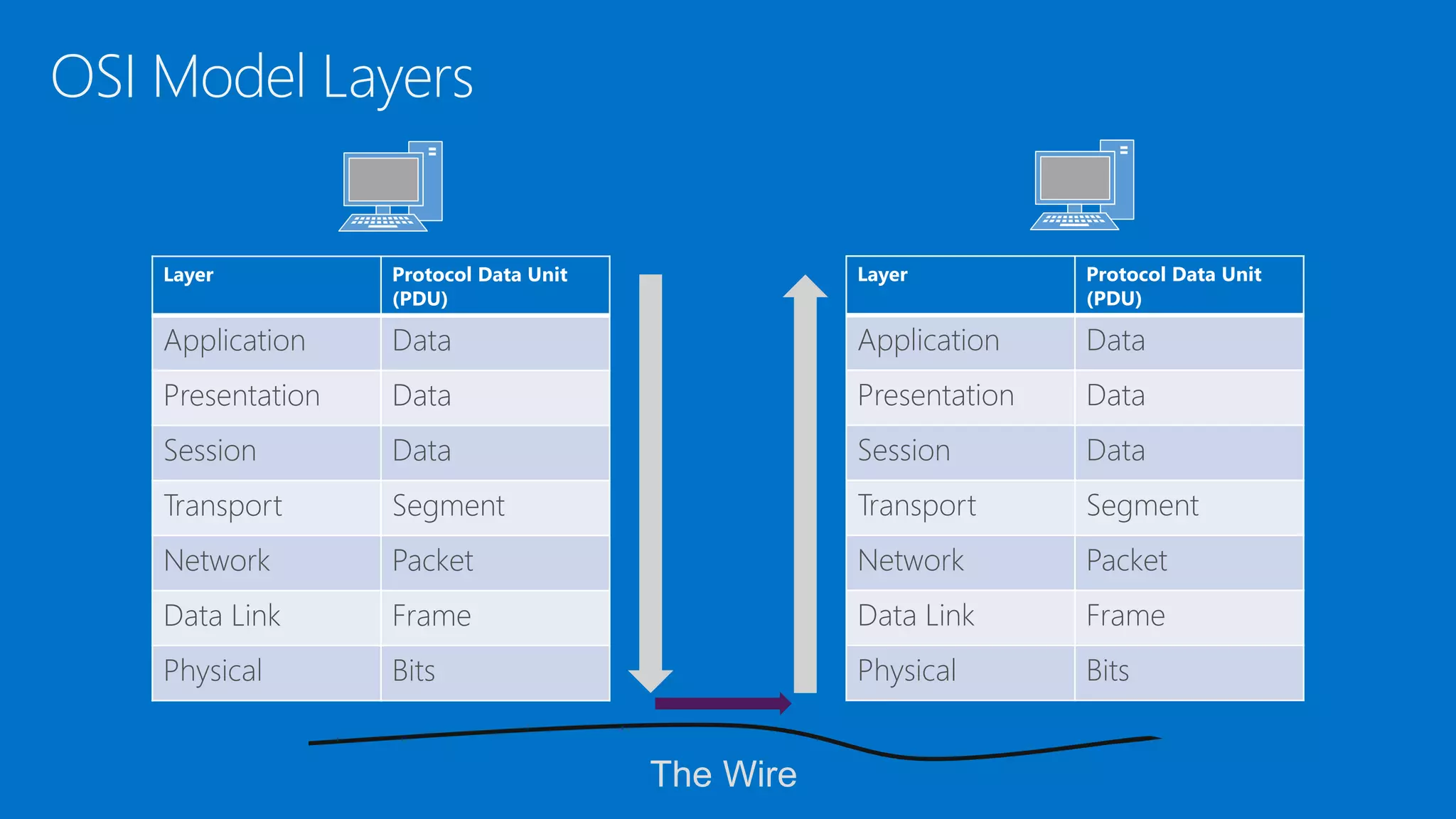
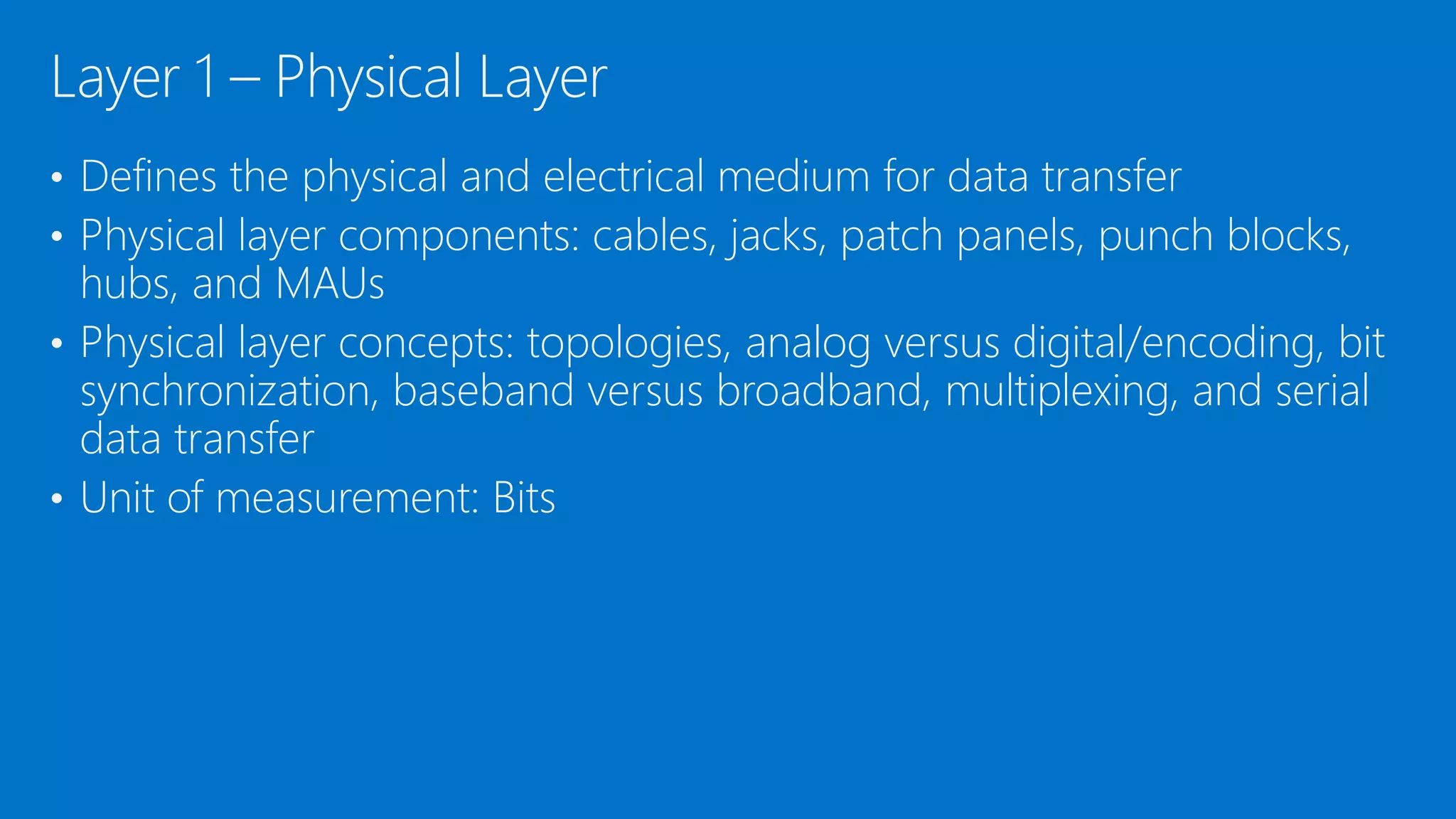
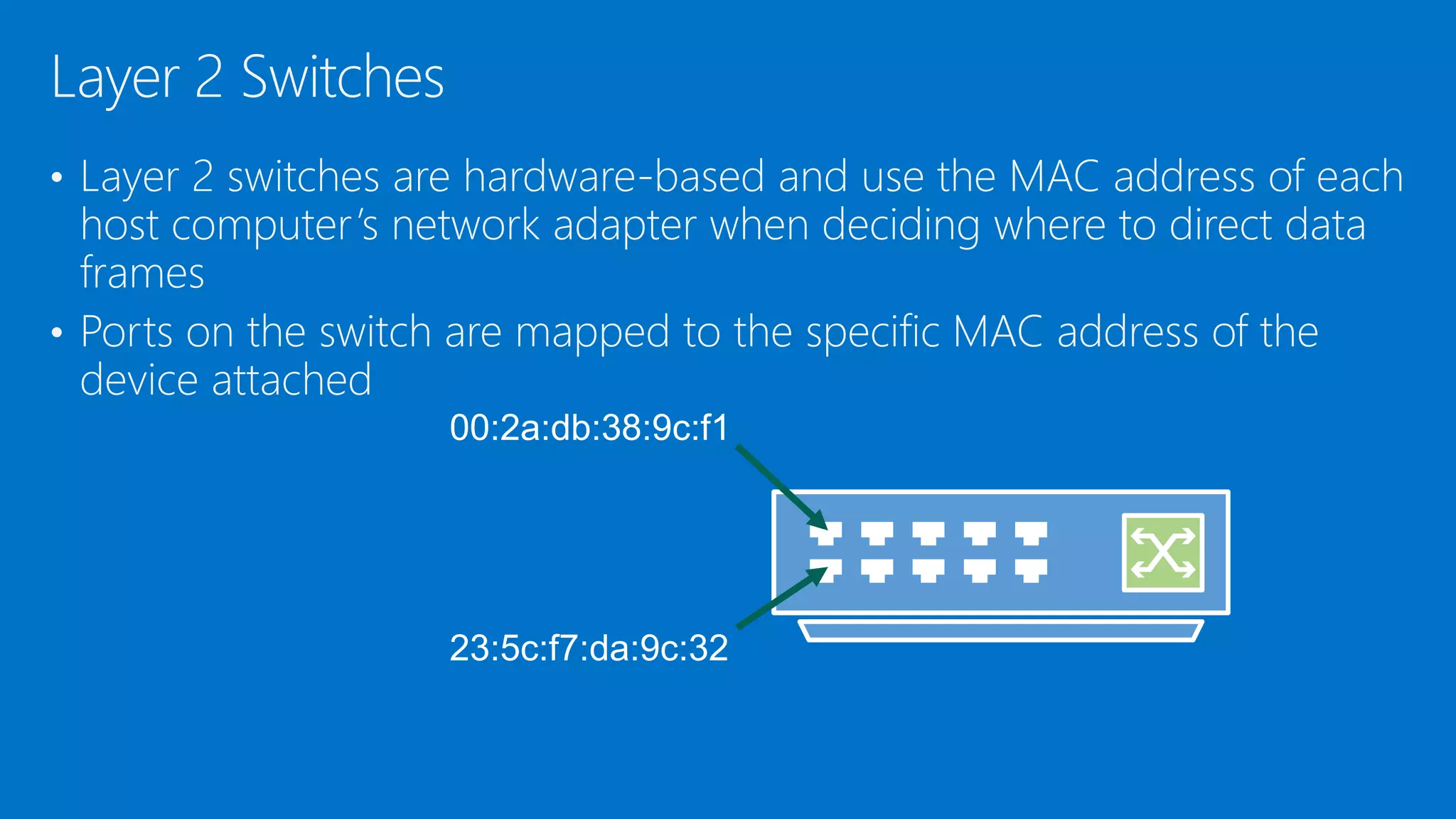
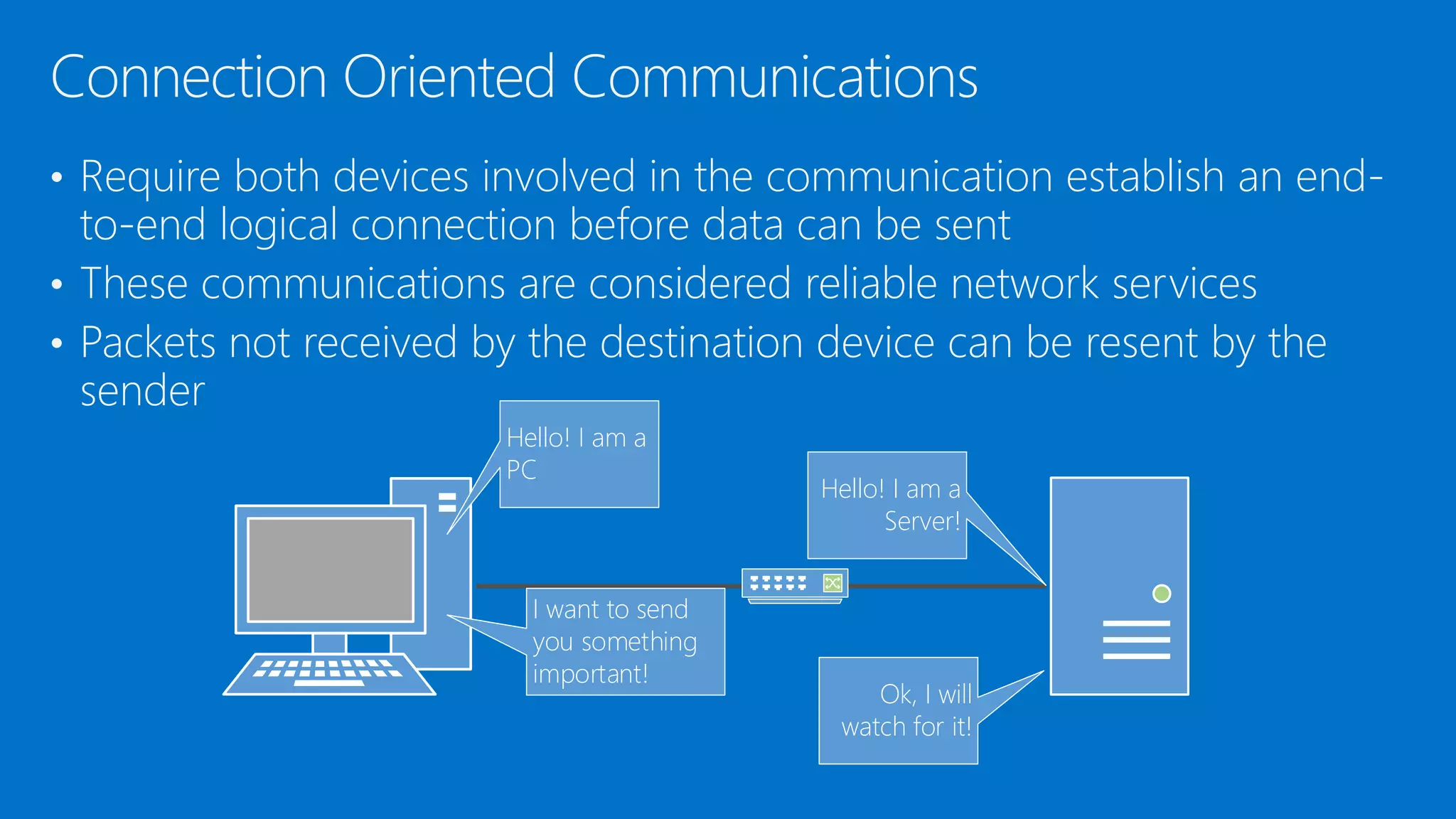
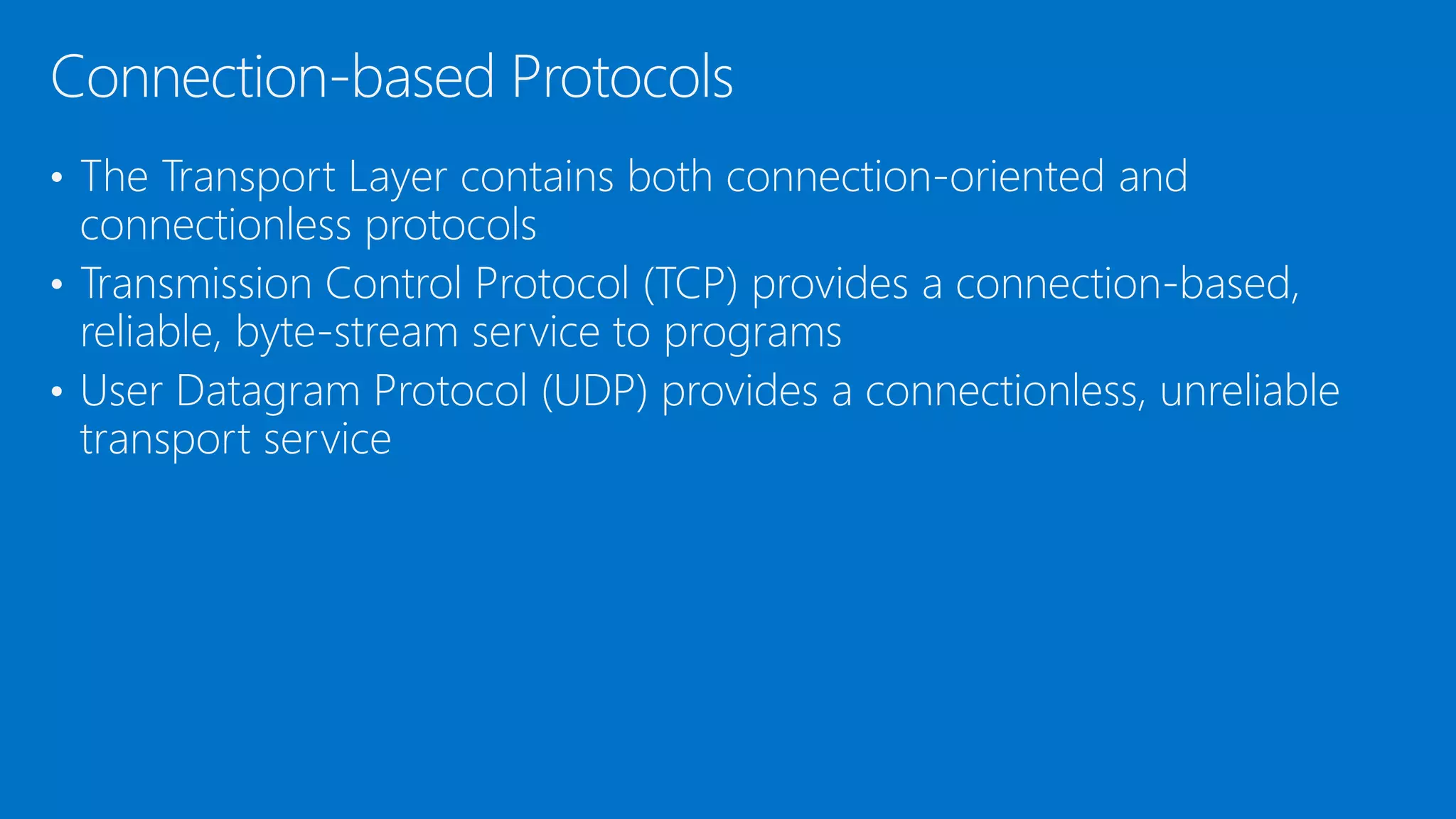
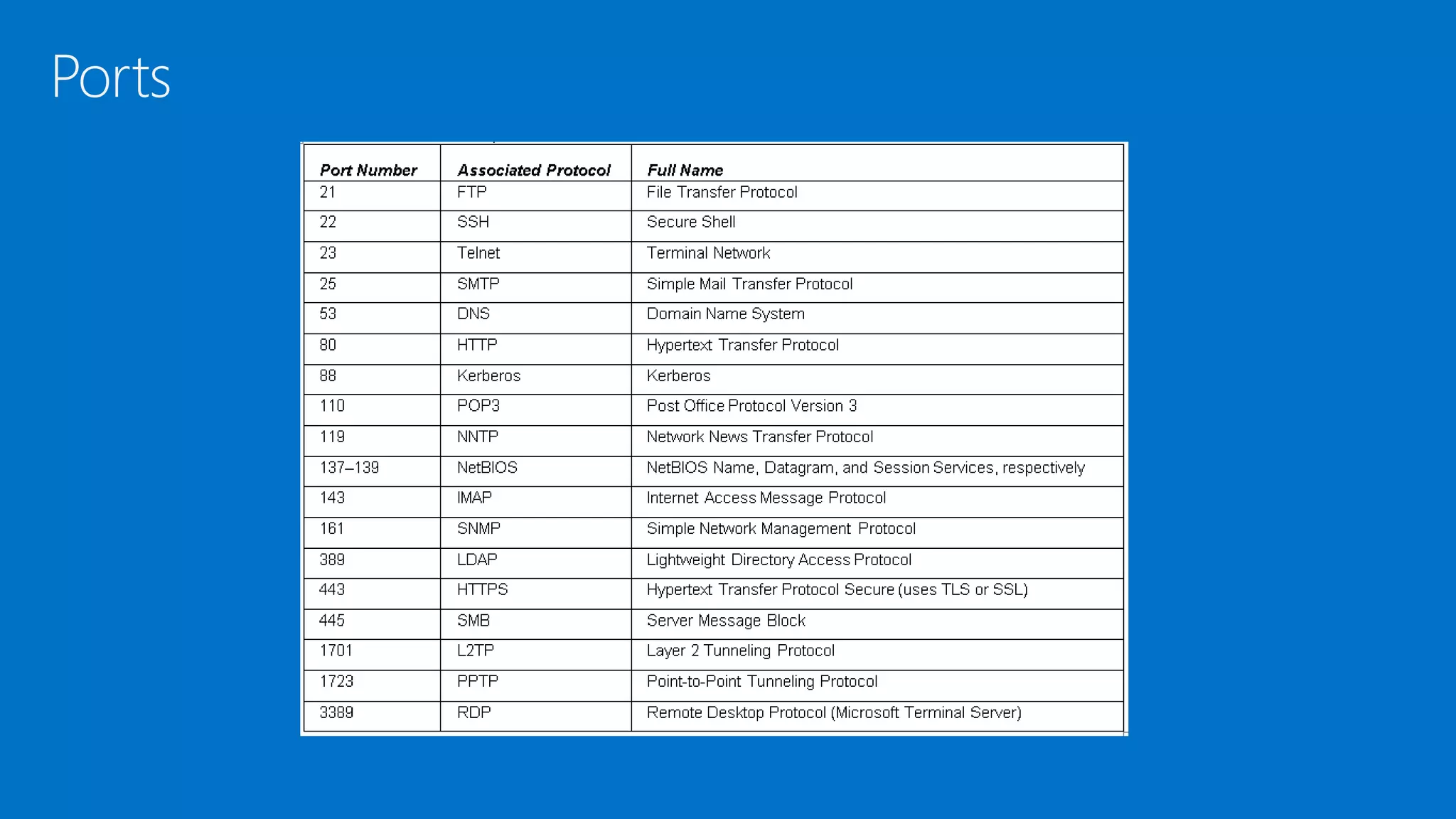
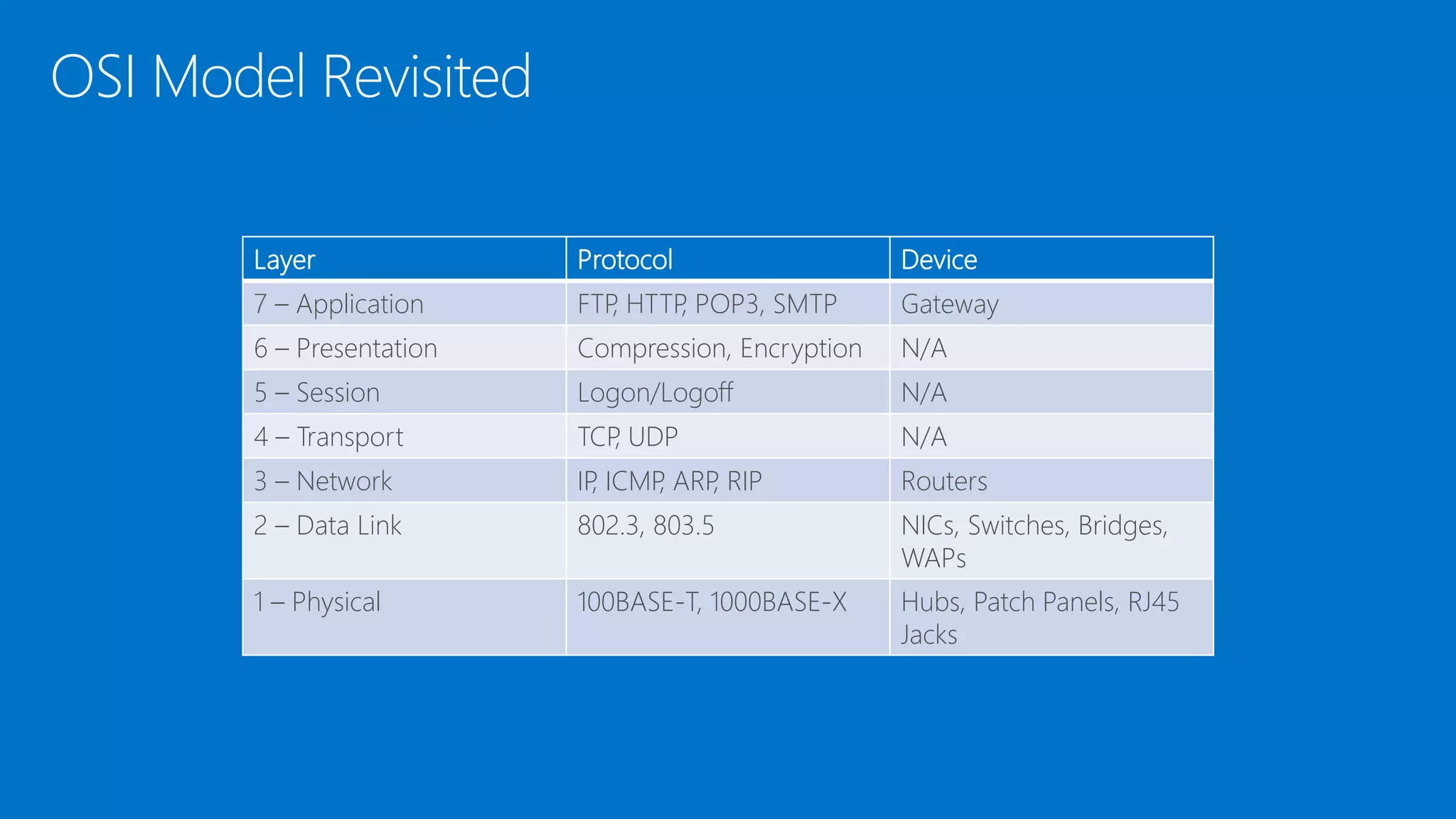
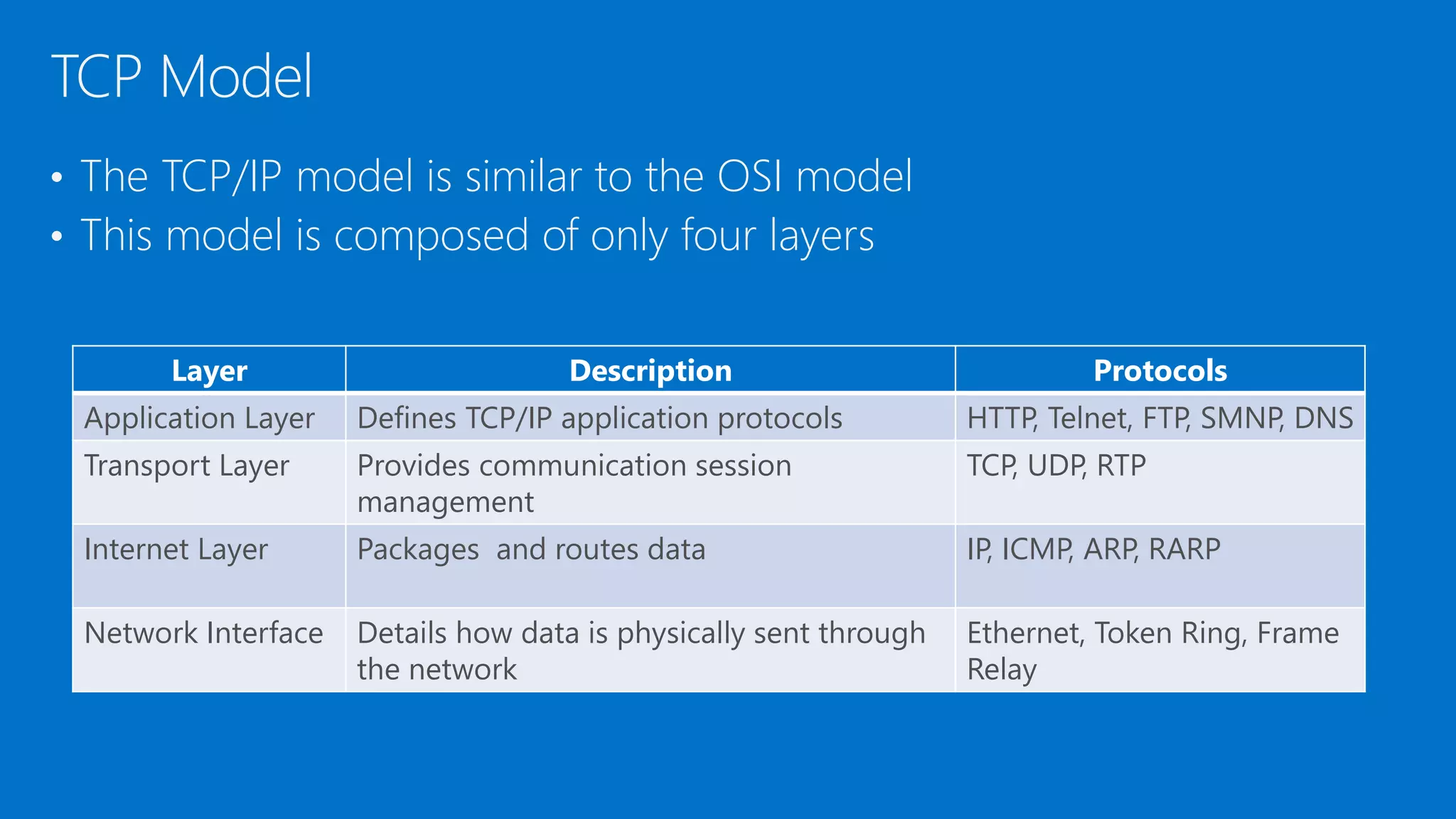
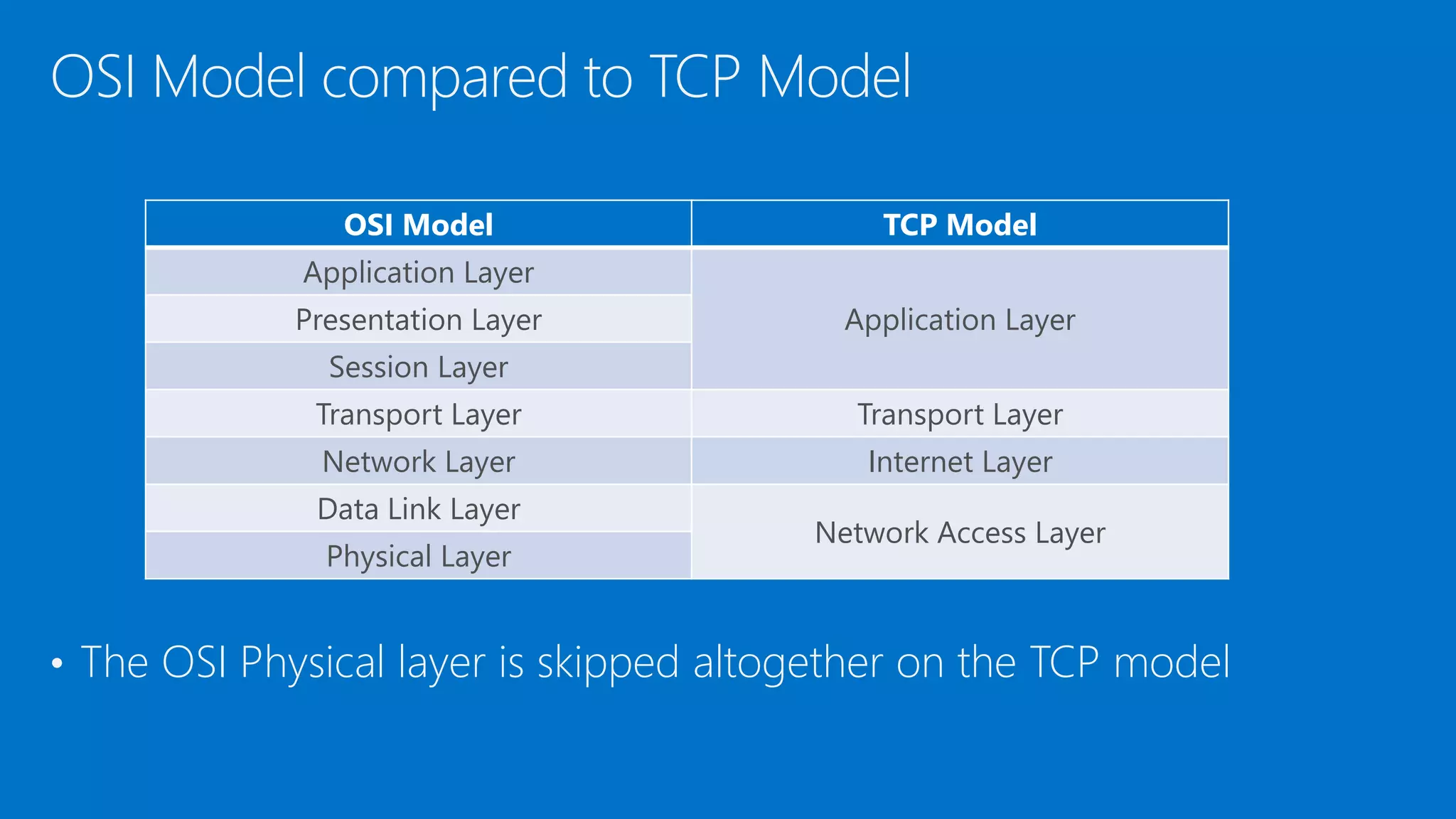
The document discusses the OSI model and networking fundamentals. It defines the seven layers of the OSI model from the physical layer to the application layer. It also compares the OSI model to the TCP model. The physical layer defines cables and physical components. The data link layer provides error-free transmission using frames and MAC addresses. The network layer uses IP addresses for routing. The transport layer segments messages and ensures reliable delivery. The session, presentation and application layers establish communication sessions and enable user applications.