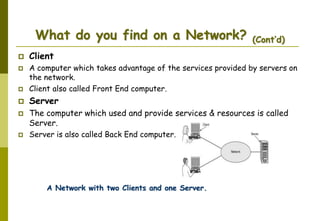
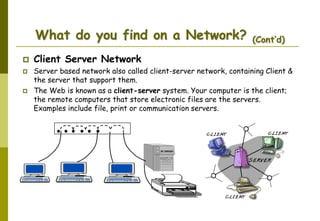
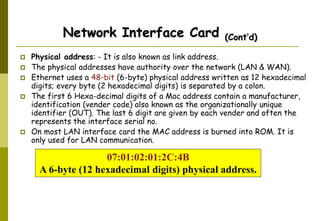
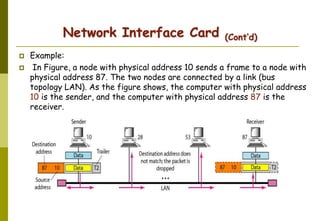
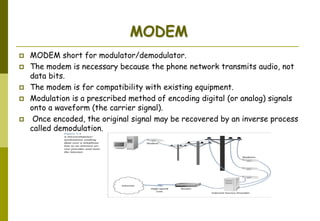
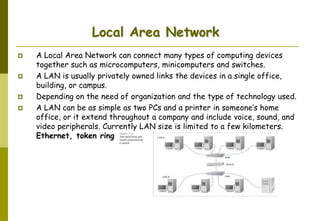
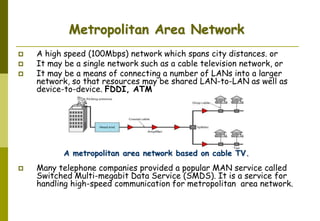
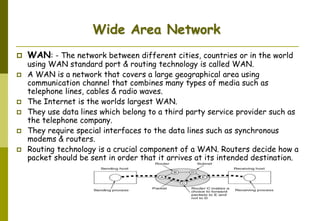
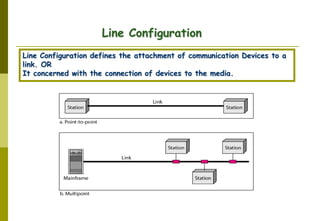
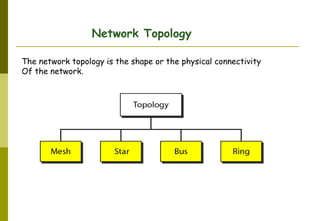
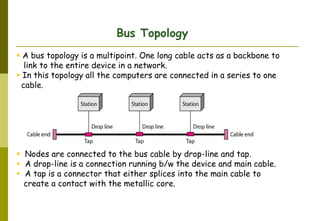
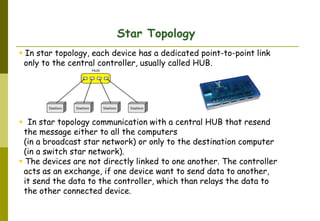
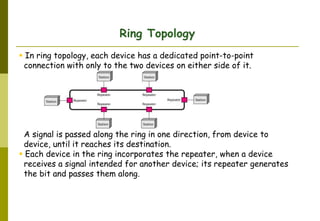
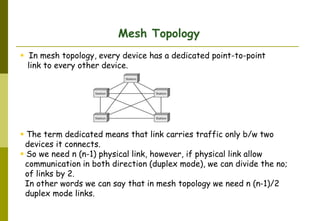
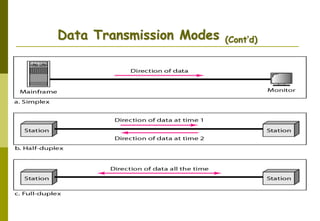
This document provides an overview of computer networks and networking concepts. It discusses network types including local area networks (LANs), metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). It also covers common network devices like hubs, switches, routers and network interface cards. Additionally, it examines network topologies (bus, star, ring, mesh), transmission modes (simplex, half-duplex, full-duplex), and the differences between baseband and broadband transmission. The document serves as a high-level introduction to foundational networking topics.