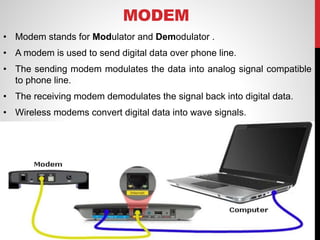
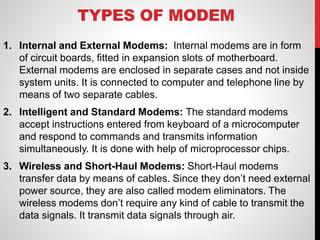
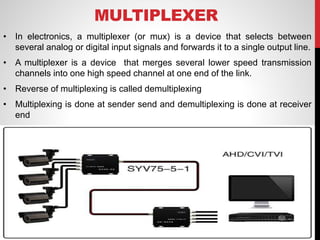
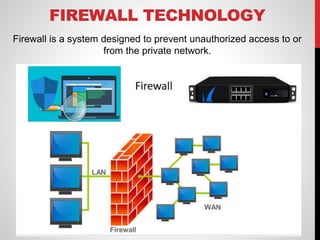
The document discusses various network connecting devices:
- Network Interface Cards (NICs) connect computers to external networks and require proper installation including setting parameters, configuration, and interfacing.
- Hubs connect multiple nodes through a single device but reduce bandwidth by broadcasting all data to all ports. Switches improve on hubs by only sending data to relevant ports.
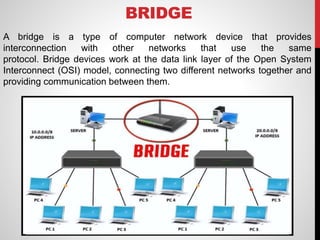
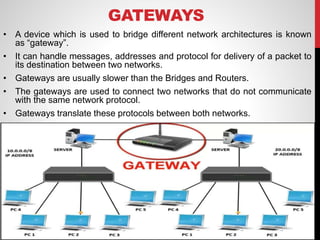
- Bridges and routers segment networks and determine the best path to send data between different network segments.